VoIP Acoustic Design - VLSI Solution
VoIP Acoustic Design - VLSI Solution
VoIP Acoustic Design - VLSI Solution
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
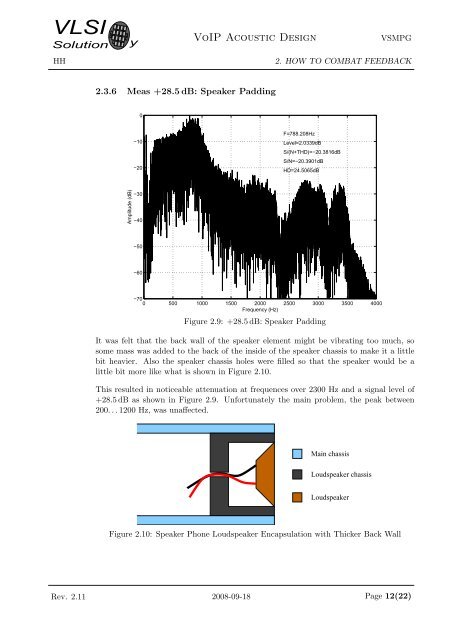
<strong>VLSI</strong><strong>Solution</strong>HHy<strong>VoIP</strong> <strong>Acoustic</strong> <strong>Design</strong>VSMPG2. HOW TO COMBAT FEEDBACK2.3.6 Meas +28.5 dB: Speaker Padding0−10−20F=788.208HzLevel=2.0339dBS/(N+THD)=−20.3816dBS/N=−20.3901dBHD=24.5065dBAmplitude (dB)−30−40−50−60−700 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000Frequency (Hz)Figure 2.9: +28.5 dB: Speaker PaddingIt was felt that the back wall of the speaker element might be vibrating too much, sosome mass was added to the back of the inside of the speaker chassis to make it a littlebit heavier. Also the speaker chassis holes were filled so that the speaker would be alittle bit more like what is shown in Figure 2.10.This resulted in noticeable attenuation at frequences over 2300 Hz and a signal level of+28.5 dB as shown in Figure 2.9. Unfortunately the main problem, the peak between200. . . 1200 Hz, was unaffected.Main chassisLoudspeaker chassisLoudspeakerFigure 2.10: Speaker Phone Loudspeaker Encapsulation with Thicker Back WallRev. 2.11 2008-09-18 Page 12(22)