ekS - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego PAN w Lublinie ...
ekS - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego PAN w Lublinie ...
ekS - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego PAN w Lublinie ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
water orientation polarization [s], h is the parameter describing interaction of<br />
water dipoles: 0 < h < 1. After substituting (17) in (15) we can have Im(ε) for the<br />
electrolyte:<br />
⎡ 1−h<br />
hπ ⎤<br />
( εs<br />
− ε ∞)<br />
⎢( ωτ ) cos<br />
2 ⎥ σ e<br />
Im( ε ) =<br />
⎣<br />
⎦<br />
+<br />
2<br />
( ) ( 1−h<br />
) 1−h<br />
hπ<br />
1+<br />
ωτ + 2( ωτ ) sin<br />
ωε 0<br />
2<br />
(18)<br />
The absolute value of the complex dielectric permittivity of electrolyte, k, is:<br />
[ Re( ε )] 2 [ Im( ε )] 2<br />
k = ε = +<br />
(19)<br />
Presenting the values from Eq. (16) and Eq. (19) for different w gives the<br />
information about the frequency dispersion of ε’ and k, ie the dependence of the<br />
related values on the frequency of the applied electric field (Malicki [54]).<br />
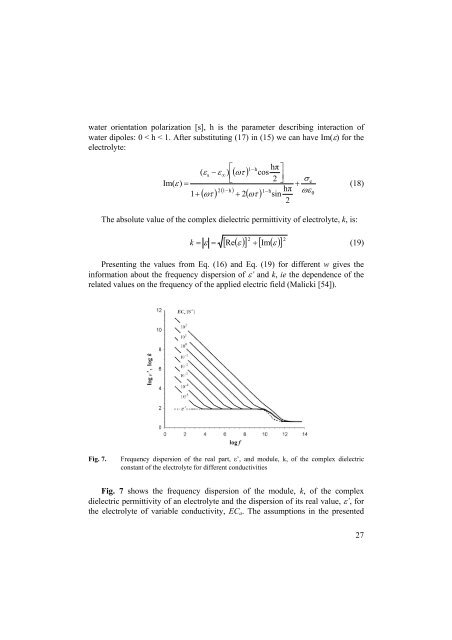
Fig. 7.<br />
Frequency dispersion of the real part, ε’, and module, k, of the complex dielectric<br />
constant of the electrolyte for different conductivities<br />
Fig. 7 shows the frequency dispersion of the module, k, of the complex<br />
dielectric permittivity of an electrolyte and the dispersion of its real value, ε’, for<br />
the electrolyte of variable conductivity, EC a . The assumptions in the presented<br />
27