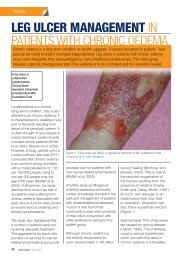
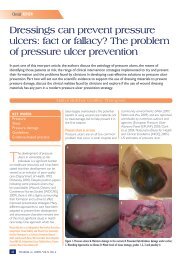
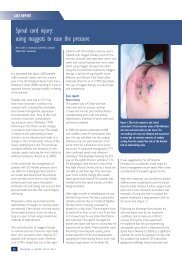
GLOBAL WOUNDCARE PLANSteps to avoid amputation: implement<strong>in</strong>g a global <strong>wound</strong> care planA Diagnosis of diabetes (+/_ peripheral sensory neuropathy)AIM: Prevent the development of a DFU1. Implement DFU prevention care plan that <strong>in</strong>cludes treatment of co-morbidities, good glycaemiccontrol and pressure offload<strong>in</strong>g2. Annually perform general <strong>foot</strong> exam<strong>in</strong>ation:— Use 10g monofilament to assess sensory status— Inspection of the feet for deformities— Inspection of <strong>foot</strong>wear for wear and tear and foreign objects that may traumatise <strong>foot</strong>— Ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> sk<strong>in</strong> hydration (consider emollient therapy) for sk<strong>in</strong> health— Offer patient education on check<strong>in</strong>g feet for trauma3. Ensure regular review and provide patient educationBCDevelopment of DFUAIM: Treat the ulcer and prevent <strong>in</strong>fection1. Determ<strong>in</strong>e cause of ulcer2. Agree treatment aims with patient and implement <strong>wound</strong> care plan:— Debride and regularly cleanse the <strong>wound</strong>— Take appropriate tissue samples for culture if <strong>in</strong>fection is suspected— Select dress<strong>in</strong>gs to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> moist <strong>wound</strong> environment and manage exudate effectively3. Initiate antibiotic treatment if <strong>in</strong>fection suspected and consider topical antimicrobial therapyif <strong>in</strong>creased bioburden is suspected4. Review offload<strong>in</strong>g device and ensure <strong>foot</strong>wear accommodates dress<strong>in</strong>g5. Optimise glycaemic control for diabetes <strong>management</strong>6. Refer for vascular assessment if cl<strong>in</strong>ically significant limb ischaemia is suspected7. Offer patient education on how to self-manage and when to raise concernsDevelopment of vascular diseaseAIM: Prevent complications associated with ischaemia1. Ensure early referral to vascular specialist for arterial reconstruction to improve blood flow <strong>in</strong>patients with an ischaemic or neuroischaemic ulcer2. Optimise diabetes controlD Ulcer becomes <strong>in</strong>fectedAIM: Prevent life- or limb-threaten<strong>in</strong>g complications1. For superficial (mild) <strong>in</strong>fections — treat with systemic antibiotics and consider topicalantimicrobials <strong>in</strong> selected cases2. For deep (moderate or severe) <strong>in</strong>fections — treat with appropriately selected empiric systemicantibiotics, modified by the results of culture and sensitivity reports3. Offload pressure correctly and optimise glycaemic control for diabetes <strong>management</strong>4. Consider therapy directed at biofilm <strong>in</strong> <strong>wound</strong>s that are slow to healACTIVE MANAGEMENT OF THE ULCER AND CO-MORBIDITIES SHOULD AIM TO PREVENT AMPUTATIONWhere amputation is not avoidable:1. Implement sk<strong>in</strong> and <strong>wound</strong> care plan to manage surgical <strong>wound</strong> and optimise heal<strong>in</strong>g2. Review regularly and implement prevention care plan to reduce risk of recurrence or further DFUon contralateral limb320 BEST PRACTICEBEST PRACTICEGUIDELINESGUIDELINES:FOR SKINWOUNDAND WOUNDMANAGEMENTCARE ININEPIDERMOLYSISDIABETIC FOOTBULLOSAULCERS
REFERENCES1. National Institute for Health and Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Excellence. Diabetic <strong>foot</strong>problems: <strong>in</strong>patient <strong>management</strong> of <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> problems. Cl<strong>in</strong>ical guidel<strong>in</strong>e119. London: NICE, 2011. Available at: http://publications.nice.org.uk/<strong>diabetic</strong>-<strong>foot</strong>-problems-cg119. Accessed March 20132. Abetz L, Sutton M, Brady L, et al. The <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> ulcer scale: aquality of life <strong>in</strong>strument for use <strong>in</strong> cl<strong>in</strong>ical trials. Pract Diab Int 2002; 19:167-75.3. Brownrigg JR, Davey J, Holt et al. The association of ulceration of the<strong>foot</strong> with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality <strong>in</strong> patients with diabetes:a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2012; 55(11): 2906-12.4. Diabetes UK. Putt<strong>in</strong>g feet first: national m<strong>in</strong>imum skills framework. Jo<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>itiative from the Diabetes UK, Foot <strong>in</strong> Diabetes UK, NHS Diabetes,the Association of British Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Diabetologists, the Primary CareDiabetes