Undergraduate Research Journal
Undergraduate Research Journal
Undergraduate Research Journal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Molecular Analysis of the Interaction Between Staphylococcus aureus Protein Sbi and Immune System Protein C3d<br />
Wilson Rodriguez<br />
Table 1. C3d-Sbi intermolecular<br />
Coulombic interactions for complex 1.<br />
Using 6Å Oxygen-Nitrogen cut-off. 11<br />
Table 2. C3d-Sbi intermolecular Coulombic<br />
interactions for complex 2. Using 6Å Oxygen-<br />
Nitrogen cut-off. 11<br />
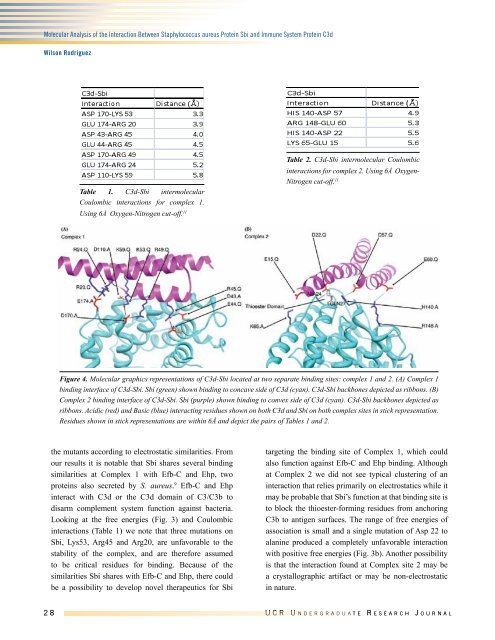
Figure 4. Molecular graphics representations of C3d-Sbi located at two separate binding sites: complex 1 and 2. (A) Complex 1<br />
binding interface of C3d-Sbi. Sbi (green) shown binding to concave side of C3d (cyan). C3d-Sbi backbones depicted as ribbons. (B)<br />
Complex 2 binding interface of C3d-Sbi. Sbi (purple) shown binding to convex side of C3d (cyan). C3d-Sbi backbones depicted as<br />
ribbons. Acidic (red) and Basic (blue) interacting residues shown on both C3d and Sbi on both complex sites in stick representation.<br />
Residues shown in stick representations are within 6Å and depict the pairs of Tables 1 and 2.<br />
the mutants according to electrostatic similarities. From<br />
our results it is notable that Sbi shares several binding<br />
similarities at Complex 1 with Efb-C and Ehp, two<br />
proteins also secreted by S. aureus. 9 Efb-C and Ehp<br />
interact with C3d or the C3d domain of C3/C3b to<br />
disarm complement system function against bacteria.<br />
Looking at the free energies (Fig. 3) and Coulombic<br />
interactions (Table 1) we note that three mutations on<br />
Sbi, Lys53, Arg45 and Arg20, are unfavorable to the<br />
stability of the complex, and are therefore assumed<br />
to be critical residues for binding. Because of the<br />
similarities Sbi shares with Efb-C and Ehp, there could<br />
be a possibility to develop novel therapeutics for Sbi<br />
targeting the binding site of Complex 1, which could<br />
also function against Efb-C and Ehp binding. Although<br />
at Complex 2 we did not see typical clustering of an<br />
interaction that relies primarily on electrostatics while it<br />
may be probable that Sbi’s function at that binding site is<br />
to block the thioester-forming residues from anchoring<br />
C3b to antigen surfaces. The range of free energies of<br />
association is small and a single mutation of Asp 22 to<br />
alanine produced a completely unfavorable interaction<br />
with positive free energies (Fig. 3b). Another possibility<br />
is that the interaction found at Complex site 2 may be<br />
a crystallographic artifact or may be non-electrostatic<br />
in nature.<br />
2 8 U C R U n d e r g r a d u a t e R e s e a r c h J o u r n a l