SUUNTO t6c RUNNING GUIDE
SUUNTO t6c RUNNING GUIDE
SUUNTO t6c RUNNING GUIDE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
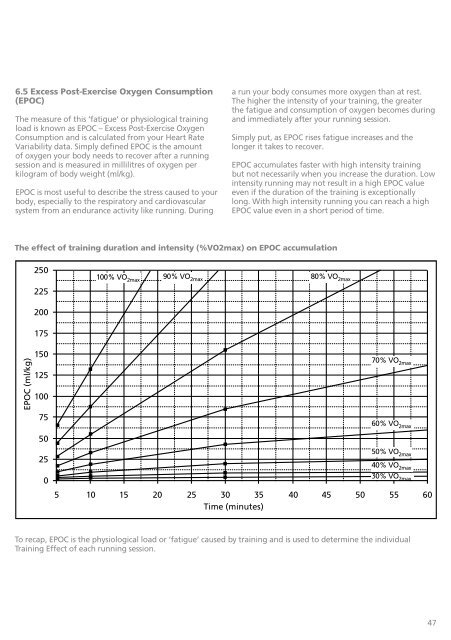
6.5 Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption(EPOC)The measure of this ‘fatigue’ or physiological trainingload is known as EPOC – Excess Post-Exercise OxygenConsumption and is calculated from your Heart RateVariability data. Simply defined EPOC is the amountof oxygen your body needs to recover after a runningsession and is measured in millilitres of oxygen perkilogram of body weight (ml/kg).EPOC is most useful to describe the stress caused to yourbody, especially to the respiratory and cardiovascularsystem from an endurance activity like running. Duringa run your body consumes more oxygen than at rest.The higher the intensity of your training, the greaterthe fatigue and consumption of oxygen becomes duringand immediately after your running session.Simply put, as EPOC rises fatigue increases and thelonger it takes to recover.EPOC accumulates faster with high intensity trainingbut not necessarily when you increase the duration. Lowintensity running may not result in a high EPOC valueeven if the duration of the training is exceptionallylong. With high intensity running you can reach a highEPOC value even in a short period of time.The effect of training duration and intensity (%VO2max) on EPOC accumulation250225200175100% VO 2max 90% VO 2max 80% VO 2max70% VO 2maxEPOC (ml/kg)150125100755025060% VO 2max50% VO 2max40% VO 2max30% VO 2max5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60Time (minutes)To recap, EPOC is the physiological load or ‘fatigue’ caused by training and is used to determine the individualTraining Effect of each running session.47