You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
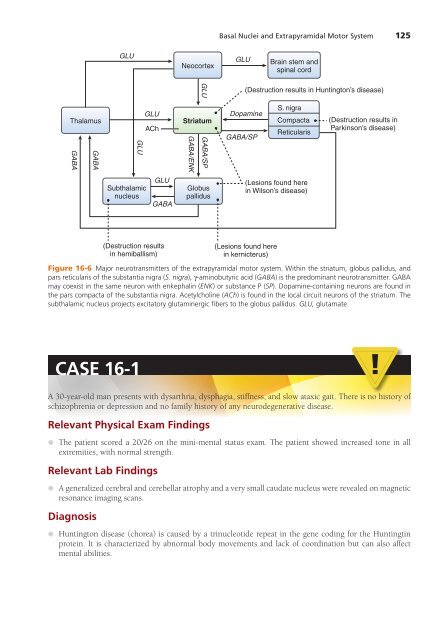
Basal Nuclei and Extrapyramidal Motor System 125<br />
GLU<br />
Neocortex<br />
GLU<br />
Brain stem and<br />
spinal cord<br />
GLU<br />
(Destruction results in Huntington’s disease)<br />
Thalamus<br />
GABA<br />
GABA<br />
GLU<br />
GLU<br />
ACh<br />
Striatum<br />
GABA/ENK<br />
GABA/SP<br />
Dopamine<br />
GABA/SP<br />
S. nigra<br />
Compacta<br />
Reticularis<br />
(Destruction results in<br />
Parkinson’s disease)<br />
Subthalamic<br />
nucleus<br />
GLU<br />
GABA<br />
Globus<br />
pallidus<br />
(Lesions found here<br />
in Wilson’s disease)<br />
(Destruction results<br />
in hemiballism)<br />
(Lesions found here<br />
in kernicterus)<br />
Figure 16-6 Major neurotransmitters of the extrapyramidal motor system. Within the striatum, globus pallidus, and<br />
pars reticularis of the substantia nigra (S. nigra), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the predominant neurotransmitter. GABA<br />
may coexist in the same neuron with enkephalin (ENK) or substance P (SP). Dopamine-containing neurons are found in<br />
the pars compacta of the substantia nigra. Acetylcholine (ACh) is found in the local circuit neurons of the striatum. The<br />
subthalamic nucleus projects excitatory glutaminergic fibers to the globus pallidus. GLU, glutamate.<br />
CASE 16-1<br />
A 30-year-old man presents with dysarthria, dysphagia, stiffness, and slow ataxic gait. There is no history of<br />
schizophrenia or depression and no family history of any neurodegenerative disease.<br />
Relevant Physical Exam Findings<br />
●<br />
The patient scored a 20/26 on the mini-mental status exam. The patient showed increased tone in all<br />
extremities, with normal strength.<br />
Relevant Lab Findings<br />
●<br />
A generalized cerebral and cerebellar atrophy and a very small caudate nucleus were revealed on magnetic<br />
resonance imaging scans.<br />
Diagnosis<br />
●<br />
Huntington disease (chorea) is caused by a trinucleotide repeat in the gene coding for the Huntingtin<br />
protein. It is characterized by abnormal body movements and lack of coordination but can also affect<br />
mental abilities.