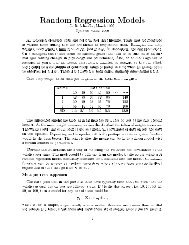
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
17.2.6 Repeatability or Reliability<br />
Variances of prediction error are often expressed as a number going from 0 to 100 % , known as<br />
repeatability or reliability (REL) (depending on the species). The general formula is<br />
REL = (V ar(True Values) − V ar(P E))/(V ar(True Values),<br />
times 100. Thus, for contemporary group 1, the reliability would be<br />
For Sire A, the REL would be<br />
REL = 100(.1667 − .1482)/(.1667) = 11.10.<br />
REL = 100(.08696 − (.0655 ∗ 1.2765))/(.08696) = 3.85.<br />
Thus, sires have smaller reliabilities than contemporary groups, but SEP for sires is smaller than<br />
for contemporary groups. This is because contemporary groups have more progeny in them than<br />
sires have, and because the variance of contemporary groups is larger than the variance of sire<br />
transmitting abilities.<br />
17.3 R Methods for MME<br />
Given the matrices X, Z, G −1 , R −1 , and y, then an R-function can be written to set up the<br />
MME, solve, and compute SSR. This function works for small examples, as given in these notes.<br />
For large problems, other methods can be used to solve the equations by iterating on the data.<br />
The function for small examples is given here.<br />
24