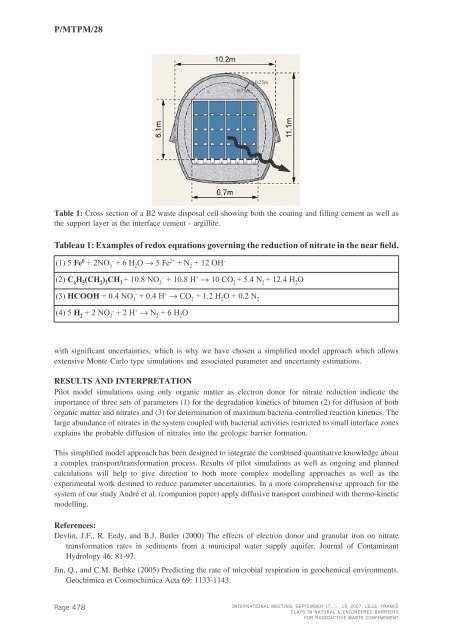
P/<strong>MTPM</strong>/280.75m0.25mTable 1: Cross section of a B2 waste disposal cell showing both the coating and filling cement as well asthe support layer at the interface cement - argillite.Tableau 1: Examples of redox equations governing the reduction of nitrate in the near field.(1) 5 Fe 0 + 2NO 3 - + 6 H 2 O → 5 Fe 2+ + N 2 + 12 OH -(2) C 6 H 5 (CH 2 ) 3 CH 3 + 10.8 NO 3- + 10.8 H + → 10 CO 2 + 5.4 N 2 + 12.4 H 2 O(3) HCOOH + 0.4 NO 3 - + 0.4 H + → CO 2+ 1.2 H 2O + 0.2 N 2(4) 5 H 2+ 2 NO 3 - + 2 H + → N 2+ 6 H 2Owith significant uncertainties, which is why we have chosen a simplified model approach which allowsextensive Monte Carlo type simulations and associated parameter and uncertainty estimations.RESULTS AND INTERPRETATIONPilot model simulations using only organic matter as electron donor for nitrate reduction indicate theimportance of three sets of parameters (1) for the degradation kinetics of bitumen (2) for diffusion of bothorganic matter and nitrates and (3) for determination of maximum bacteria-controlled reaction kinetics. Thelarge abundance of nitrates in the system coupled with bacterial activities restricted to small interface zonesexplains the probable diffusion of nitrates into the geologic barrier formation.This simplified model approach has been designed to integrate the combined quantitative knowledge abouta complex transport/transformation process. Results of pilot simulations as well as ongoing and plannedcalculations will help to give direction to both more complex modelling approaches as well as theexperimental work destined to reduce parameter uncertainties. In a more comprehensive approach for thesystem of our study André et al. (companion paper) apply diffusive transport combined with thermo-kineticmodelling.References:Devlin, J.F., R. Eedy, and B.J. Butler (2000) The effects of electron donor and granular iron on nitratetransformation rates in sediments from a municipal water supply aquifer. Journal of ContaminantHydrology 46: 81-97.Jin, Q., and C.M. Bethke (2005) Predicting the rate of microbial respiration in geochemical environments.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69: 1133-1143.Page 478INTERNATIONAL MEETING, SEPTEMBER 17...>...18, 2007, LILLE, FRANCECLAYS IN NATURAL & ENGINEERED BARRIERSFOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE CONFINEMENT
P/<strong>MTPM</strong>/29EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON GASPERMEABILITY OF THE CALLOVO-OXFORDIAN ARGILLITE OF MHMJoël.Billiotte 1 , Diansen Yang 1 , Kun Su 21. Centre de géologie de l’ingénieur, université de Marne-la-Vallée, bât .IFI, 5, bd Descartes,Champs-sur- Marne, 77454 Marne-la-Vallée Cedex 2, France (joël.billiotte@ensmp.fr)2. Agence nationale pour la gestion des déchets radioactifs (ANDRA), 92298 Châtenay-MalabryCedex, FranceINTRODUCTIONThe very low permeability of the Callovo-Oxfordian argillite formation of MHM (the Meuse/Haute-Marne,France ), which is approximately 500 m deep and 130 m thick, is its principal advantage as a medium forwaste disposal. Because the permeability depends on the geometry and connectivity of pores, the changein permeability is a representative parameter indicating the structural changes. One can determine theextension and amplitude of disturbance or damage zone around drift by considering the evolution ofpermeability. Based on this consideration, a transient method of gas permeability on very low permeabilityrock is developed. Measurements on some samples obtained from the underground research laboratory(URL) of MHM site are realised.EXPERIMENTAL METHOD AND CONDITIONTransient method has been employed widely in the laboratory and in field to measure the hydraulicproperties of rock with low permeability.Basing on this method, a measurement as illustrated in Fig.A has been designed in the laboratory C.G.I.The measurement consists of a triaxial cell connected to two gas vessels. After the uniform of gas pressurein the system, an incremental pressure between two vessels is applied in the upstream vessel. We chooseargon and helium as the gas inert in our tests. The gas pressures are recorded by the captures. The loadingand unloading test is possible to realize in this system by GDS. A linear voltage displacement transducer(LVDT) measures axial displacement. The variation of temperature is well controlled in the range of +/-0.1˚C in order to reduce the affect of temperature. After the calibration of system, the minimumpermeability that could be measured was determined to be 10 -22 m 2 .For characterising the damage induced by the excavation, argillite cores samples were taken from thedifferent distances (0.07m to 12.73m) to the wall of the main access shaft of the MHM URL. The diameterof samples is about 40mm and their height ranges from 26.20mm to 52.46mm. The confining pressurekeeps constant (9MPa or 11MPa) and the axial pressure ranges from 11MPa to 28MPa.EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS AND INTERPRETATIONPermeability measured on the referenced sample (far away from the wall of the shaft) ranges from 3.10 -21to 2.10 -22 m 2 under axial loading cycle. This indicates that the permeability decreases with the increasing ofthe deviatoric stress and the unloading of axial stress show that the permeability reduction is irreversible.(Fig. B). The permeability between the reference sample and the sample near the wall of the shaft doesn’tchange significantly, which indicates that the micro-cracks in the near filed induced by excavation of theshaft are very limited.In order to comprehend the mechanism of transfer of gas within in situ water content samples, we carefullycheck the changes in mass of samples before and after test. Firstly, we observe the surface connected tothe upstream vessel is drier than that connected to the downstream vessel. This difference of humidity atthe level of sample faces confirms that the transfer of gas can induce the flow of pore water even if theINTERNATIONAL MEETING, SEPTEMBER 17...>...18, 2007, LILLE, FRANCECLAYS IN NATURAL & ENGINEERED BARRIERSFOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE CONFINEMENTPage 479