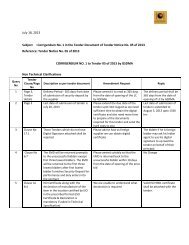
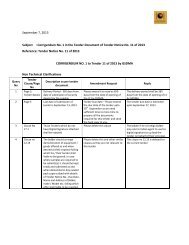
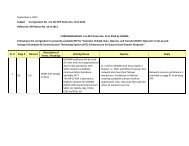
- Page 3 and 4: GUJARAT STATECHEMICAL DISASTERMANAG
- Page 5 and 6: TABLE OF CONTENT3.4 Strengthening o
- Page 7 and 8: TABLE OF CONTENT4.8.13 Develop Cris
- Page 9 and 10: TABLE OF CONTENTAPPENDIX A: ROLES A
- Page 12: ABBREVIATIONSAAARABCALOHAALSAPELLAP
- Page 19 and 20: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYThe DMP is a plan
- Page 21 and 22: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYAt the State level
- Page 23 and 24: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY124°35'0"N2ABCDTo
- Page 25: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYThe next focus are
- Page 29 and 30: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYINCIDENT RESPONSE
- Page 32 and 33: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYMEDICAL EMERGENCY
- Page 34 and 35: EXECUTIVE SUMMARYRECOVERY ACTIONSIn
- Page 36 and 37: 1INTRODUCTION1.3 APPROACH TO PREPAR
- Page 39 and 40: 1INTRODUCTION1.7 LOCAL RESPONSE TO
- Page 41 and 42: 1INTRODUCTIONRULES:• The Gujarat
- Page 43 and 44: 1INTRODUCTIONSECRETARY (ENVIRONMENT
- Page 46 and 47: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITYA
- Page 48 and 49: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITY
- Page 52: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITY
- Page 55 and 56: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITY
- Page 57 and 58: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITY
- Page 59 and 60: 2HAZARD ANALYSIS AND VULNERABILITY
- Page 61 and 62: 323.1 INTRODUCTIONPREVENTION AND MI
- Page 63 and 64:
3PREVENTION AND MITIGATIONof “ext
- Page 65 and 66:
3PREVENTION AND MITIGATIONmay bridg
- Page 67 and 68:
3PREVENTION AND MITIGATIONto be ins
- Page 69 and 70:
3PREVENTION AND MITIGATION• Condu
- Page 71 and 72:
3PREVENTION AND MITIGATIONTable 6.S
- Page 73 and 74:
4PREPAREDNESSThe following are reco
- Page 75:
4PREPAREDNESS• DPOs at district l
- Page 78 and 79:
4PREPAREDNESSunder US laws and focu
- Page 80 and 81:
4PREPAREDNESS4.3.3 DEVELOPMENT AND
- Page 82 and 83:
4PREPAREDNESSTable 7. District Capa
- Page 84 and 85:
4PREPAREDNESSTable 8. Capability As
- Page 86 and 87:
4PREPAREDNESSTYPE OF FIRE SERVICEEM
- Page 88:
4PREPAREDNESS4.4.4 INCIDENT RESPONS
- Page 91 and 92:
4PREPAREDNESSmaintain equipment com
- Page 94 and 95:
4PREPAREDNESSmeeting the specific s
- Page 96 and 97:
4PREPAREDNESSHAZWOPER training guid
- Page 98 and 99:
4PREPAREDNESS• Level A Ensemble -
- Page 100 and 101:
4PREPAREDNESS4.5.7.3 SUPPLIES• Ne
- Page 102 and 103:
4PREPAREDNESSintegrated with corres
- Page 104 and 105:
4PREPAREDNESSbe based at the ICP al
- Page 106 and 107:
4PREPAREDNESSDepartment of Revenue
- Page 108 and 109:
4PREPAREDNESS4.7.7 EMERGENCY PUBLIC
- Page 110 and 111:
4PREPAREDNESSRESPONSIBLE OFFICERINC
- Page 112 and 113:
4PREPAREDNESSFigure 15. Schematic o
- Page 114 and 115:
4PREPAREDNESSand essential medicine
- Page 116 and 117:
4PREPAREDNESScontinued from page 81
- Page 118 and 119:
5RESPONSE4. Wherever applicable, mu
- Page 120 and 121:
5RESPONSEmutual aid partners, GVK 1
- Page 122 and 123:
5RESPONSEthe core of SCG and form t
- Page 124 and 125:
5RESPONSEcivil defence groups, neig
- Page 126 and 127:
5RESPONSEe. Care in transit: The em
- Page 128 and 129:
5RESPONSEdone systematically, it is
- Page 130 and 131:
5RESPONSEj. Suggested protective ac
- Page 132 and 133:
5RESPONSEfall inadequate.3. The DG
- Page 134 and 135:
5RESPONSEthe logistics branch under
- Page 136 and 137:
5RESPONSEtracking the movement in t
- Page 138 and 139:
5RESPONSE3. Volunteer agencies, suc
- Page 140 and 141:
5RESPONSETable 13. Stakeholder Role
- Page 142 and 143:
6RECOVERY, RECONSTRUCTION ANDREHABI
- Page 144 and 145:
6RECOVERY, RECONSTRUCTION AND REHAB
- Page 146 and 147:
7AUTHORIZATION AND PLAN MAINTENANCE
- Page 148 and 149:
APPENDIX A: ROLES AND RESPONSIBILIT
- Page 150 and 151:
APPENDIX A: ROLES AND RESPONSIBILIT
- Page 152 and 153:
APPENDIX B: SITE SAFETY PLAN TEMPLA
- Page 154 and 155:
Initial Isolation and Protective Ac
- Page 156 and 157:
MATERIALSPRESENT ORSUSPECTED AT SIT
- Page 158 and 159:
NOTE: Contingency level of protecti
- Page 160 and 161:
Project-Specific Industrial Hygiene
- Page 162 and 163:
Site Map:128 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRI
- Page 164 and 165:
APPROVAL AND SIGN-OFF FORMProject #
- Page 166 and 167:
