BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
BIOLOGY IN FOCUS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CELLS AND THE CELL THEORY<br />
(b)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
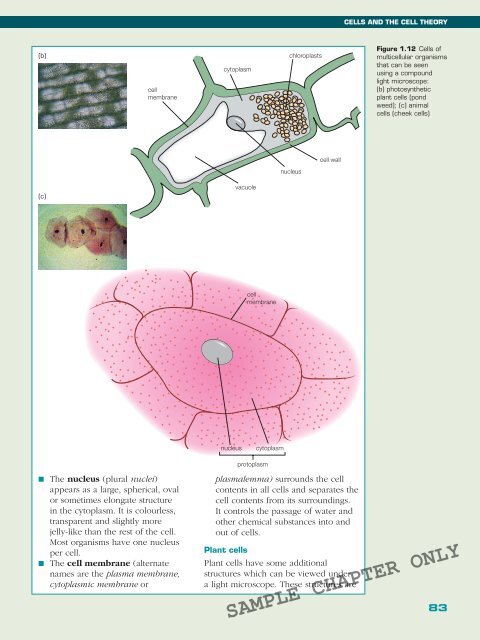
Figure 1.12 Cells of<br />
multicellular organisms<br />
that can be seen<br />
using a compound<br />
light microscope:<br />
(b) photosynthetic<br />
plant cells (pond<br />
weed); (c) animal<br />
cells (cheek cells)<br />
<br />
<br />
(c)<br />
<br />
cell<br />
membrane<br />
nucleus<br />
cytoplasm<br />
protoplasm<br />
■ The nucleus (plural nuclei)<br />
appears as a large, spherical, oval<br />
or sometimes elongate structure<br />
in the cytoplasm. It is colourless,<br />
transparent and slightly more<br />
jelly-like than the rest of the cell.<br />
Most organisms have one nucleus<br />
per cell.<br />
■ The cell membrane (alternate<br />
names are the plasma membrane,<br />
cytoplasmic membrane or<br />
plasmalemma) surrounds the cell<br />
contents in all cells and separates the<br />
cell contents from its surroundings.<br />
It controls the passage of water and<br />
other chemical substances into and<br />
out of cells.<br />
Plant cells<br />
Plant cells have some additional<br />
structures which can be viewed under<br />
a light microscope. These structures are<br />
SAMPLE CHAPTER ONLY<br />
83