Analog Electronics Basic Op-Amp Applications - LIGO
Analog Electronics Basic Op-Amp Applications - LIGO
Analog Electronics Basic Op-Amp Applications - LIGO
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5.9. GENERALIZED IMPEDANCE CONVERTER (GIC) 121<br />
5.9 Generalized Impedance Converter (GIC)<br />
A<br />
+<br />
−<br />
Z 1<br />
Z 2<br />
Z 3<br />
+<br />
−<br />
Z 4<br />
Z 5<br />
A<br />
Z<br />
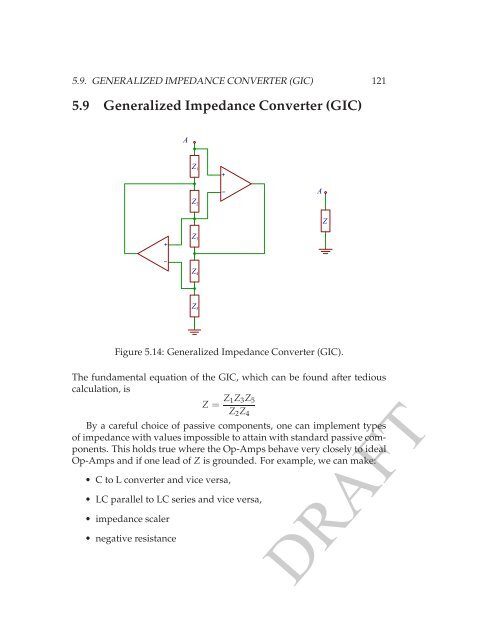
Figure 5.14: Generalized Impedance Converter (GIC).<br />
The fundamental equation of the GIC, which can be found after tedious<br />
calculation, is<br />
Z = Z 1Z 3 Z 5<br />
Z 2 Z 4<br />
By a careful choice of passive components, one can implement types<br />
of impedance with values impossible to attain with standard passive components.<br />
This holds true where the <strong>Op</strong>-<strong>Amp</strong>s behave very closely to ideal<br />
<strong>Op</strong>-<strong>Amp</strong>s and if one lead of Z is grounded. For example, we can make:<br />
• C to L converter and vice versa,<br />
• LC parallel to LC series and vice versa,<br />
• impedance scaler<br />
• negative resistance<br />
DRAFT