Management of pregnancy - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines ...
Management of pregnancy - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines ...
Management of pregnancy - VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guidelines ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>VA</strong>/<strong>DoD</strong> <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Practice</strong> Guideline<br />
For Pregnancy <strong>Management</strong><br />
returning to work before the eight-week time frame. As facilities switch to liquid-based cytology, new studies will<br />
be needed to evaluate the number <strong>of</strong> false positives at six versus eight weeks postpartum to optimize visit timing.<br />
The postpartum Pap smear is <strong>of</strong> value in identifying a significant yield <strong>of</strong> dysplasia. The sensitivity <strong>of</strong> the prenatal<br />
Pap test may be less than desired. The rate <strong>of</strong> abnormal postpartum smears in pregnant women with normal prenatal<br />
smears ranges from 2.8 (Londo et al., 1994) to over 5 percent (Weiss et al., 1989). These studies are challenged by a<br />
smaller study by Jazayeri and colleagues, who found that in patients without risk factors for cervical intraepithelial<br />
neoplasia and a normal Pap smear during <strong>pregnancy</strong>, there was no significant difference between their prenatal and<br />
postpartum smears (Jazayeri et al., 1999).<br />
Women with a history <strong>of</strong> GDM are at increased risk <strong>of</strong> developing diabetes. Some women will be diagnosed shortly<br />
after <strong>pregnancy</strong>, suggesting they had pre-existing diabetes. Although the ADA advocates use <strong>of</strong> fasting blood<br />
glucose determination, the oral GTT will more accurately identify those women with impaired glucose tolerance.<br />
Unfortunately, the incidence <strong>of</strong> postpartum screening in women with GDM is poor.<br />
There is no evidence to recommend for or against discussion <strong>of</strong> specific topics at the post partum visit. Topics to be<br />
addressed at this visit are ultimately based on the discretion <strong>of</strong> the provider and the needs <strong>of</strong> the woman.<br />
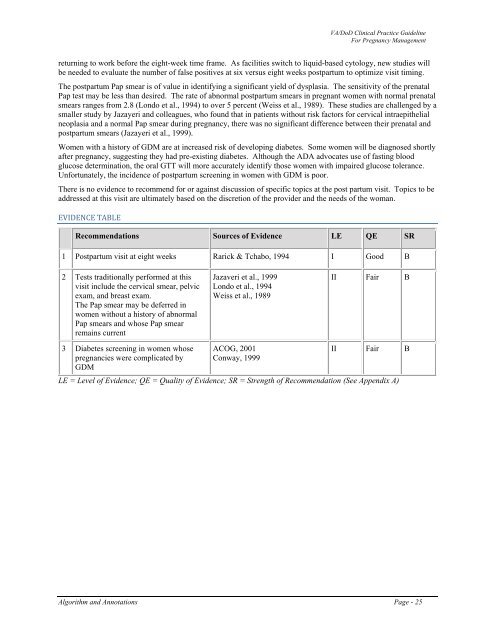
EVIDENCE TABLE<br />
Recommendations Sources <strong>of</strong> Evidence LE QE SR<br />
1 Postpartum visit at eight weeks Rarick & Tchabo, 1994 I Good B<br />
2 Tests traditionally performed at this<br />
visit include the cervical smear, pelvic<br />
exam, and breast exam.<br />
The Pap smear may be deferred in<br />
women without a history <strong>of</strong> abnormal<br />
Pap smears and whose Pap smear<br />
remains current<br />
Jazaveri et al., 1999<br />
Londo et al., 1994<br />
Weiss et al., 1989<br />
II Fair B<br />
3 Diabetes screening in women whose<br />
pregnancies were complicated by<br />
GDM<br />
ACOG, 2001<br />
Conway, 1999<br />
II Fair B<br />
LE = Level <strong>of</strong> Evidence; QE = Quality <strong>of</strong> Evidence; SR = Strength <strong>of</strong> Recommendation (See Appendix A)<br />
Algorithm and Annotations Page - 25