Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
Use of oxytocin and misoprostol for induction or ... - POPPHI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
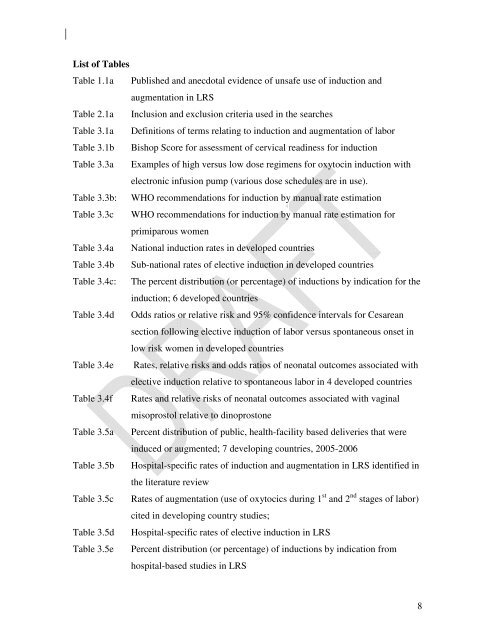
List <strong>of</strong> Tables<br />
Table 1.1a Published <strong>and</strong> anecdotal evidence <strong>of</strong> unsafe use <strong>of</strong> <strong>induction</strong> <strong>and</strong><br />
augmentation in LRS<br />
Table 2.1a Inclusion <strong>and</strong> exclusion criteria used in the searches<br />
Table 3.1a Definitions <strong>of</strong> terms relating to <strong>induction</strong> <strong>and</strong> augmentation <strong>of</strong> lab<strong>or</strong><br />
Table 3.1b Bishop Sc<strong>or</strong>e <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> assessment <strong>of</strong> cervical readiness <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> <strong>induction</strong><br />
Table 3.3a Examples <strong>of</strong> high versus low dose regimens <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> <strong>oxytocin</strong> <strong>induction</strong> with<br />
electronic infusion pump (various dose schedules are in use).<br />
Table 3.3b: WHO recommendations <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> <strong>induction</strong> by manual rate estimation<br />
Table 3.3c WHO recommendations <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> <strong>induction</strong> by manual rate estimation <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong><br />
primiparous women<br />
Table 3.4a National <strong>induction</strong> rates in developed countries<br />
Table 3.4b Sub-national rates <strong>of</strong> elective <strong>induction</strong> in developed countries<br />
Table 3.4c: The percent distribution (<strong>or</strong> percentage) <strong>of</strong> <strong>induction</strong>s by indication <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> the<br />
<strong>induction</strong>; 6 developed countries<br />
Table 3.4d Odds ratios <strong>or</strong> relative risk <strong>and</strong> 95% confidence intervals <strong>f<strong>or</strong></strong> Cesarean<br />
section following elective <strong>induction</strong> <strong>of</strong> lab<strong>or</strong> versus spontaneous onset in<br />
low risk women in developed countries<br />
Table 3.4e Rates, relative risks <strong>and</strong> odds ratios <strong>of</strong> neonatal outcomes associated with<br />
elective <strong>induction</strong> relative to spontaneous lab<strong>or</strong> in 4 developed countries<br />
Table 3.4f Rates <strong>and</strong> relative risks <strong>of</strong> neonatal outcomes associated with vaginal<br />
<strong>misoprostol</strong> relative to dinoprostone<br />
Table 3.5a Percent distribution <strong>of</strong> public, health-facility based deliveries that were<br />
induced <strong>or</strong> augmented; 7 developing countries, 2005-2006<br />
Table 3.5b Hospital-specific rates <strong>of</strong> <strong>induction</strong> <strong>and</strong> augmentation in LRS identified in<br />
the literature review<br />
Table 3.5c Rates <strong>of</strong> augmentation (use <strong>of</strong> oxytocics during 1 st <strong>and</strong> 2 nd stages <strong>of</strong> lab<strong>or</strong>)<br />
cited in developing country studies;<br />
Table 3.5d Hospital-specific rates <strong>of</strong> elective <strong>induction</strong> in LRS<br />
Table 3.5e Percent distribution (<strong>or</strong> percentage) <strong>of</strong> <strong>induction</strong>s by indication from<br />
hospital-based studies in LRS<br />
8