Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
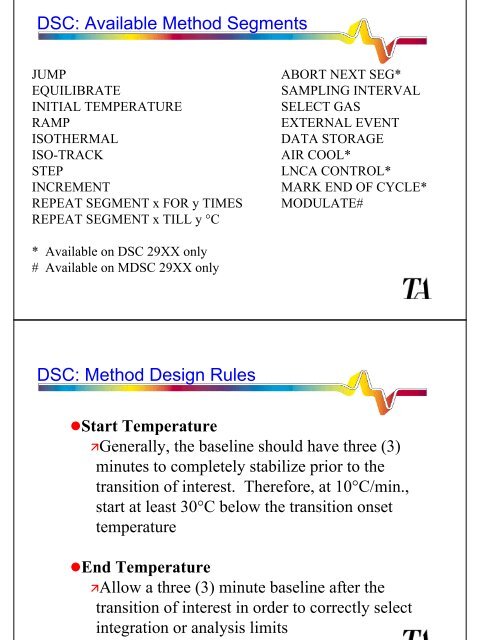
<strong>DSC</strong>: Available Method Segments<br />
JUMP ABORT NEXT SEG*<br />
EQUILIBRATE SAMPLING INTERVAL<br />
INITIAL TEMPERATURE SELECT GAS<br />
RAMP EXTERNAL EVENT<br />
ISOTHERMAL DATA STORAGE<br />
ISO-TRACK AIR COOL*<br />
STEP LNCA CONTROL*<br />
INCREMENT MARK END OF CYCLE*<br />
REPEAT SEGMENT x FOR y TIMES MODULATE#<br />
REPEAT SEGMENT x TILL y °C<br />
* Available on <strong>DSC</strong> 29XX only<br />
# Available on M<strong>DSC</strong> 29XX only<br />
<strong>DSC</strong>: Method Design Rules<br />
�Start Temperature<br />
�Generally, the baseline should have three (3)<br />
minutes to completely stabilize prior to the<br />
transition of interest. Therefore, at 10°C/min.,<br />
start at least 30°C below the transition onset<br />
temperature<br />
�End Temperature<br />
�Allow a three (3) minute baseline after the<br />
transition of interest in order to correctly select<br />
integration or analysis limits