Contents - Akademi Sains Malaysia
Contents - Akademi Sains Malaysia
Contents - Akademi Sains Malaysia
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
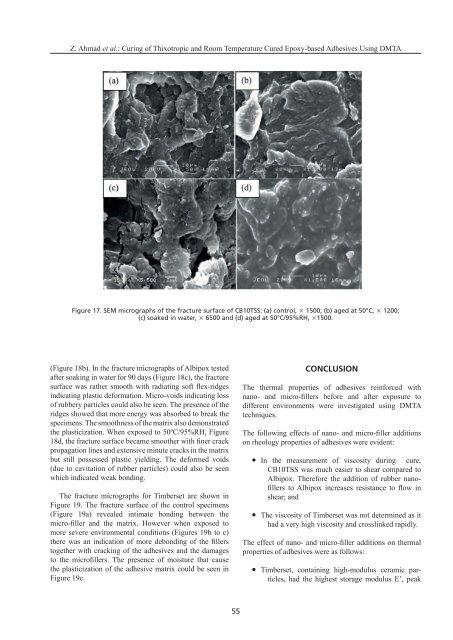
Z. Ahmad et alFigure 17. SEM micrographs of the fracture surface of CB10TSS: (a) control, 3 1500; (b) aged at 50°C, 3 1200;(c) soaked in water, 3 6500 and (d) aged at 50°C/95%RH, 31500.(Figure 18b). In the fracture micrographs of Albipox tested indicating plastic deformation. Micro-voids indicating lossof rubbery particles could also be seen. The presence of theridges showed that more energy was absorbed to break thespecimens. The smoothness of the matrix also demonstratedpropagation lines and extensive minute cracks in the matrixbut still possessed plastic yielding. The deformed voids(due to cavitation of rubber particles) could also be seenwhich indicated weak bonding.The fracture micrographs for Timberset are shown inFigure 19. The fracture surface of the control specimens(Figure 19a) revealed intimate bonding between the more severe environmental conditions (Figures 19b to c) together with cracking of the adhesives and the damages the plasticization of the adhesive matrix could be seen inFigure 19c.CONCLUSIONThe thermal properties of adhesives reinforced with different environments were investigated using DMTAtechniques.on rheology properties of adhesives were evident: In the measurement of viscosity during cure,Albipox. Therefore the addition of rubber nano- shear; and The viscosity of Timberset was not determined as ithad a very high viscosity and crosslinked rapidly.properties of adhesives were as follows: Timberset, containing high-modulus ceramic particles,had the highest storage modulus E’, peak55