Development of Circularly Polarized Microstrip ... - CEReS - åè大å¦
Development of Circularly Polarized Microstrip ... - CEReS - åè大å¦
Development of Circularly Polarized Microstrip ... - CEReS - åè大å¦
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
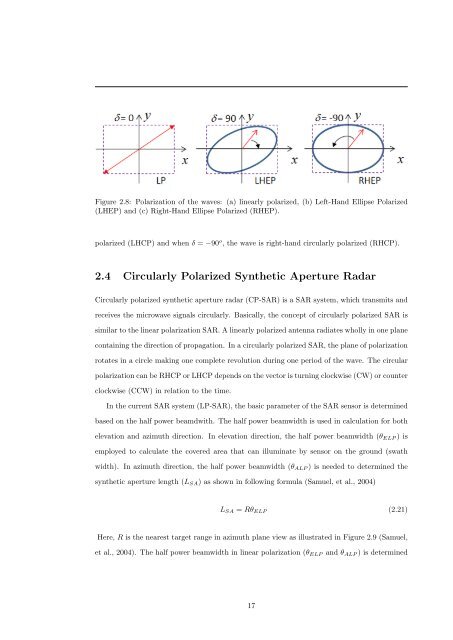
Figure 2.8: Polarization <strong>of</strong> the waves: (a) linearly polarized, (b) Left-Hand Ellipse <strong>Polarized</strong><br />
(LHEP) and (c) Right-Hand Ellipse <strong>Polarized</strong> (RHEP).<br />
polarized (LHCP) and when δ = −90 o , the wave is right-hand circularly polarized (RHCP).<br />
2.4 <strong>Circularly</strong> <strong>Polarized</strong> Synthetic Aperture Radar<br />
<strong>Circularly</strong> polarized synthetic aperture radar (CP-SAR) is a SAR system, which transmits and<br />
receives the microwave signals circularly. Basically, the concept <strong>of</strong> circularly polarized SAR is<br />
similar to the linear polarization SAR. A linearly polarized antenna radiates wholly in one plane<br />
containing the direction <strong>of</strong> propagation. In a circularly polarized SAR, the plane <strong>of</strong> polarization<br />
rotates in a circle making one complete revolution during one period <strong>of</strong> the wave. The circular<br />
polarization can be RHCP or LHCP depends on the vector is turning clockwise (CW) or counter<br />
clockwise (CCW) in relation to the time.<br />
In the current SAR system (LP-SAR), the basic parameter <strong>of</strong> the SAR sensor is determined<br />
based on the half power beamdwith. The half power beamwidth is used in calculation for both<br />
elevation and azimuth direction. In elevation direction, the half power beamwidth (θ ELP ) is<br />
employed to calculate the covered area that can illuminate by sensor on the ground (swath<br />
width). In azimuth direction, the half power beamwidth (θ ALP ) is needed to determined the<br />
synthetic aperture length (L SA ) as shown in following formula (Samuel, et al., 2004)<br />
L SA = Rθ ELP (2.21)<br />
Here, R is the nearest target range in azimuth plane view as illustrated in Figure 2.9 (Samuel,<br />
et al., 2004). The half power beamwidth in linear polarization (θ ELP and θ ALP ) is determined<br />
17