- Page 1:
World Health Organization Regional
- Page 4 and 5:
Air Quality Guidelines for Europe S
- Page 6 and 7:
World Health Organization Regional
- Page 8 and 9:
Contents introduction Foreword ....
- Page 10 and 11:
�������� introducti
- Page 12 and 13:
Preface introduction The first edit
- Page 14:
PART I GENERAL
- Page 17 and 18:
2 chapter 1 increased rapidly since
- Page 19 and 20:
4 chapter 1 NATURE OF THE GUIDELINE
- Page 21 and 22:
6 chapter 1 exposure influence the
- Page 23 and 24:
8 chapter 1 In addition to the 35 p
- Page 25 and 26:
10 chapter 1 9. Acute effects on he
- Page 27 and 28:
12 chapter 2 atmospheric concentrat
- Page 29 and 30:
14 chapter 2 decision as to whether
- Page 31 and 32:
16 chapter 2 uncertainty of the dat
- Page 33 and 34:
18 chapter 2 uncertainty factor, be
- Page 35 and 36:
20 chapter 2 A similar situation oc
- Page 37 and 38:
22 chapter 2 Box 1. Classification
- Page 39 and 40:
24 chapter 2 The results of calcula
- Page 41 and 42:
26 chapter 2 however, several scien
- Page 43 and 44:
28 chapter 2 and the impact of expo
- Page 45 and 46:
30 chapter 2 permitted only an eval
- Page 47 and 48:
introduction chapter 3 Summary of t
- Page 49 and 50:
34 chapter 3 guidelines for differe
- Page 51 and 52:
36 chapter 3 Table 3. Rationale and
- Page 53 and 54:
38 chapter 3 Table 5. Risk estimate
- Page 55 and 56:
40 chapter 3 pollutants that may ad
- Page 57 and 58:
42 chapter 4 DEFINITIONS Several te
- Page 59 and 60:
44 chapter 4 address these economic
- Page 61 and 62:
46 chapter 4 Exposure-response rela
- Page 63 and 64:
48 chapter 4 uncertainties on the r
- Page 65 and 66:
50 chapter 4 substantially owing to
- Page 67 and 68:
52 chapter 4 use of epidemiological
- Page 69 and 70:
54 chapter 4 pollution from neighbo
- Page 71:
PART II EVALUATION OF RISKS TO HUMA
- Page 74 and 75:
organic pollutants 5.1 Acrylonitril
- Page 76 and 77:
organic pollutants carcinogen. No s
- Page 78 and 79:
organic pollutants 63 demonstrated
- Page 80 and 81:
organic pollutants Table 9. Model-d
- Page 82 and 83:
organic pollutants 5.3 Butadiene Ex
- Page 84 and 85:
organic pollutants Estimates of hum
- Page 86 and 87:
organic pollutants 5.4 Carbon disul
- Page 88 and 89:
organic pollutants selecting the si
- Page 90 and 91:
organic pollutants 5.5 Carbon monox
- Page 92 and 93:
organic pollutants than the non-pre
- Page 94 and 95:
organic pollutants 15. LONGO, L.D.
- Page 96 and 97:
organic pollutants giving quantitat
- Page 98 and 99:
organic pollutants 5.7 Dichlorometh
- Page 100 and 101:
organic pollutants 4. HARKOV, R. ET
- Page 102 and 103:
organic pollutants 5.8 Formaldehyde
- Page 104 and 105:
organic pollutants systems (3). The
- Page 106 and 107:
organic pollutants 7. HANSEN, J. &
- Page 108 and 109:
organic pollutants airborne particl
- Page 110 and 111:
organic pollutants some recent anim
- Page 112 and 113:
organic pollutants 5.10 Polychlorin
- Page 114 and 115:
organic pollutants assessed using t
- Page 116 and 117:
organic pollutants 101 11. Levels o
- Page 118 and 119:
organic pollutants 103 differences
- Page 120 and 121:
organic pollutants 105 3. THEELEN,
- Page 122 and 123:
organic pollutants 107 Guidelines A
- Page 124 and 125:
organic pollutants 5.13 Tetrachloro
- Page 126 and 127:
organic pollutants On the basis of
- Page 128 and 129:
organic pollutants With regard to s
- Page 130 and 131:
organic pollutants 5.15 Trichloroet
- Page 132 and 133:
organic pollutants 117 5. Technical
- Page 134 and 135:
organic pollutants 119 standardized
- Page 136 and 137:
organic pollutants 121 7. BARNES, A
- Page 139 and 140:
inorganic pollutants 6.1 Arsenic Ex
- Page 141 and 142:
inorganic pollutants 127 Guidelines
- Page 143 and 144:
inorganic pollutants 129 from data
- Page 145 and 146:
inorganic pollutants The dose-respo
- Page 147 and 148:
inorganic pollutants This risk esti
- Page 149 and 150:
inorganic pollutants 20. DEMENT, J.
