Mass Transfer & Porous Media (MTPM) - Andra
Mass Transfer & Porous Media (MTPM) - Andra
Mass Transfer & Porous Media (MTPM) - Andra
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
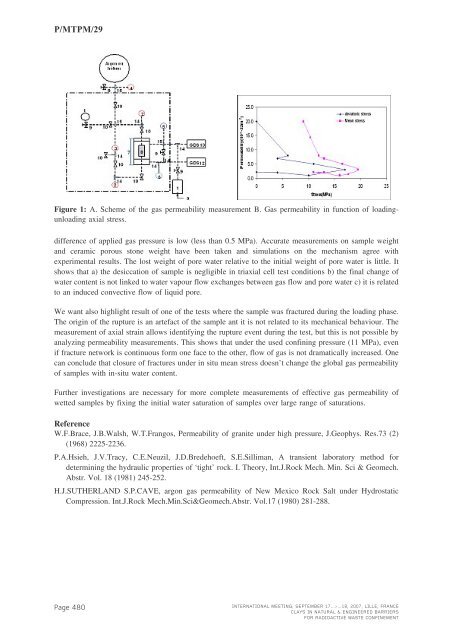
P/<strong>MTPM</strong>/29Figure 1: A. Scheme of the gas permeability measurement B. Gas permeability in function of loadingunloadingaxial stress.difference of applied gas pressure is low (less than 0.5 MPa). Accurate measurements on sample weightand ceramic porous stone weight have been taken and simulations on the mechanism agree withexperimental results. The lost weight of pore water relative to the initial weight of pore water is little. Itshows that a) the desiccation of sample is negligible in triaxial cell test conditions b) the final change ofwater content is not linked to water vapour flow exchanges between gas flow and pore water c) it is relatedto an induced convective flow of liquid pore.We want also highlight result of one of the tests where the sample was fractured during the loading phase.The origin of the rupture is an artefact of the sample ant it is not related to its mechanical behaviour. Themeasurement of axial strain allows identifying the rupture event during the test, but this is not possible byanalyzing permeability measurements. This shows that under the used confining pressure (11 MPa), evenif fracture network is continuous form one face to the other, flow of gas is not dramatically increased. Onecan conclude that closure of fractures under in situ mean stress doesn’t change the global gas permeabilityof samples with in-situ water content.Further investigations are necessary for more complete measurements of effective gas permeability ofwetted samples by fixing the initial water saturation of samples over large range of saturations.ReferenceW.F.Brace, J.B.Walsh, W.T.Frangos, Permeability of granite under high pressure, J.Geophys. Res.73 (2)(1968) 2225-2236.P.A.Hsieh, J.V.Tracy, C.E.Neuzil, J.D.Bredehoeft, S.E.Silliman, A transient laboratory method fordetermining the hydraulic properties of ‘tight’ rock. I. Theory, Int.J.Rock Mech. Min. Sci & Geomech.Abstr. Vol. 18 (1981) 245-252.H.J.SUTHERLAND S.P.CAVE, argon gas permeability of New Mexico Rock Salt under HydrostaticCompression. Int.J.Rock Mech.Min.Sci&Geomech.Abstr. Vol.17 (1980) 281-288.Page 480INTERNATIONAL MEETING, SEPTEMBER 17...>...18, 2007, LILLE, FRANCECLAYS IN NATURAL & ENGINEERED BARRIERSFOR RADIOACTIVE WASTE CONFINEMENT