njit-etd2000-029 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
njit-etd2000-029 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
njit-etd2000-029 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
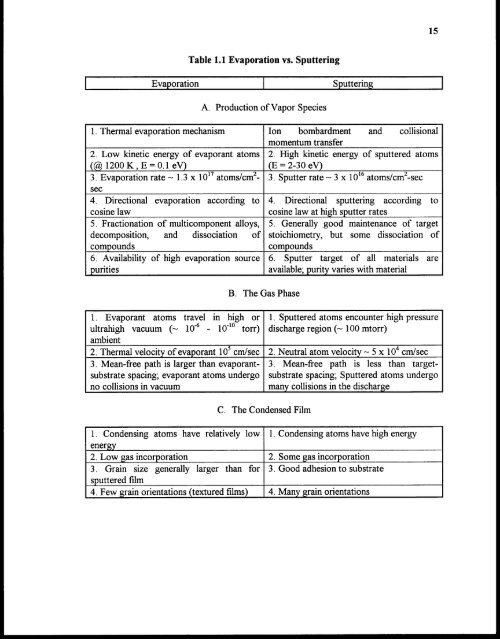
15<br />
Table 1.1 Evaporation vs. Sputtering<br />
Evaporation Sputtering<br />
A. Production <strong>of</strong> Vapor Species<br />
1. Thermal evaporation mechanism Ion bombardment and collisional<br />
momentum transfer<br />
2. Low kinetic energy <strong>of</strong> evaporant atoms 2. High kinetic energy <strong>of</strong> sputtered atoms<br />
(@ 1200K , E = 0.1 eV)<br />
(E = 2-30 eV)<br />
3. Evaporation rate — 1.3 x 10 17 atoms/cm2- 3. Sputter rate ~ 3 x 10 16 atoms/cm2-sec<br />
sec<br />
4. Directional evaporation according to 4. Directional sputtering according to<br />
cosine law<br />
cosine law at high sputter rates<br />
5. Fractionation <strong>of</strong> multicomponent alloys, 5. Generally good maintenance <strong>of</strong> target<br />
decomposition, and dissociation <strong>of</strong> stoichiometry, but some dissociation <strong>of</strong><br />
compounds<br />
compounds<br />
6. Availability <strong>of</strong> high evaporation source<br />
purities<br />
1. Evaporant atoms travel in high or<br />
ultrahigh vacuum (~ 10-6 - 10-10 ton)<br />
ambient<br />
B. The Gas Phase<br />
6. Sputter target <strong>of</strong> all materials are<br />
available; purity varies with material<br />
1. Sputtered atoms encounter high pressure<br />
discharge region (~ 100 mtorr)<br />
2. Thermal velocity <strong>of</strong> evaporant 10 5 cm/sec 2. Neutral atom velocity ~ 5 x 104 cm/sec<br />
3. Mean-free path is larger than evaporantsubstrate<br />
spacing; evaporant atoms undergo substrate spacing; Sputtered atoms undergo<br />
3. Mean-free path is less than target-<br />
no collisions in vacuum<br />
many collisions in the discharge<br />
C. The Condensed Film<br />
1. Condensing atoms have relatively low 1. Condensing atoms have high energy<br />
energy<br />
2. Low gas incorporation 2. Some gas incorporation<br />
3. Grain size generally larger than for 3. Good adhesion to substrate<br />
sputtered film<br />
4. Few grain orientations (textured films) 4. Many grain orientations