- Page 151 and 152:
inorganic pollutants 137 of subject
- Page 153 and 154:
inorganic pollutants 6.4 Chromium 1
- Page 155 and 156:
inorganic pollutants estimate, the
- Page 157 and 158:
inorganic pollutants 6.5 Fluoride 1
- Page 159 and 160:
inorganic pollutants 145 2. SARIC,
- Page 161 and 162:
inorganic pollutants Table 16. Hydr
- Page 163 and 164:
inorganic pollutants 6.7 Lead 149 E
- Page 165 and 166:
inorganic pollutants reported for g
- Page 167 and 168:
inorganic pollutants 6. SEPPÄLÄIN
- Page 169 and 170:
inorganic pollutants BMDL 5 values
- Page 171 and 172:
inorganic pollutants 6.9 Mercury 15
- Page 173 and 174:
inorganic pollutants 159 Since thes
- Page 175 and 176:
inorganic pollutants 161 5. Inorgan
- Page 177 and 178:
inorganic pollutants 163 In general
- Page 179 and 180:
inorganic pollutants 165 8. INTEGRA
- Page 181 and 182:
inorganic pollutants 167 In early s
- Page 183 and 184:
inorganic pollutants 169 While cis-
- Page 185 and 186:
Table 21. Respiratory effects after
- Page 187:
introduction chapter 7 Classical po
- Page 190 and 191:
176 chapter 7 Nitrogen dioxide incr
- Page 192 and 193:
178 chapter 7 for exaggerated respo
- Page 194 and 195:
180 chapter 7 2. LINN, W.S. & HACKN
- Page 196 and 197:
182 chapter 7 Ozone exposure has al
- Page 198 and 199:
184 chapter 7 Table 23. Health outc
- Page 200 and 201:
186 chapter 7 7.3 Particulate matte
- Page 202 and 203:
188 chapter 7 suggest that the publ
- Page 204 and 205:
190 chapter 7 Evaluation of the eff
- Page 206 and 207: 192 chapter 7 increase in the long-
- Page 208 and 209: 194 chapter 7 7.4 Sulfur dioxide Ex
- Page 210 and 211: 196 chapter 7 earlier years. Cohort
- Page 212 and 213: 198 chapter 7 17. ANDERSON, H.R. ET
- Page 215 and 216: indoor air pollutants 8.1 Environme
- Page 217 and 218: indoor air pollutants 203 uncertain
- Page 219 and 220: indoor air pollutants 205 syndrome.
- Page 221 and 222: indoor air pollutants 207 dose-rela
- Page 223 and 224: indoor air pollutants 8.3 Radon 209
- Page 225 and 226: Greece 73 1988 6 months Hungary 122
- Page 227 and 228: indoor air pollutants Fig. 1. Estim
- Page 229 and 230: indoor air pollutants 215 25 Bq/m 3
- Page 231 and 232: indoor air pollutants 217 21.WRIXON
- Page 233 and 234: introduction chapter 9 General appr
- Page 235 and 236: general approach Table 30. Differen
- Page 237 and 238: general approach 223 sulfur dioxide
- Page 239 and 240: general approach 225 Programme for
- Page 241 and 242: effects of sulfur dioxide on vegeta
- Page 243 and 244: effects of sulfur dioxide on vegeta
- Page 245 and 246: effects of nitrogen-containing air
- Page 247 and 248: effects of nitrogen-containing air
- Page 249 and 250: effects of ozone on vegetation vege
- Page 251 and 252: effects of ozone on vegetation 237
- Page 253 and 254: introduction chapter 13 Indirect ef
- Page 255: indirect effects of acidifying comp
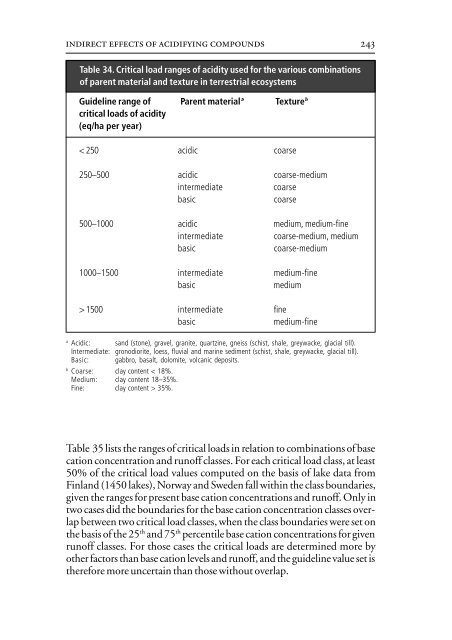
- Page 259 and 260: indirect effects of acidifying comp
- Page 261 and 262: effects of airborne nitrogen pollut
- Page 263 and 264: effects of airborne nitrogen pollut
- Page 265 and 266: effects of airborne nitrogen pollut
- Page 267 and 268: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 269 and 270: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 271 and 272: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 273 and 274: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 275 and 276: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 277 and 278: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 279 and 280: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 281 and 282: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 283 and 284: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 285 and 286: participants at who air quality gui
- Page 287: participants at who air quality gui