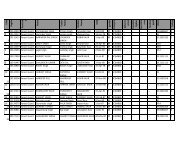
AS-IS STATUS REPORT - Pbforests.gov.in
AS-IS STATUS REPORT - Pbforests.gov.in
AS-IS STATUS REPORT - Pbforests.gov.in
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Figure 1 Map of Punjab and its DistrictsBACKGROUND1 BACKGROUNDForests are a renewable resource and performproductive as well as protective functions.Apart from provid<strong>in</strong>g various products, forestsreduce soil erosion, regulate the flow of water,control floods, moderate climate, <strong>in</strong>creasera<strong>in</strong>fall and enrich genetic reserve of flora andfauna. Forests play an important role <strong>in</strong>improv<strong>in</strong>g the quality of environment.1.1 Forests <strong>in</strong> Punjab:With over 6% of the state‟s geographical areaas forests, substantial tracts of areas outsideforests where tree plant<strong>in</strong>g is taken up, and thelarger need to balance the requirements ofconservation and development <strong>in</strong> Punjab, theimportance of forests <strong>in</strong> the socio-economicdevelopment of Punjab cannot beoveremphasized. Forests <strong>in</strong> the state spanmany forest types <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the Tropical DryDeciduous, Tropical Thorn and Sub-tropicalP<strong>in</strong>e Forests, <strong>in</strong> addition to other specializedforest types. Additionally, wildlife areas takentogether with the forests, present a mosaic ofhabitat types <strong>in</strong> the state. Figure 1 br<strong>in</strong>gs out amap of the state with its ma<strong>in</strong> districts.1.2 Threats to the forests <strong>in</strong> PunjabPunjab is short of the national goal of hav<strong>in</strong>g am<strong>in</strong>imum of one-third of the total land area ofthe country under forest or tree coverenunciated <strong>in</strong> the National Forest Policy, 1988.The obvious reason for the same is that most ofthe geographical area of the State is underagriculture. Concrete and susta<strong>in</strong>ed efforts arerequired to <strong>in</strong>crease forest and tree cover <strong>in</strong>the state significantly. Therefore, forestryactivities should not only be aimed atimprov<strong>in</strong>g the tree cover but also encourag<strong>in</strong>gplantations on farmlands through agro/farmforestry <strong>in</strong> a big way.Multiplicity of ThreatsThe forest areas <strong>in</strong> Punjab are however, underserious threat due to a number of factors.Whereas prior to the 19 th century forests wereprotected by local rulers, vegetation coverstarted decl<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g due to unrestricted fell<strong>in</strong>gand over graz<strong>in</strong>g when these areas weretransferred to villages. Subsequent enactmentof the Punjab Land Preservation Act, 1900provided power to the <strong>gov</strong>ernment totemporarily regulate, restrict or prohibitcerta<strong>in</strong> activities <strong>in</strong> forest areas and take upreforestation and soil conservationprogrammes.High Anthropogenic Pressure on ForestsPoor enforcement of the Act has led todeterioration of forests <strong>in</strong> Punjab. Further,large displacement of population and its resettlement<strong>in</strong> the wake of partition of Punjabalso led to diversion of large tracts of forestareas for habitation and agriculture and caus<strong>in</strong>gland degradation <strong>in</strong> general. Forests <strong>in</strong> thestate are dist<strong>in</strong>guished not just by their“patchy” nature, but also by the extent ofanthropogenic pressures be<strong>in</strong>g faced ow<strong>in</strong>g tothe dependence of large sections of thepopulation on the forests.To reduce this dependence, there is an urgentneed to take various measures like12