Mitel Technical Specification 22
Mitel Technical Specification 22
Mitel Technical Specification 22
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
MiNET <strong>Specification</strong><br />
MT Octet 1<br />
Start address<br />
Octet 2<br />
Start address<br />
End address<br />
Octet 5<br />
Octet 6<br />
End address<br />
Expected checksum<br />
Expected checksum<br />
Octet 9<br />
Octet 10<br />
Octet 11<br />
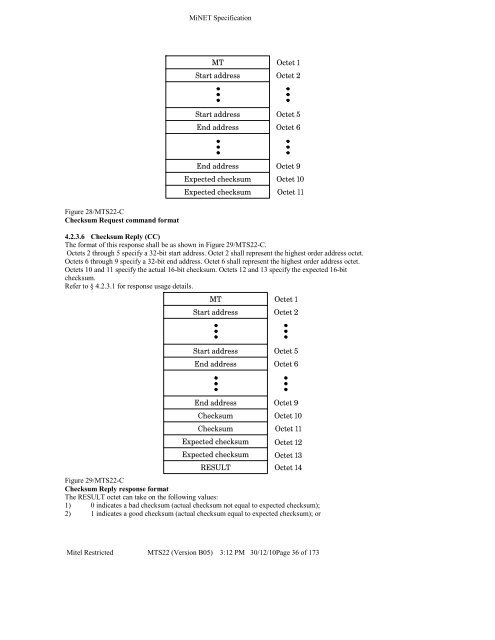
Figure 28/MTS<strong>22</strong>-C<br />
Checksum Request command format<br />
4.2.3.6 Checksum Reply (CC)<br />
The format of this response shall be as shown in Figure 29/MTS<strong>22</strong>-C.<br />
Octets 2 through 5 specify a 32-bit start address. Octet 2 shall represent the highest order address octet.<br />
Octets 6 through 9 specify a 32-bit end address. Octet 6 shall represent the highest order address octet.<br />
Octets 10 and 11 specify the actual 16-bit checksum. Octets 12 and 13 specify the expected 16-bit<br />
checksum.<br />
Refer to § 4.2.3.1 for response usage details.<br />
MT Octet 1<br />
Start address<br />
Octet 2<br />
Start address<br />
End address<br />
Octet 5<br />
Octet 6<br />
End address<br />
Checksum<br />
Checksum<br />
Expected checksum<br />
Expected checksum<br />
RESULT<br />
Octet 9<br />
Octet 10<br />
Octet 11<br />
Octet 12<br />
Octet 13<br />
Octet 14<br />
Figure 29/MTS<strong>22</strong>-C<br />
Checksum Reply response format<br />
The RESULT octet can take on the following values:<br />
1) 0 indicates a bad checksum (actual checksum not equal to expected checksum);<br />
2) 1 indicates a good checksum (actual checksum equal to expected checksum); or<br />
<strong>Mitel</strong> Restricted MTS<strong>22</strong> (Version B05) 3:12 PM 30/12/10Page 36 of 173