Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW.
Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW.
Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences - SGGW.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
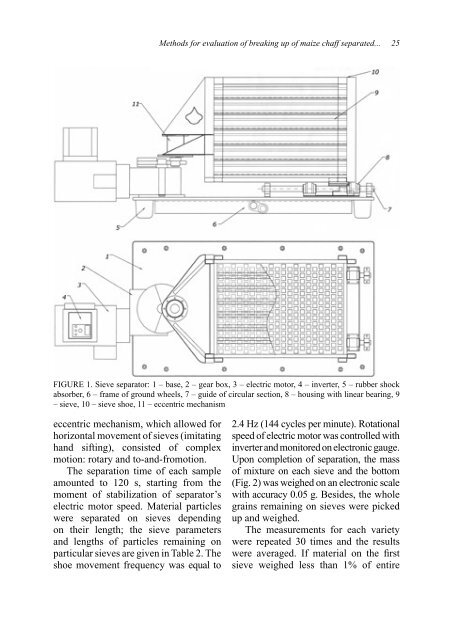
Methods for evaluation <strong>of</strong> breaking up <strong>of</strong> maize chaff separated... 25FIGURE 1. Sieve separator: 1 – base, 2 – gear box, 3 – electric motor, 4 – inverter, 5 – rubber shockabsorber, 6 – frame <strong>of</strong> ground wheels, 7 – guide <strong>of</strong> circular section, 8 – housing with linear bearing, 9– sieve, 10 – sieve shoe, 11 – eccentric mechanismeccentric mechanism, which allowed forhorizontal movement <strong>of</strong> sieves (imitatinghand sifting), consisted <strong>of</strong> complexmotion: rotary and to-and-fromotion.The separation time <strong>of</strong> each sampleamounted to 120 s, starting from themoment <strong>of</strong> stabilization <strong>of</strong> separator’selectric motor speed. Material particleswere separated on sieves dependingon their length; the sieve parametersand lengths <strong>of</strong> particles remaining onparticular sieves are given in Table 2. Theshoe movement frequency was equal to2.4 Hz (144 cycles per minute). Rotationalspeed <strong>of</strong> electric motor was controlled withinverter and monitored on electronic gauge.Upon completion <strong>of</strong> separation, the mass<strong>of</strong> mixture on each sieve and the bottom(Fig. 2) was weighed on an electronic scalewith accuracy 0.05 g. Besides, the wholegrains remaining on sieves were pickedup and weighed.The measurements for each varietywere repeated 30 times and the resultswere averaged. If material on the firstsieve weighed less than 1% <strong>of</strong> entire