Society, the Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists. London:Diabetes UK, 2011. Available at: http://diabetes.org.uk/putt<strong>in</strong>g-feetfirst.Accessed March 2013.5. Kerr M. Foot care for people with diabetes: the economic case for change.NHS Diabetes, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, 2012. Available at: http://bit.ly/xjY7FS. Accessed March 2013.6. S<strong>in</strong>gh N, Armstrong DA, Lipsky BA. Prevent<strong>in</strong>g <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong> <strong>in</strong> patientswith diabetes. JAMA 2005; 293: 217-28.7. Bakker K, Apelqvist J, Schaper NC on behalf of the International Work<strong>in</strong>gGroup on the Diabetic Foot Editorial Board. Practical <strong>guidel<strong>in</strong>es</strong> on the<strong>management</strong> and prevention of the <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> 2011. Diabetes Metab ResRev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225-31.8. Diabetes UK. State of the nation 2012 – England. London: Diabetes UK,2012. Available at: http://bit.ly/Kcg0TU. Accessed March 2013.9. Ramsay SD, Newton K, Blough D, et al. Incidence, outcomes, andcost of <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong> <strong>in</strong> patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999; 22:382-87.10. Assal JP, Mehnert H, Tritschler HS, et al. ‘On your feet’ workshop on the<strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>. J Diabet Comp 2002; 16: 183-94.11. Rathur HM, Boulton AJM. The <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>. Cl<strong>in</strong> Dermatol 2007; 25:109-20.12. Prompers L, Huijberts M, Schaper N, et al. Resource utilisation andcosts associated with the treatment of <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong>. Prospectivedata from the EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 1826-34.13. Young MJ, McCardle JE, Randall LE, et al. Improved survival of<strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> ulcer patients 1995-2008: possible impact of aggressivecardiovascular risk <strong>management</strong>. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 2143-47.14. H<strong>in</strong>chcliffe RJ, Andros G, Apelqvist J, et al. A systematic review ofthe effectiveness of revascularisation of the ulcerated <strong>foot</strong> <strong>in</strong> patientswith diabetes and peripheral arterial disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev2012; 28(Suppl 1): 179-217.15. Muller IS, Bartel<strong>in</strong>k ML, Wim JC, et al. Foot ulceration and lower limbamputation <strong>in</strong> type 2 <strong>diabetic</strong> patients <strong>in</strong> Dutch Primary Health Care.Diabetes Care 2002; 25(3): 570-74.16. Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, et al. The global burdenof <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> disease. Lancet 2005; 366: 1719-1724.17. Frykberg RG. Diabetic <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong>: pathogenesis and <strong>management</strong>. AmFam Physician 2002; 66(9): 1655-62.18. Berthel M, Ehrler S. Aspects épidémiologiques de l'amputation demembre <strong>in</strong>férieur en france. K<strong>in</strong>esitherapie Scientifique 2010; 7(512): 5-8.19. Armstrong DG, Wrobel J, Robb<strong>in</strong>s JM. Guest editorial: are diabetesrelated<strong>wound</strong>s and amputations worse than cancer? Int Wound J 2007;4: 286-87.20. Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM. Pathways to <strong>diabetic</strong> limb amputation.Basis for prevention. Diabetes Care 1990; 13(5): 513-21.21. Chadwick P, Jeffcoate W, McIntosh C. How can we improve the care ofthe <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>? Wounds UK 2008; 4(4): 144-48.22. TRIEPodD-UK. Podiatry competency framework for <strong>in</strong>tegrated <strong>diabetic</strong><strong>foot</strong> care — a user’s guide. London: TRIEpodD-UK, 2012.23. Prompers L, Schaper N, Apelqvist J, et al. Prediction of outcome <strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>dividuals with <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong>: focus on the differences between<strong>in</strong>dividuals with and without peripheral arterial disease. The EURODI-ALE Study. Diabetologia 2008; 51(5): 747-55.24. Lavery LA, Armstrong DA, Wunderlich RP, et al. Risk factors for <strong>foot</strong><strong>in</strong>fections <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dividuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006; 29(6):1288-93.25. Rogers LC. Prevent<strong>in</strong>g amputation <strong>in</strong> patients with diabetes. PodiatryToday 2008; 21(3): 44-50.26. International Work<strong>in</strong>g Group on the Diabetic Foot. International consensuson the <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> and practical <strong>guidel<strong>in</strong>es</strong> on the <strong>management</strong> and theprevention of the <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>. Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2011.27. International Diabetes Federation Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Guidel<strong>in</strong>es Taskforce. Globalguidel<strong>in</strong>e for type 2 diabetes. Brussels: IDF, 2012. Available at: http://www.idf.org. Accessed March 2013.28. Boulton AJ, Armstrong DG, Albert SF, et al. Comprehensive <strong>foot</strong> exam<strong>in</strong>ationand risk assessment. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 1679-85.29. Reiber GE, Vileikyte L, Boyko EJ, et al. Causal pathways for <strong>in</strong>cidentlower-extremity <strong>ulcers</strong> <strong>in</strong> patients with diabetes from two sett<strong>in</strong>gs.Diabetes Care 1999; 22: 157–62.30. Wu S, Driver VR, Wrobel JS, et al. Foot <strong>ulcers</strong> <strong>in</strong> the <strong>diabetic</strong> patient,prevention and treatment. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2007; 3(1): 65–76.31. Boulton AJM. What you can’t feel can hurt you. J Am Pod Med Assoc2010; 100(5): 349-52.32. Gregg EW, Sorlie P, Paulose-Ram R, et al. Prevalence of lower-extremitydisease <strong>in</strong> the US adult population ≥40 years of age with and withoutdiabetes: 1999-2000 national health and nutrition exam<strong>in</strong>ation survey.Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1591–97.33. Huijberts MS, Schaper NC, Schalkwijk CG. Advanced glycation endproducts and <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong> disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2008;24(Suppl 1): S19-S24.34. Apelqvist J. Diagnostics and treatment of the <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>. Endocr<strong>in</strong>e2012; 41(3): 384-97.35. Armstrong DG, Cohen K, Courric S, et al. Diabetic <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong> and vascular<strong>in</strong>sufficiency: our population has changed, but our methods havenot. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2011; 5(6): 1591-95.36. AWMF [National cl<strong>in</strong>ical <strong>practice</strong> guidel<strong>in</strong>e Type 2 diabetes: prevention andtreatment strategies for <strong>foot</strong> complications] Guidel<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> German. AWMFonl<strong>in</strong>e 2011. Available from: www.awmf.org/leitl<strong>in</strong>ien/detail/ll/nvl-001c.html Accessed April 2013.37. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidel<strong>in</strong>es Network. Management of diabetes.A national cl<strong>in</strong>ical guidel<strong>in</strong>e. Guidel<strong>in</strong>e no 116. Ed<strong>in</strong>burgh: SIGN, 2010.Available at: http:// http://www.sign.ac.uk/<strong>guidel<strong>in</strong>es</strong>/fulltext/116/<strong>in</strong>dex.html. Accessed March 2013.38. Mulder G, Armstrong D, Seaman S. Standard, appropriate, and advancedcare and medical-legal considerations: part one — <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>ulcerations. Wounds 2003; 15(4): 92-106.39. Ousey K, Cook L. Wound assessment Made Easy. Wounds UK 2012;8(2). Available at: http://www.<strong>wound</strong>s-uk.com/made-easy/<strong>wound</strong>assessment-made-easy.Accessed April 2013.40. Clayton W, Elasy TA. A review of the pathophysiology, classification,and treatment of <strong>foot</strong> <strong>ulcers</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>diabetic</strong> patients. Cl<strong>in</strong> Diabetes 2009;27(2): 52-58.41. Malik R, Baker N, Bartlett K, et al. Diabetic Foot J 2010; 13(4): S1-S7.42. Armstrong DW, Tob<strong>in</strong> C, Matangi MF. The accuracy of the physicalexam<strong>in</strong>ation for the detection of lower extremity peripheral arterialdisease. Can J Cardiol 2010; 26(10): e346-50.43. LoGerfo FW, Coffman JD. Vascular and microvascular disease of the<strong>foot</strong> <strong>in</strong> diabetes. N Engl J Med 1984; 311: 1615-19.44. Hirsch AT, Haskal ZJ, Hertzer NR, et al. ACC/AHA <strong>guidel<strong>in</strong>es</strong> forthe <strong>management</strong> of patients with peripheral arterial disease (lowerextremity, renal, mesenteric, and abdom<strong>in</strong>al aortic): a collaborativereport from the American Association for Vascular Surgery/Society forVascular Surgery, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions,Society of Interventional Radiology, Society for Vascular Medic<strong>in</strong>eand Biology, and the American College of Cardiology/American HeartAssociation Task Force on Practice Guidel<strong>in</strong>es. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47(6): 1239-1312.45. Edmonds ME, Foster AVM. Manag<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>diabetic</strong> <strong>foot</strong>. Oxford: BlackwellScience, 2005.BEST PRACTICE GUIDELINES: WOUND MANAGEMENT IN DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS 21