in vivo
in vivo
in vivo
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
eos<strong>in</strong>ophil-mediated asthma responses. These<br />
results <strong>in</strong>dicate that E4BP4 controls the <strong>in</strong>duction<br />
of a unique T subset, Th1/13, to possibly <strong>in</strong>itiate<br />
allergic <strong>in</strong>cidents <strong>in</strong> otherwise chronic Th1<br />
biased situations. Our f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs provide a novel<br />
<strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the traditional dogma of Th1 and<br />
Th2 balance <strong>in</strong> allergic diseases.<br />
Identification of the molecular basis of<br />
Th2 bias<br />
Genetic background is known to <strong>in</strong>fluence<br />
the type of immune responses, and the<br />
molecular basis of TH2 bias has been a longstand<strong>in</strong>g<br />
mystery <strong>in</strong> the field of immunology.<br />
Genetic l<strong>in</strong>kage analyses have been used <strong>in</strong> a<br />
comparison of BALB/c versus B10.D2 stra<strong>in</strong>s<br />
with respect to their ability to produce IL-4<br />
upon <strong>in</strong>itial TCR stimulation. These studies<br />
have identified Determ<strong>in</strong>ant of IL-4 commitment<br />
(Dice)1.2 on chromosome16 as one trait locus<br />
that controls Th2 bias . We found that Myc<strong>in</strong>duced<br />
nuclear antigen with a molecular mass<br />
of 53kDa (m<strong>in</strong>a53)expression was consistently<br />
higher <strong>in</strong> Th1- prone stra<strong>in</strong>s (B10.D2) than Th2-<br />
prone stra<strong>in</strong>s (BALB/c). The genome sequences<br />
of the 5’ flank<strong>in</strong>g sequence and the first <strong>in</strong>tron<br />
region conta<strong>in</strong>ed multiple SNPs among different<br />
mouse stra<strong>in</strong>s, and these tightly associate with<br />
the propensity to produce <strong>in</strong>itial IL-4. Interest<strong>in</strong>gly,<br />
The SNPs <strong>in</strong> the promoter region of human<br />
m<strong>in</strong>a53 gene associated with severity of allergic<br />
asthma. These results <strong>in</strong>dicated that M<strong>in</strong>a53 is<br />
a useful genetic maker for Th2 bias and allergic<br />
predisposition <strong>in</strong> mouse and human.<br />
Role of memory phenotype CD4 T cells <strong>in</strong><br />
Th17 mediated immune-regulation<br />
The distal 3’ enhancer <strong>in</strong> the Il4 locus<br />
corresponds to a highly conserved region termed<br />
conserved non-cod<strong>in</strong>g sequences (CNS)-2.<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g a transgenic GFP reporter system,<br />
we demonstrated that the CNS-2 enhancer<br />
regulated the <strong>in</strong>itial expression of IL-4 <strong>in</strong> CD44 hi<br />
memory phenotype (MP) CD4 T cells. These<br />
IL-4 produc<strong>in</strong>g MP-CD4 cells co-expressed<br />
IFN-γ, while GFP - IL-4 non-produc<strong>in</strong>g MP cells<br />
expressed robust IL-17 and IFN-γ. The IL-17<br />
produc<strong>in</strong>g MP (MP-Th17) cells appeared to be<br />
