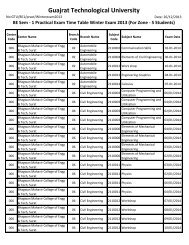
751-Sabar Institute Of Management, Tajpur - Gujarat Technological ...
751-Sabar Institute Of Management, Tajpur - Gujarat Technological ...
751-Sabar Institute Of Management, Tajpur - Gujarat Technological ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Voting System<br />
The voter has two votes. The Federal Election System distinguishes between 'First' and 'Second'<br />
vote. However, these terms do neither refer to a hierarchical order (of importance) of the votes,<br />
nor do they refer to a logical (chronological) sequence in a valid election process.<br />
According to public polls, about 70% (2002) to 63% (2005) of the voters mistakenly thought the<br />
first vote to be more important than the second. In some State Election Systems that have two<br />
voting systems which are modeled after the Federal Election setup, the votes are called 'vote for<br />
person' and 'vote for list'. It is important that both votes have distinct functions.<br />
Like all political system the German has its strength & weakness.<br />
The great strength of german political system- a deliberate feature of the post war constitutes- is<br />
the consensual nature of its decision-making process. The Bundesrate serves as a control<br />
mechanism on the Bundestag. Since the executive & legislative functions are closely intertwined<br />
in any parliamentary system, the Bundesrat’s ability to revisit & slow down legislative process<br />
could be seen as making up for that loss of separation. On the other hand, it can be argued that<br />
the system makes decision making paque. Some observers claim that the opposing majorities in<br />
the two chambers lead to an increase in backroom politics where small groups of high level<br />
leaders make all the important decisions & then the Bundestag representatives only have a choice<br />
between agreeing with them or not getting anything done at all Political events in various parts<br />
of the world during the past decade have attracted new attention to the strengths and weaknesses<br />
of federal solutions as a means of resolving political problems.<br />
Conceptual distinctions have been drawn between “federalism” as a normative term, “federal<br />
political systems” as a descriptive term referring to a broad genus of federal arrangements, and<br />
“federation” as a particular species within that genus.<br />
The extensive literature on the design and operation of federal systems is reviewed, with<br />
particular attention to asymmetry among constituent units, degrees of no centralization, financial<br />
relationships, the impact of federative institutions and the courts, and the development of multitiered<br />
federal systems. Federal processes illustrated by patterns of formation and evolution, the<br />
significance of the increasingly global economy, intergovernmental relations, the impact of<br />
cultural, ethnic and national diversities, and the pathology of federal systems are also considered.<br />
13