TERENA COMPENDIUM - Géant
TERENA COMPENDIUM - Géant
TERENA COMPENDIUM - Géant
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
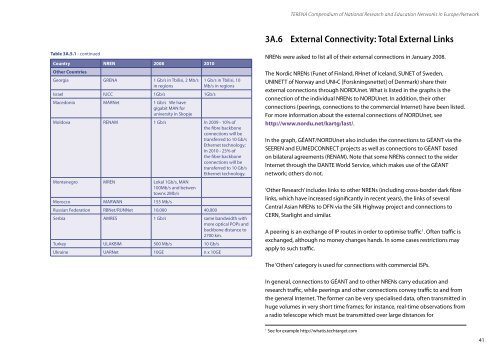
<strong>TERENA</strong> Compendium of National Research and Education Networks In Europe /Network3A.6 External Connectivity: Total External LinksTable 3A.5.1 - continuedCountry NREN 2008 2010Other CountriesGeorgia GRENA 1 Gb/s in Tbilisi, 2 Mb/sin regions1 Gb/s in Tbilisi, 10Mb/s in regionsIsrael IUCC 1Gb/s 1Gb/sMacedonia MARNet 1 Gb/s We havegigabit MAN foruniversity in SkopjeMoldova RENAM 1 Gb/s In 2009 - 10% ofthe fibre backboneconnections will betransferred to 10 Gb/sEthernet technology;In 2010 - 25% ofthe fibre backboneconnections will betransferred to 10 Gb/sEthernet technology.Montenegro MREN Lokal 1Gb/s, MAN100Mb/s and betwentowns 2Mb/sMorocco MARWAN 155 Mb/sRussian Federation RBNet/RUNNet 10,000 40,000Serbia AMRES 1 Gb/s same bandwidth withmore optical POPs andbackbone distance to2700 km.Turkey ULAKBIM 500 Mb/s 10 Gb/sUkraine UARNet 10GE n x 10GENRENs were asked to list all of their external connections in January 2008.The Nordic NRENs (Funet of Finland, RHnet of Iceland, SUNET of Sweden,UNINETT of Norway and UNI•C [Forskningsnettet] of Denmark) share theirexternal connections through NORDUnet. What is listed in the graphs is theconnection of the individual NRENs to NORDUnet. In addition, their otherconnections (peerings, connections to the commercial Internet) have been listed.For more information about the external connections of NORDUnet, seehttp://www.nordu.net/kartg/last/.In the graph, GÉANT/NORDUnet also includes the connections to GÉANT via theSEEREN and EUMEDCONNECT projects as well as connections to GÉANT basedon bilateral agreements (RENAM). Note that some NRENs connect to the widerInternet through the DANTE World Service, which makes use of the GÉANTnetwork; others do not.‘Other Research’ includes links to other NRENs (including cross-border dark fibrelinks, which have increased significantly in recent years), the links of severalCentral Asian NRENs to DFN via the Silk Highway project and connections toCERN, Starlight and similar.A peering is an exchange of IP routes in order to optimise traffic 1 . Often traffic isexchanged, although no money changes hands. In some cases restrictions mayapply to such traffic.The ‘Others’ category is used for connections with commercial ISPs.In general, connections to GÉANT and to other NRENs carry education andresearch traffic, while peerings and other connections convey traffic to and fromthe general Internet. The former can be very specialised data, often transmitted inhuge volumes in very short time frames; for instance, real-time observations froma radio telescope which must be transmitted over large distances for1See for example http://whatis.techtarget.com41