Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
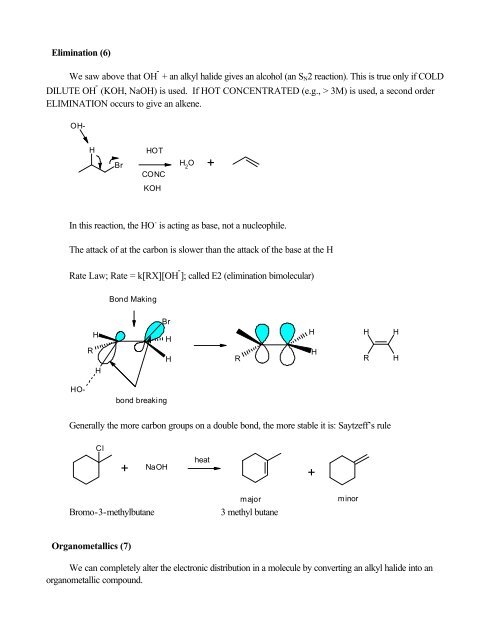
Elimination (6)We saw above that OH - + an alkyl halide gives an alcohol (an S N 2 reaction). This is true only if COLDDILUTE OH - (KOH, NaOH) is used. If HOT CONCENTRATED (e.g., > 3M) is used, a second orderELIMINATION occurs to give an alkene.HBrHOTCONCH 2O +KOHIn this reaction, the HO - is acting as base, not a nucleophile.The attack <strong>of</strong> at the carbon is slower than the attack <strong>of</strong> the base at the HRate Law; Rate = k[RX][OH - ]; called E2 (elimination bimolecular)Bond MakingBrHHHHHRHRHRHHOH-HO-bond breakingGenerally the more carbon groups on a double bond, the more stable it is: Saytzeff’s ruleCl+ NaOHheat+Bromo-3-methylbutanemajor3 methyl butaneminorOrganometallics (7)We can completely alter the electronic distribution in a molecule by converting an alkyl halide into anorganometallic compound.