You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
6 Chapter 1<br />
3. Lateral ventricles (see Figure 1-5)—ependyma-lined cavities of the cerebral hemispheres that<br />
contain CSF and choroid plexus. They communicate with the third ventricle via two interventricular<br />
foramina (of Monro) and are separated from each other by the septum pellucidum.<br />
4. Cerebral cortex consists of a thin layer or mantle of gray matter that covers the surface of each<br />
cerebral hemisphere and is folded into gyri that are separated by sulci.<br />
5. White matter includes the cerebral commissures and the internal capsule.<br />
a. Cerebral commissures (see Figure 1-2) interconnect the cerebral hemispheres and include<br />
the following structures:<br />
● Corpus callosum—the largest commissure of the brain and it interconnects the two hemispheres.<br />
It has four parts, including the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium.<br />
● Anterior commissure—interconnects the olfactory bulbs with the middle and inferior<br />
temporal lobes.<br />
● Hippocampal commissure (commissure of the fornix)—located between the fornices<br />
and inferior to the splenium of the corpus callosum.<br />
b. Internal capsule (see Figure 1-5) consists of the white matter located between the basal nuclei<br />
and the thalamus. It has five parts:<br />
● Anterior limb—located between the caudate nucleus and putamen and contains a mixture<br />
of ascending and descending fibers.<br />
● Genu—located between the anterior and posterior limbs and contains primarily the corticonuclear<br />
(corticobulbar) fibers.<br />
● Posterior limb—located between the thalamus and lentiform nucleus (comprising the<br />
putamen and the globus pallidus) and is primarily made up of corticospinal fibers.<br />
● Retrolenticular portion—located posterior to the lentiform nucleus and contains the<br />
optic radiations.<br />
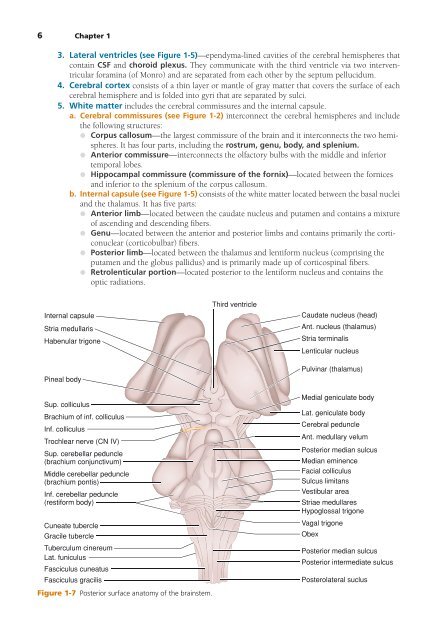
Internal capsule<br />
Stria medullaris<br />
Habenular trigone<br />
Pineal body<br />
Third ventricle<br />
Caudate nucleus (head)<br />
Ant. nucleus (thalamus)<br />
Stria terminalis<br />
Lenticular nucleus<br />
Pulvinar (thalamus)<br />
Sup. colliculus<br />
Brachium of inf. colliculus<br />
Inf. colliculus<br />
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)<br />
Sup. cerebellar peduncle<br />
(brachium conjunctivum)<br />
Middle cerebellar peduncle<br />
(brachium pontis)<br />
Inf. cerebellar peduncle<br />
(restiform body)<br />
Cuneate tubercle<br />
Gracile tubercle<br />
Tuberculum cinereum<br />
Lat. funiculus<br />
Fasciculus cuneatus<br />
Fasciculus gracilis<br />
Figure 1-7 Posterior surface anatomy of the brainstem.<br />
Medial geniculate body<br />
Lat. geniculate body<br />
Cerebral peduncle<br />
Ant. medullary velum<br />
Posterior median sulcus<br />
Median eminence<br />
Facial colliculus<br />
Sulcus limitans<br />
Vestibular area<br />
Striae medullares<br />
Hypoglossal trigone<br />
Vagal trigone<br />
Obex<br />
Posterior median sulcus<br />
Posterior intermediate sulcus<br />
Posterolateral suclus