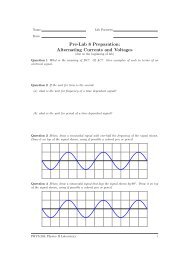
Pre-LAB 4 Assignment Fundamentals of Circuits II: Currents ...
Pre-LAB 4 Assignment Fundamentals of Circuits II: Currents ...
Pre-LAB 4 Assignment Fundamentals of Circuits II: Currents ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Fundamentals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Circuits</strong> <strong>II</strong>: <strong>Currents</strong> & <strong>Circuits</strong> v 0.3<br />
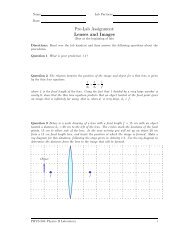
<strong>Pre</strong>diction 1.2 Consider reversing the batteries in the circuits shown in Fig. 1. What<br />
will happen to the brightness <strong>of</strong> bulbs A, B and C if the positive and negative terminals <strong>of</strong><br />
the battery are reversed? Explain the reason(s) for your prediction.<br />
Step 2: Test your prediction by reversing the terminals <strong>of</strong> the battery in each <strong>of</strong> your circuits.<br />
Question 1.2 Did your observation agree with your prediction? Explain. Identify any assumptions(s)<br />
which you have now falsified.<br />
Question 1.3 Considering the observations you have made above, without knowing how the<br />
battery is hooked up, does the brightness <strong>of</strong> the bulbs tell you what the direction <strong>of</strong> the current<br />
is? Explain.<br />
Activity 1.2: Current in a Simple Circuit with Bulbs<br />
This activity is designed to further investigate how a bulb and a series <strong>of</strong> bulbs affects the<br />
current in a circuit.<br />
<strong>Pre</strong>diction 1.3 How do you predict the currents going through each <strong>of</strong> the bulbs in Fig. 1 will<br />
compare? Write down your predicted rankings <strong>of</strong> the currents through bulbs A, B and C, and<br />
explain your reasoning.<br />
You will test your prediction by using current probes. We want the current probe to measure<br />
the current which goes through a bulb. Therefore we must connect the current probes so that<br />
the current which passes through a bulb also passes through the current probe. Study Fig. 3<br />
and convince yourself that the the current probes there measure the currents as described in<br />
the figure caption.<br />
Real-Time Physics Comment: “In carrying out your measurements, it is important to realize<br />
that the measurements made by the current probes are only as good as their calibrations. Small<br />
differences in calibration can result in small differences in readings.”<br />
Step 1: Open the file L2A1-2 (Two <strong>Currents</strong>). You should see two sets <strong>of</strong> current axes similar<br />
to the picture below.<br />
Step 2: Zero the probes with them disconnected from the circuit.<br />
PHYS-204:Physics <strong>II</strong> Laboratory 5