BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PATTERNS <strong>IN</strong> NATURE<br />
exclusive to plant cells and therefore<br />
not usually found in animal cells.<br />
■ Chloroplasts are organelles that are<br />
green in colour, due to the presence<br />
of a pigment called chlorophyll.<br />
Chloroplasts are responsible for<br />
photosynthesis—the manufacturing<br />
of sugar in plants, using the energy<br />
of sunlight. Chloroplasts are not<br />
present in all plant cells, they are<br />
only found in the green tissue of<br />
plants that can photosynthesise.<br />
Under the light microscope, they<br />
appear as green, disc-shaped<br />
structures, smaller than the nucleus.<br />
An electron microscope is needed to<br />
see the detailed interior.<br />
■ Vacuoles in plant cells are large,<br />
permanent, fluid-filled sacs in the<br />
cytoplasm of mature cells. Each<br />
vacuole consists of a watery solution<br />
called cell sap, surrounded by<br />
single membrane, the tonoplast.<br />
Cell sap contains substances such<br />
as mineral salts, sugars and amino<br />
acids dissolved in water. It may also<br />
contain dissolved pigments that<br />
give cells their colour, for example<br />
the reds, pinks and purples seen in<br />
some flower petals. Besides having<br />
a storage function, vacuoles play<br />
a very important role in providing<br />
support to plant cells. By filling<br />
up with water, the vacuole pushes<br />
outwards with the cytoplasm,<br />
exerting a pressure on the cell wall,<br />
keeping it firm. As a result of the<br />
outward pressure of the cell contents<br />
and the resisting pressure of the<br />
cell wall, the cell becomes firm or<br />
turgid. (Small, temporary vesicles<br />
may sometimes be found in animal<br />
cells, but these do not play a role in<br />
cell support, so permanent vacuoles<br />
that give turgidity are considered to<br />
be a feature excusive to plant cells.)<br />
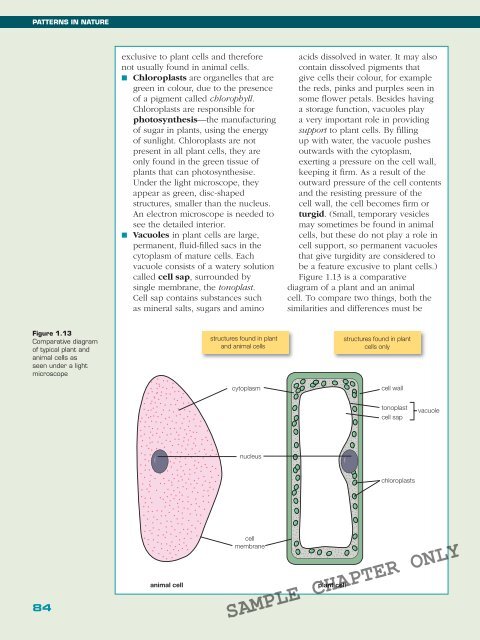
Figure 1.13 is a comparative<br />
diagram of a plant and an animal<br />
cell. To compare two things, both the<br />
similarities and differences must be<br />
Figure 1.13<br />
Comparative diagram<br />
of typical plant and<br />
animal cells as<br />
seen under a light<br />
microscope<br />
structures found in plant<br />
and animal cells<br />
cytoplasm<br />
structures found in plant<br />
cells only<br />
cell wall<br />
tonoplast<br />
cell sap<br />
vacuole<br />
nucleus<br />
chloroplasts<br />
84<br />
animal cell<br />
cell<br />
membrane<br />
plant cell<br />
SAMPLE CHAPTER ONLY