Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
Prediction Theory 1 Introduction 2 General Linear Mixed Model
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
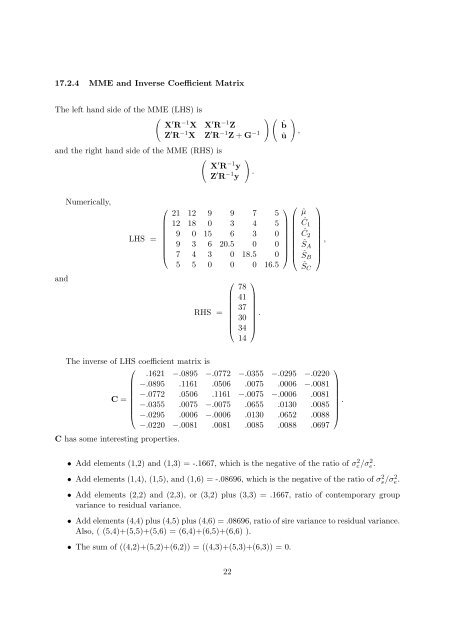
17.2.4 MME and Inverse Coefficient Matrix<br />
The left hand side of the MME (LHS) is<br />
( ) (<br />
X ′ R −1 X X ′ R −1 Z<br />
ˆb<br />
Z ′ R −1 X Z ′ R −1 Z + G −1 û<br />
and the right hand side of the MME (RHS) is<br />
(<br />
X ′ R −1 y<br />
Z ′ R −1 y<br />
)<br />
.<br />
)<br />
,<br />
and<br />
Numerically,<br />
LHS =<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
21 12 9 9 7 5<br />
12 18 0 3 4 5<br />
9 0 15 6 3 0<br />
9 3 6 20.5 0 0<br />
7 4 3 0 18.5 0<br />
5 5 0 0 0 16.5<br />
RHS =<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
78<br />
41<br />
37<br />
30<br />
34<br />
14<br />
⎞<br />
.<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
⎞ ⎛ ⎞<br />
ˆµ<br />
Ĉ 1<br />
Ĉ 2<br />
⎟<br />
Ŝ ,<br />
A<br />
⎠ ⎜ ⎟<br />
⎝ ŜB ⎠<br />
ŜC<br />
The inverse of LHS coefficient matrix is<br />
⎛<br />
⎞<br />
.1621 −.0895 −.0772 −.0355 −.0295 −.0220<br />
−.0895 .1161 .0506 .0075 .0006 −.0081<br />
−.0772 .0506 .1161 −.0075 −.0006 .0081<br />
C =<br />
.<br />
−.0355 .0075 −.0075 .0655 .0130 .0085<br />
⎜<br />
⎟<br />
⎝ −.0295 .0006 −.0006 .0130 .0652 .0088 ⎠<br />
−.0220 −.0081 .0081 .0085 .0088 .0697<br />
C has some interesting properties.<br />
• Add elements (1,2) and (1,3) = -.1667, which is the negative of the ratio of σ 2 c /σ 2 e.<br />
• Add elements (1,4), (1,5), and (1,6) = -.08696, which is the negative of the ratio of σ 2 s/σ 2 e.<br />
• Add elements (2,2) and (2,3), or (3,2) plus (3,3) = .1667, ratio of contemporary group<br />
variance to residual variance.<br />
• Add elements (4,4) plus (4,5) plus (4,6) = .08696, ratio of sire variance to residual variance.<br />
Also, ( (5,4)+(5,5)+(5,6) = (6,4)+(6,5)+(6,6) ).<br />
• The sum of ((4,2)+(5,2)+(6,2)) = ((4,3)+(5,3)+(6,3)) = 0.<br />
22