dist<strong>in</strong>ct population from canonical Th17 cells<br />
s<strong>in</strong>ce MP-Th17 cells developed <strong>in</strong> the absence<br />
of IL-6, which is required for Th17 differentiation.<br />
The MP-Th17 cells had an alternative role to<br />
<strong>in</strong>duce IL-17 production by dendritic cells (DC)<br />
<strong>in</strong> an IL-17 dependent manner. These results<br />
demonstrated that rapid IL-17 production by<br />
MP-Th17 cell resulted <strong>in</strong> the secondary<br />
production of this cytok<strong>in</strong>e by DCs to exacerbate<br />
<strong>in</strong>flammatory responses.<br />
Recent publications<br />
Seki, Y., Yang, J., Okamoto,<br />
M., Tanaka, S., Goizuka, Farrar,<br />
M.A., R., and Kubo, M., ; The<br />
role of IL-7/STAT5 pathway and<br />
suppressor of cytok<strong>in</strong>e signal<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1 <strong>in</strong> ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of naive and<br />
memory CD4 T cells <strong>in</strong> peripheral<br />
lymphoid organs. J. Immunol.<br />
1;178(1):262-70, 2007<br />
Numata, K., Kubo, M., Watanabe,<br />
H., Takagi, K., Mizuta, H., Okada,<br />
S., Ito, T., and Matsukawa, A.,;<br />
Overexpression of Suppressor<br />
of Cytok<strong>in</strong>e Signal<strong>in</strong>g-3 <strong>in</strong> T cells<br />
Exacerbates Acetam<strong>in</strong>ophen–<br />
<strong>in</strong>duced Hepatotoxicity. J. Immunol.<br />
178 3777-3785, 2007<br />
Yoshimura, A., Naka, T., Kubo, M.,;<br />
SOCS prote<strong>in</strong>s, cytok<strong>in</strong>e signall<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and immune regulation. Nature<br />
Review Immunology 7, 454-465,<br />
2007<br />
Yagi, R., Tanaka, S., Motomura, Y.,<br />
and Kubo, M., The regulation of Il4<br />
gene expression <strong>in</strong> mast cells and<br />
basophils is regulated by dist<strong>in</strong>ct<br />
proximal and distal 3’ enhancers.<br />
Mol. Cell. Biol. 27(23), 8087-8097,<br />
2007<br />
Kano, S., Sato, K., Morishita,<br />
Y., Vollstedt, S., Kim, S., Taki,<br />
S., Honda, K., Kubo, M., &<br />
Taniguchi, T.; Regulation of Th1<br />
vs. Th17 differentiation: Selective<br />
contribution of thetranscription<br />
factor IRF1 to the IFN-γ-IL-12 axis<br />
of signal<strong>in</strong>g networks <strong>in</strong> CD4 + T<br />
cells. Nature Immunology 9, 34 -<br />
41, 2008<br />
Figure<br />
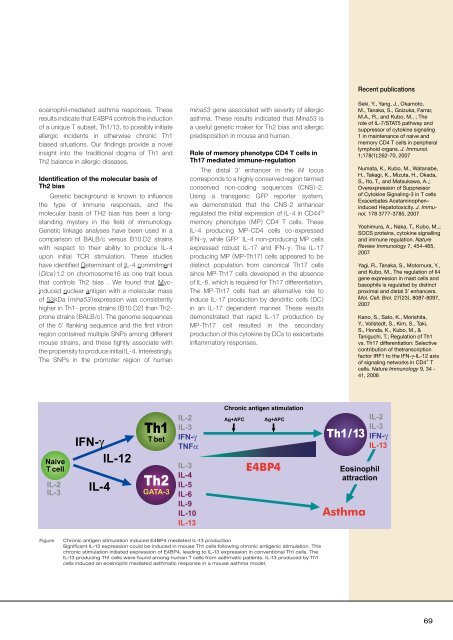
Chronic antigen stimulation <strong>in</strong>duced E4BP4 mediated IL-13 production<br />
Significant IL-13 expression could be <strong>in</strong>duced <strong>in</strong> mouse Th1 cells follow<strong>in</strong>g chronic antigenic stimulation. This<br />
chronic stimulation <strong>in</strong>itiated expression of E4BP4, lead<strong>in</strong>g to IL-13 expression <strong>in</strong> conventional Th1 cells. The<br />
IL-13 produc<strong>in</strong>g Th1 cells were found among human T cells from asthmatic patients. IL-13 produced by Th1<br />
cells <strong>in</strong>duced an eos<strong>in</strong>ophil mediated asthmatic response <strong>in</strong> a mouse asthma model.<br />
69