bok%3A978-3-658-02462-8.pdf?auth66=1398409209_a0514c2b8e531c058ab8b810a0cad74d&ext=
bok%3A978-3-658-02462-8.pdf?auth66=1398409209_a0514c2b8e531c058ab8b810a0cad74d&ext=
bok%3A978-3-658-02462-8.pdf?auth66=1398409209_a0514c2b8e531c058ab8b810a0cad74d&ext=
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
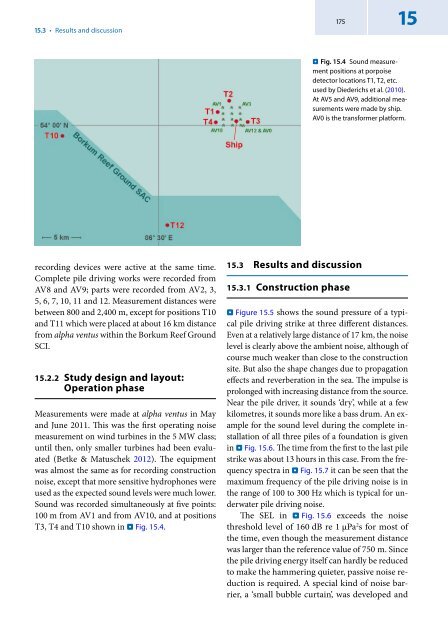
15.3 • Results and discussion175 15..Fig. 15.4 Sound measurementpositions at porpoisedetector locations T1, T2, etc.used by Diederichs et al. (2010).At AV5 and AV9, additional measurementswere made by ship.AV0 is the transformer platform.recording devices were active at the same time.Complete pile driving works were recorded fromAV8 and AV9; parts were recorded from AV2, 3,5, 6, 7, 10, 11 and 12. Measurement distances werebetween 800 and 2,400 m, except for positions T10and T11 which were placed at about 16 km distancefrom alpha ventus within the Borkum Reef GroundSCI.15.2.2 Study design and layout:Operation phaseMeasurements were made at alpha ventus in Mayand June 2011. This was the first operating noisemeasurement on wind turbines in the 5 MW class;until then, only smaller turbines had been evaluated(Betke & Matuschek 2012). The equipmentwas almost the same as for recording constructionnoise, except that more sensitive hydrophones wereused as the expected sound levels were much lower.Sound was recorded simultaneously at five points:100 m from AV1 and from AV10, and at positionsT3, T4 and T10 shown in . Fig. 15.4.15.3 Results and discussion15.3.1 Construction phase. Figure 15.5 shows the sound pressure of a typicalpile driving strike at three different distances.Even at a relatively large distance of 17 km, the noiselevel is clearly above the ambient noise, although ofcourse much weaker than close to the constructionsite. But also the shape changes due to propagationeffects and reverberation in the sea. The impulse isprolonged with increasing distance from the source.Near the pile driver, it sounds ‘dry’, while at a fewkilometres, it sounds more like a bass drum. An examplefor the sound level during the complete installationof all three piles of a foundation is givenin . Fig. 15.6. The time from the first to the last pilestrike was about 13 hours in this case. From the frequencyspectra in . Fig. 15.7 it can be seen that themaximum frequency of the pile driving noise is inthe range of 100 to 300 Hz which is typical for underwaterpile driving noise.The SEL in . Fig. 15.6 exceeds the noisethreshold level of 160 dB re 1 µPa 2 s for most ofthe time, even though the measurement distancewas larger than the reference value of 750 m. Sincethe pile driving energy itself can hardly be reducedto make the hammering quieter, passive noise reductionis required. A special kind of noise barrier,a ‘small bubble curtain’, was developed and