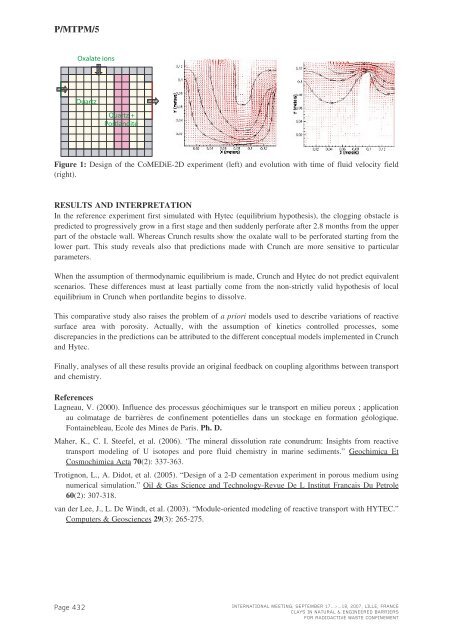
P/<strong>MTPM</strong>/5Oxalate ionsQuartzQuartz +PortlanditeFigure 1: Design of the CoMEDiE-2D experiment (left) and evolution with time of fluid velocity field(right).RESULTS AND INTERPRETATIONIn the reference experiment first simulated with Hytec (equilibrium hypothesis), the clogging obstacle ispredicted to progressively grow in a first stage and then suddenly perforate after 2.8 months from the upperpart of the obstacle wall. Whereas Crunch results show the oxalate wall to be perforated starting from thelower part. This study reveals also that predictions made with Crunch are more sensitive to particularparameters.When the assumption of thermodynamic equilibrium is made, Crunch and Hytec do not predict equivalentscenarios. These differences must at least partially come from the non-strictly valid hypothesis of localequilibrium in Crunch when portlandite begins to dissolve.This comparative study also raises the problem of a priori models used to describe variations of reactivesurface area with porosity. Actually, with the assumption of kinetics controlled processes, somediscrepancies in the predictions can be attributed to the different conceptual models implemented in Crunchand Hytec.Finally, analyses of all these results provide an original feedback on coupling algorithms between transportand chemistry.ReferencesLagneau, V. (2000). Influence des processus géochimiques sur le transport en milieu poreux ; applicationau colmatage de barrières de confinement potentielles dans un stockage en formation géologique.Fontainebleau, Ecole des Mines de Paris. Ph. D.Maher, K., C. I. Steefel, et al. (2006). ‘The mineral dissolution rate conundrum: Insights from reactivetransport modeling of U isotopes and pore fluid chemistry in marine sediments.” Geochimica EtCosmochimica Acta 70(2): 337-363.Trotignon, L., A. Didot, et al. (2005). “Design of a 2-D cementation experiment in porous medium usingnumerical simulation.” Oil & Gas Science and Technology-Revue De L Institut Francais Du Petrole60(2): 307-318.van der Lee, J., L. De Windt, et al. (2003). “Module-oriented modeling of reactive transport with HYTEC.”Computers & Geosciences 29 (3): 265-275.Page 432INTERNATIONAL MEETING, SEPTEMBER 17...>...18, 2007, LILLE, FRANCECLAYS IN NATURAL & ENGINEERED BARRIERSFOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE CONFINEMENT
P/<strong>MTPM</strong>/6LARGE-SCALE GAS INJECTION TEST(LASGIT) AT THE ÄSPO HARD ROCKLABORATORY IN SWEDEND.J. Birchall 1 , J.F. Harrington 1 , D.J. Noy 1 and P. Sellin 21. British Geological Survey, Keyworth, NG12 5GG, UK (dbirch@bgs.ac.uk/+44 115 9363120),2. Svensk Kärbränslehantering AB (SKB), Stockholm, Sweden (skbps@skb.se/+46 8 6624974).INTRODUCTIONIn the Swedish disposal concept, canisters containing spent nuclear fuel will be placed in large diameterdisposal boreholes drilled into the floor of the repository tunnels. Each full canister will weigh up to27 tonnes. The canister consists of a 50mm thick outer copper skin, which acts as a corrosion barrier inthe oxygen-poor groundwater of the crystalline rock selected for disposal, and a nodular iron insert toprovide strength and rigidity. The space around each canister will be filled with pre-compacted bentoniteblocks which, once hydrated, will act as a low permeability diffusional barrier. The unique physicochemicalproperties of the bentonite depend on its colloidal behaviour and enormous specific surface.These include high sorption capacity, very high plasticity and excellent fracture self-sealing characteristics,severely limiting the migration of any radionuclides released from a canister after closure of the repository.The metal canisters are expected to have a very substantial life in the repository environment. However,for purposes of performance assessment (PA), the possible impact of groundwater penetrating one of thecanisters must be considered. Under anoxic conditions, corrosion of the steel inner will lead to theformation of hydrogen gas. Radioactive decay of the waste and the radiolysis of water will produce someadditional gas in the container. Depending on the gas production rate and the rate of diffusion of gasmolecules in the pores of the bentonite, it is possible that gas will accumulate in the void space of thecanister, entering the bentonite when the gas pressure exceeds the critical entry pressure specific to thismaterial. Since water penetration of the canister is a prerequisite for the occurrence of hydrogen gas in thebuffer, the timing of gas movement in the clay might coincide with that of radionuclide release into thebuffer porewater. The possibility of an interaction between gas and radionuclide migration thereforeemerges as an important issue in PA.As part of an ongoing programme of research, the Swedish waste management company SKBcommissioned BGS to undertake a series of detailed laboratory studies aimed at resolving specific issuesrelating to the gas migration process. It has been shown that gas moves through the clay followingpressure-induced pathways. The clay tends to dilate when these pathways are formed with both theporewater pressure and the total stress acting within the clay, strongly affected by the passage of gas. Thelaboratory work has highlighted a number of uncertainties, notably the sensitivity of the gas migrationprocess to experimental boundary conditions and possible scale-dependency of the measured responses.These issues are best addressed by undertaking a large-scale gas injection test or “Lasgit”.Lasgit is being undertaken at the Äspö Hard Rock Laboratory (HRL), around 360km south of Stockholmin the municipality of Oskarshamn. The underlying diorite formation is representative of the geologicalconditions likely to be encountered in a Swedish conceptual nuclear repository. Lasgit is a full-scaledemonstration project conducted in the Assembly Hall Area of the HRL at a depth of 420m. This is a“mock test” which does not use any radioactive materials. A deposition hole, 8.5m deep and 1.8m indiameter, was drilled in to the gallery floor. Canister defects are mimicked by placing thirteen circularfilters of varying dimensions on the surface of a copper canister to provide point sources of gas. Thesefilters are used to inject water during the initial hydration phase. Helium gas will be used as a safesubstitute for hydrogen during gas testing. Once the pre-compacted bentonite blocks were installed, theINTERNATIONAL MEETING, SEPTEMBER 17...>...18, 2007, LILLE, FRANCECLAYS IN NATURAL & ENGINEERED BARRIERSFOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE CONFINEMENTPage 433