Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
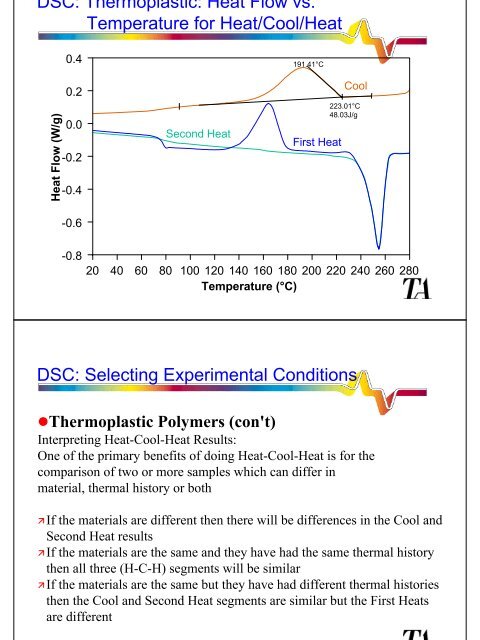
<strong>DSC</strong>: Thermoplastic: Heat Flow vs.<br />
Temperature for Heat/Cool/Heat<br />
Heat Flow (W/g)<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0.0<br />
-0.2<br />
-0.4<br />
-0.6<br />
Second Heat<br />
191.41°C<br />
First Heat<br />
Cool<br />
223.01°C<br />
48.03J/g<br />
-0.8<br />
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280<br />
Temperature (°C)<br />
<strong>DSC</strong>: Selecting Experimental Conditions<br />
�Thermoplastic Polymers (con't)<br />
Interpreting Heat-Cool-Heat Results:<br />
One of the primary benefits of doing Heat-Cool-Heat is for the<br />
comparison of two or more samples which can differ in<br />
material, thermal history or both<br />
�If the materials are different then there will be differences in the Cool and<br />
Second Heat results<br />
�If the materials are the same and they have had the same thermal history<br />
then all three (H-C-H) segments will be similar<br />
�If the materials are the same but they have had different thermal histories<br />
then the Cool and Second Heat segments are similar but the First Heats<br />
are different