Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
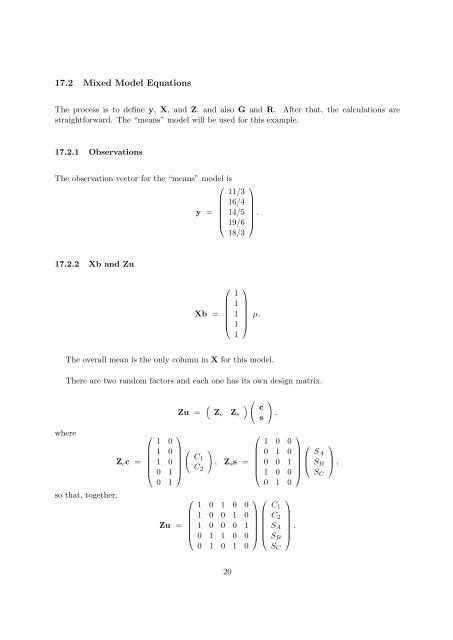
17.2 <strong>Mixed</strong> <strong>Model</strong> Equations<br />
The process is to define y, X, and Z, and also G and R. After that, the calculations are<br />
straightforward. The “means” model will be used for this example.<br />
17.2.1 Observations<br />
The observation vector for the “means” model is<br />
⎛ ⎞<br />
11/3<br />
16/4<br />
y =<br />
14/5<br />
.<br />
⎜ ⎟<br />
⎝ 19/6 ⎠<br />
18/3<br />
17.2.2 Xb and Zu<br />
Xb =<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
⎞<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
µ.<br />
The overall mean is the only column in X for this model.<br />
There are two random factors and each one has its own design matrix.<br />
where<br />
so that, together,<br />
Z c c =<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
1 0<br />
1 0<br />
1 0<br />
0 1<br />
0 1<br />
Zu =<br />
⎞<br />
Zu =<br />
(<br />
Z c<br />
Z s<br />
) ( c<br />
s<br />
( )<br />
C1<br />
, Z<br />
⎟ C s s =<br />
⎠ 2<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
1 0 1 0 0<br />
1 0 0 1 0<br />
1 0 0 0 1<br />
0 1 1 0 0<br />
0 1 0 1 0<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
⎞ ⎛<br />
⎟ ⎜<br />
⎠ ⎝<br />
)<br />
,<br />
1 0 0<br />
0 1 0<br />
0 0 1<br />
1 0 0<br />
0 1 0<br />
C 1<br />
C 2<br />
S A<br />
S B<br />
S C<br />
⎞<br />
.<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
⎞<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
S A<br />
S B<br />
S C<br />
⎞<br />
⎟<br />
⎠ ,<br />
20