Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
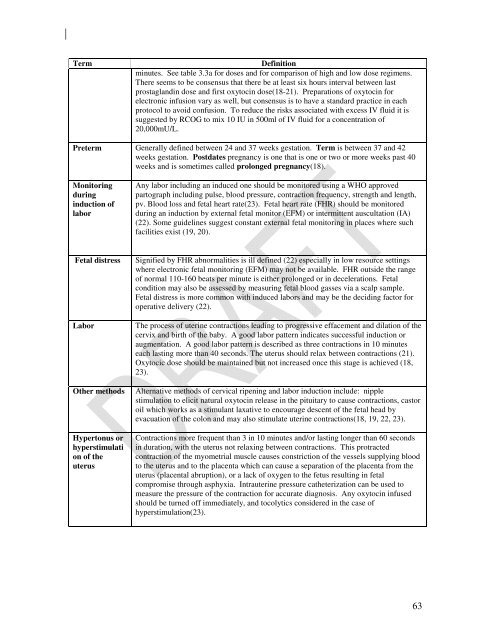
Term<br />
Definition<br />
minutes. See table 3.3a <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> doses <strong>and</strong> <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> comparison <strong>of</strong> high <strong>and</strong> low dose regimens.<br />
There seems to be consensus that there be at least six hours interval between last<br />
prostagl<strong>and</strong>in dose <strong>and</strong> first <strong>oxytocin</strong> dose(18-21). Preparations <strong>of</strong> <strong>oxytocin</strong> <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong><br />
electronic infusion vary as well, but consensus is to have a st<strong>and</strong>ard practice in each<br />
protocol to avoid confusion. To reduce the risks associated with excess IV fluid it is<br />
suggested by RCOG to mix 10 IU in 500ml <strong>of</strong> IV fluid <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> a concentration <strong>of</strong><br />
20,000mU/L.<br />
Preterm Generally defined between 24 <strong>and</strong> 37 weeks gestation. Term is between 37 <strong>and</strong> 42<br />
weeks gestation. Postdates pregnancy is one that is one <strong>or</strong> two <strong>or</strong> m<strong>or</strong>e weeks past 40<br />
weeks <strong>and</strong> is sometimes called prolonged pregnancy(18).<br />
Monit<strong>or</strong>ing<br />
during<br />
<strong>induction</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
lab<strong>or</strong><br />
Any lab<strong>or</strong> including an induced one should be monit<strong>or</strong>ed using a WHO approved<br />
partograph including pulse, blood pressure, contraction frequency, strength <strong>and</strong> length,<br />
pv. Blood loss <strong>and</strong> fetal heart rate(23). Fetal heart rate (FHR) should be monit<strong>or</strong>ed<br />
during an <strong>induction</strong> by external fetal monit<strong>or</strong> (EFM) <strong>or</strong> intermittent auscultation (IA)<br />
(22). Some guidelines suggest constant external fetal monit<strong>or</strong>ing in places where such<br />
facilities exist (19, 20).<br />
Fetal distress<br />
Lab<strong>or</strong><br />
Other methods<br />
Hypertonus <strong>or</strong><br />
hyperstimulati<br />
on <strong>of</strong> the<br />
uterus<br />
Signified by FHR abn<strong>or</strong>malities is ill defined (22) especially in low resource settings<br />
where electronic fetal monit<strong>or</strong>ing (EFM) may not be available. FHR outside the range<br />
<strong>of</strong> n<strong>or</strong>mal 110-160 beats per minute is either prolonged <strong>or</strong> in decelerations. Fetal<br />
condition may also be assessed by measuring fetal blood gasses via a scalp sample.<br />
Fetal distress is m<strong>or</strong>e common with induced lab<strong>or</strong>s <strong>and</strong> may be the deciding fact<strong>or</strong> <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong><br />
operative delivery (22).<br />
The process <strong>of</strong> uterine contractions leading to progressive effacement <strong>and</strong> dilation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
cervix <strong>and</strong> birth <strong>of</strong> the baby. A good lab<strong>or</strong> pattern indicates successful <strong>induction</strong> <strong>or</strong><br />
augmentation. A good lab<strong>or</strong> pattern is described as three contractions in 10 minutes<br />
each lasting m<strong>or</strong>e than 40 seconds. The uterus should relax between contractions (21).<br />
Oxytocic dose should be maintained but not increased once this stage is achieved (18,<br />
23).<br />
Alternative methods <strong>of</strong> cervical ripening <strong>and</strong> lab<strong>or</strong> <strong>induction</strong> include: nipple<br />
stimulation to elicit natural <strong>oxytocin</strong> release in the pituitary to cause contractions, cast<strong>or</strong><br />
oil which w<strong>or</strong>ks as a stimulant laxative to encourage descent <strong>of</strong> the fetal head by<br />
evacuation <strong>of</strong> the colon <strong>and</strong> may also stimulate uterine contractions(18, 19, 22, 23).<br />
Contractions m<strong>or</strong>e frequent than 3 in 10 minutes <strong>and</strong>/<strong>or</strong> lasting longer than 60 seconds<br />
in duration, with the uterus not relaxing between contractions. This protracted<br />
contraction <strong>of</strong> the myometrial muscle causes constriction <strong>of</strong> the vessels supplying blood<br />
to the uterus <strong>and</strong> to the placenta which can cause a separation <strong>of</strong> the placenta from the<br />
uterus (placental abruption), <strong>or</strong> a lack <strong>of</strong> oxygen to the fetus resulting in fetal<br />
compromise through asphyxia. Intrauterine pressure catheterization can be used to<br />
measure the pressure <strong>of</strong> the contraction <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> accurate diagnosis. Any <strong>oxytocin</strong> infused<br />
should be turned <strong>of</strong>f immediately, <strong>and</strong> tocolytics considered in the case <strong>of</strong><br />
hyperstimulation(23).<br />
63