SN2PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPRIMA
- Page 168 and 169:
SN34PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPRIM
- Page 170 and 171:
SN56.7PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPR
- Page 172 and 173:
SN111213141516PERSON ACTION COMMUNI
- Page 174 and 175:
SNPERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPRIMAR
- Page 176 and 177:
2SN1PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPRIM
- Page 178 and 179:
6SN5PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPRIM
- Page 180 and 181:
SN1011PERSON ACTION COMMUNICATIONPR
- Page 182 and 183:
APPENDIX E: DIRECTORY OF KEY CONTAC
- Page 184 and 185:
SN PERSON SATELLITE PHONE NO ALLOTT
- Page 186 and 187:
APPENDIX F: RESPONSE RESOURCES IN G
- Page 188 and 189:
FIRESTATION ZONETYPE NAME CONTACTFA
- Page 190 and 191:
FIRESTATION ZONETYPE NAME CONTACTFA
- Page 192 and 193:
FIRESTATION ZONETYPE NAME CONTACTFA
- Page 194 and 195:
FIRESTATION ZONETYPE NAME CONTACTFA
- Page 196 and 197:
SN NAME PHONE NO.10 Local Hospital,
- Page 198 and 199:
SN NAME PHONE NO.1 Civil Hospital,
- Page 200 and 201:
SN NAME PHONE NO.4 Shree Mahavir Ho
- Page 202 and 203:
Table 22. List of Community Health
- Page 204 and 205:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 206 and 207:
Table 23. List of Primary Health Ce
- Page 208 and 209:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 210 and 211:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 212 and 213:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 214 and 215:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 216 and 217:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 218 and 219:
DISTRICT TALUKA VILLAGE DISTRICT TA
- Page 220 and 221:
Table 24. Contact Information of Ci
- Page 222 and 223:
SN NAME STD CODE OFFICE HOSPITAL8.
- Page 224 and 225:
SNEQUIPMENTNAME OFSUPPLIERADDRESS P
- Page 226 and 227:
29640 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 228 and 229:
29642 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 230 and 231:
29644 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 232 and 233:
29646 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 234 and 235:
29648 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 236 and 237:
29650 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 238 and 239:
29652 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 240 and 241:
29654 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 242 and 243:
29656 Federal Register / Vol. 52, N
- Page 244 and 245:
APPENDIX H: GUIDELINES FOR REPORTAB
- Page 246 and 247:
212 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 248 and 249:
214 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 250 and 251:
216 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 252 and 253:
218 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 254 and 255:
220 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 256 and 257:
222 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 258 and 259:
224 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 260 and 261:
226 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 262 and 263:
228 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 264 and 265:
230 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 266 and 267:
232 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 268 and 269:
234 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 270 and 271:
236 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 272 and 273:
238 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 274 and 275:
240 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 276 and 277:
242 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 278 and 279:
244 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 280 and 281:
246 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 282 and 283:
248 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 284 and 285:
250 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 286 and 287:
252 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 288 and 289:
254 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 290 and 291:
256 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 292 and 293:
258 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 294 and 295:
260 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 296 and 297:
262 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL
- Page 298 and 299:
264 GUJARAT STATE INDUSTRIAL