best practice guidelines: wound management in diabetic foot ulcers
best practice guidelines: wound management in diabetic foot ulcers
best practice guidelines: wound management in diabetic foot ulcers
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
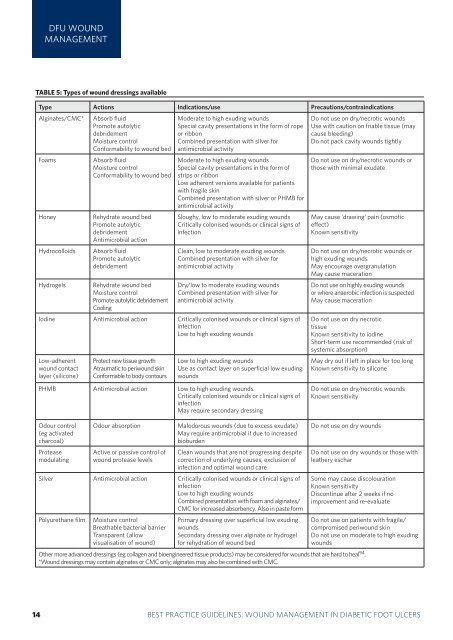
DFU WOUNDMANAGEMENTTABLE 5: Types of <strong>wound</strong> dress<strong>in</strong>gs availableType Actions Indications/use Precautions/contra<strong>in</strong>dicationsAlg<strong>in</strong>ates/CMC*FoamsHoneyHydrocolloidsHydrogelsAbsorb fluidPromote autolyticdebridementMoisture controlConformability to <strong>wound</strong> bedAbsorb fluidMoisture controlConformability to <strong>wound</strong> bedRehydrate <strong>wound</strong> bedPromote autolyticdebridementAntimicrobial actionAbsorb fluidPromote autolyticdebridementRehydrate <strong>wound</strong> bedMoisture controlPromote autolytic debridementCool<strong>in</strong>gModerate to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sSpecial cavity presentations <strong>in</strong> the form of ropeor ribbonComb<strong>in</strong>ed presentation with silver forantimicrobial activityModerate to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sSpecial cavity presentations <strong>in</strong> the form ofstrips or ribbonLow adherent versions available for patientswith fragile sk<strong>in</strong>Comb<strong>in</strong>ed presentation with silver or PHMB forantimicrobial activitySloughy, low to moderate exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sCritically colonised <strong>wound</strong>s or cl<strong>in</strong>ical signs of<strong>in</strong>fectionClean, low to moderate exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sComb<strong>in</strong>ed presentation with silver forantimicrobial activityDry/low to moderate exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sComb<strong>in</strong>ed presentation with silver forantimicrobial activityIod<strong>in</strong>e Antimicrobial action Critically colonised <strong>wound</strong>s or cl<strong>in</strong>ical signs of<strong>in</strong>fectionLow to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sLow-adherent<strong>wound</strong> contactlayer (silicone)Protect new tissue growthAtraumatic to peri<strong>wound</strong> sk<strong>in</strong>Conformable to body contoursLow to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sUse as contact layer on superficial low exud<strong>in</strong>g<strong>wound</strong>sDo not use on dry/necrotic <strong>wound</strong>sUse with caution on friable tissue (maycause bleed<strong>in</strong>g)Do not pack cavity <strong>wound</strong>s tightlyDo not use on dry/necrotic <strong>wound</strong>s orthose with m<strong>in</strong>imal exudateMay cause 'draw<strong>in</strong>g' pa<strong>in</strong> (osmoticeffect)Known sensitivityDo not use on dry/necrotic <strong>wound</strong>s orhigh exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sMay encourage overgranulationMay cause macerationDo not use on highly exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sor where anaerobic <strong>in</strong>fection is suspectedMay cause macerationDo not use on dry necrotictissueKnown sensitivity to iod<strong>in</strong>eShort-term use recommended (risk ofsystemic absorption)May dry out if left <strong>in</strong> place for too longKnown sensitivity to siliconePHMB Antimicrobial action Low to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sCritically colonised <strong>wound</strong>s or cl<strong>in</strong>ical signs of<strong>in</strong>fectionMay require secondary dress<strong>in</strong>gDo not use on dry/necrotic <strong>wound</strong>sKnown sensitivityOdour control(eg activatedcharcoal)Proteasemodulat<strong>in</strong>gOdour absorptionActive or passive control of<strong>wound</strong> protease levelsMalodorous <strong>wound</strong>s (due to excess exudate)May require antimicrobial if due to <strong>in</strong>creasedbioburdenClean <strong>wound</strong>s that are not progress<strong>in</strong>g despitecorrection of underly<strong>in</strong>g causes, exclusion of<strong>in</strong>fection and optimal <strong>wound</strong> careSilver Antimicrobial action Critically colonised <strong>wound</strong>s or cl<strong>in</strong>ical signs of<strong>in</strong>fectionLow to high exud<strong>in</strong>g <strong>wound</strong>sComb<strong>in</strong>ed presentation with foam and alg<strong>in</strong>ates/CMC for <strong>in</strong>creased absorbency. Also <strong>in</strong> paste formPolyurethane filmMoisture controlBreathable bacterial barrierTransparent (allowvisualisation of <strong>wound</strong>)Primary dress<strong>in</strong>g over superficial low exud<strong>in</strong>g<strong>wound</strong>sSecondary dress<strong>in</strong>g over alg<strong>in</strong>ate or hydrogelfor rehydration of <strong>wound</strong> bedDo not use on dry <strong>wound</strong>sDo not use on dry <strong>wound</strong>s or those withleathery escharSome may cause discolourationKnown sensitivityDiscont<strong>in</strong>ue after 2 weeks if noimprovement and re-evaluateDo not use on patients with fragile/compromised peri<strong>wound</strong> sk<strong>in</strong>Do not use on moderate to high exud<strong>in</strong>g<strong>wound</strong>sOther more advanced dress<strong>in</strong>gs (eg collagen and bioeng<strong>in</strong>eered tissue products) may be considered for <strong>wound</strong>s that are hard to heal 94 .*Wound dress<strong>in</strong>gs may conta<strong>in</strong> alg<strong>in</strong>ates or CMC only; alg<strong>in</strong>ates may also be comb<strong>in</strong>ed with CMC.314 BEST PRACTICEBEST PRACTICEGUIDELINESGUIDELINES:FOR SKINWOUNDAND WOUNDMANAGEMENTCARE ININEPIDERMOLYSISDIABETIC FOOTBULLOSAULCERS