Vol.18- No.1 (Jan-Mar2011) - INFLIBNET Centre
Vol.18- No.1 (Jan-Mar2011) - INFLIBNET Centre
Vol.18- No.1 (Jan-Mar2011) - INFLIBNET Centre
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
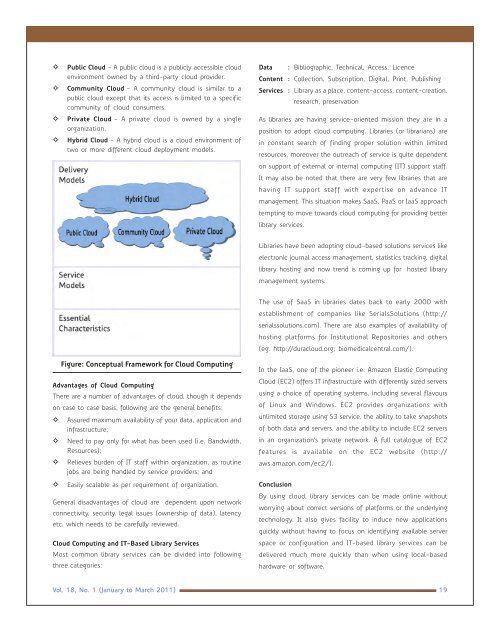
GGGGPublic Cloud - A public cloud is a publicly accessible cloudenvironment owned by a third-party cloud provider.Community Cloud - A community cloud is similar to apublic cloud except that its access is limited to a specificcommunity of cloud consumers.Private Cloud - A private cloud is owned by a singleorganization.Hybrid Cloud - A hybrid cloud is a cloud environment oftwo or more different cloud deployment models.Data : Bibliographic, Technical, Access, LicenceContent : Collection, Subscription, Digital, Print, PublishingServices : Library as a place, content-access, content-creation,research, preservationAs libraries are having service-oriented mission they are in aposition to adopt cloud computing. Libraries (or librarians) arein constant search of finding proper solution within limitedresources, moreover the outreach of service is quite dependenton support of external or internal computing (IT) support staff.It may also be noted that there are very few libraries that arehaving IT support staff with expertise on advance ITmanagement. This situation makes SaaS, PaaS or IaaS approachtempting to move towards cloud computing for providing betterlibrary services.Libraries have been adopting cloud-based solutions services likeelectronic journal access management, statistics tracking, digitallibrary hosting and now trend is coming up for hosted librarymanagement systems.The use of SaaS in libraries dates back to early 2000 withestablishment of companies like SerialsSolutions (http://serialssolutions.com). There are also examples of availability ofhosting platforms for Institutional Repositories and others(eg. http://duracloud.org; biomedicalcentral.com/).Figure: Conceptual Framework for Cloud ComputingAdvantages of Cloud ComputingThere are a number of advantages of cloud, though it dependson case to case basis, following are the general benefits:GGGGAssured maximum availability of your data, application andinfrastructure;Need to pay only for what has been used (i.e. Bandwidth,Resources);Relieves burden of IT staff within organization, as routinejobs are being handled by service providers; andEasily scalable as per requirement of organization.General disadvantages of cloud are dependent upon networkconnectivity, security, legal issues (ownership of data), latencyetc. which needs to be carefully reviewed.Cloud Computing and IT-Based Library ServicesMost common library services can be divided into followingthree categories:In the IaaS, one of the pioneer i.e. Amazon Elastic ComputingCloud (EC2) offers IT infrastructure with differently sized serversusing a choice of operating systems, including several flavoursof Linux and Windows. EC2 provides organizations withunlimited storage using S3 service, the ability to take snapshotsof both data and servers, and the ability to include EC2 serversin an organization’s private network. A full catalogue of EC2features is available on the EC2 website (http://aws.amazon.com/ec2/).ConclusionBy using cloud, library services can be made online withoutworrying about correct versions of platforms or the underlyingtechnology. It also gives facility to induce new applicationsquickly without having to focus on identifying available serverspace or configuration and IT-based library services can bedelivered much more quickly than when using local-basedhardware or software.Vol. 18, No. 1 (<strong>Jan</strong>uary to March 2011) 19





![Uni of Delhi_MA_History[1]. - INFLIBNET Centre](https://img.yumpu.com/48586372/1/190x245/uni-of-delhi-ma-history1-inflibnet-centre.jpg?quality=85)









