- Page 2 and 3: Thank you for purchasing this e-boo
- Page 5 and 6: TM FIFTH EDITION Neuroanatomy Dougl
- Page 7: I dedicate this work to my beloved
- Page 10 and 11: CONTENTS Preface vii 1 GROSS STRUCT
- Page 12 and 13: x Contents Lesions of the Brainstem
- Page 14 and 15: xii Contents V Cerebellar Dysfuncti
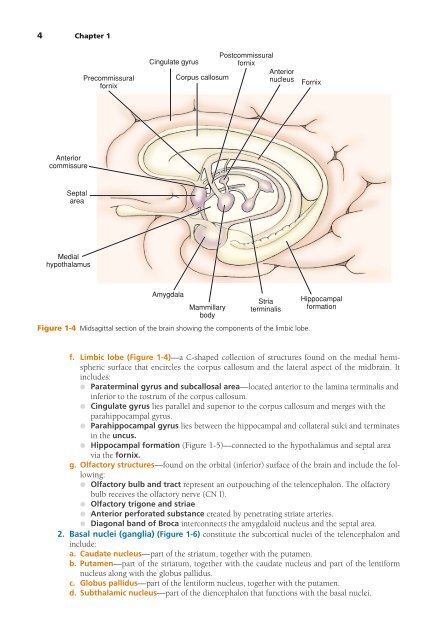
- Page 16 and 17: 2 Chapter 1 Superior frontal sulcus
- Page 20 and 21: 6 Chapter 1 3. Lateral ventricles (
- Page 22 and 23: 8 Chapter 1 c. Inferior colliculus
- Page 24 and 25: CHAPTER 2 Development of the Nervou
- Page 26 and 27: 12 Chapter 2 Three primary vesicles
- Page 28 and 29: 14 Chapter 2 Figure 2-6 Midsagittal
- Page 30 and 31: 16 Chapter 2 H. Holoprosencephaly r
- Page 32 and 33: 18 Chapter 3 Sensory (receptor) neu
- Page 34 and 35: 20 Chapter 3 A Normal neuron Site o
- Page 36 and 37: 22 Chapter 3 Germinomas )
- Page 38 and 39: 24 Chapter 3 CASE 3-1 A 44-year-old
- Page 40 and 41: 26 Chapter 4 Cerebral arterial circ
- Page 42 and 43: 28 Chapter 4 B. Basilar Artery—fo
- Page 44 and 45: 30 Chapter 4 A 12 B 6 1 11 10 2 15
- Page 46 and 47: 32 Chapter 4 Callosomarginal artery
- Page 48 and 49: 34 Chapter 4 Outer table Diploë Du
- Page 50 and 51: CHAPTER 5 Meninges, Ventricles, and
- Page 52 and 53: 38 Chapter 5 a. Common causes i. Ne
- Page 54 and 55: 40 Chapter 5 1 2 3 8 4 5 6 7 9 Figu
- Page 56 and 57: 42 Chapter 5 A B C D Figure 5-6 Com
- Page 58 and 59: CHAPTER 6 Spinal Cord Objectives 1.
- Page 60 and 61: 46 Chapter 6 Posterior side Anterio
- Page 62 and 63: 48 Chapter 6 Ia afferent Excitatory
- Page 64 and 65: 50 Chapter 6 Thalamus Internal caps
- Page 66 and 67: 52 Chapter 6 Corpus callosum Thalam
- Page 68 and 69:
54 Chapter 6 C. Course of the Later
- Page 70 and 71:
56 Chapter 6 A B C D E F G H Figure
- Page 72 and 73:
58 Chapter 6 C. Unilateral muscle a
- Page 74 and 75:
Optic nerve Anterior perforated sub
- Page 76 and 77:
62 Chapter 7 Spinal nucleus and tra
- Page 78 and 79:
64 Chapter 7 Superior medullary vel
- Page 80 and 81:
66 Chapter 7 4. Spinal nucleus and
- Page 82 and 83:
68 Chapter 7 B. Vagal Nerve (CN X).
- Page 84 and 85:
CHAPTER 8 Autonomic Nervous System
- Page 86 and 87:
72 Chapter 8 Midbrain Accessory occ
- Page 88 and 89:
74 Chapter 8 Table 8-1: Sympathetic
- Page 90 and 91:
76 Chapter 9 Mammillary bodies Ocul
- Page 92 and 93:
78 Chapter 9 A Figure 9-2 Paralysis
- Page 94 and 95:
80 Chapter 9 VI The Abducent Nerve
- Page 96 and 97:
82 Chapter 9 5. The GVE component i
- Page 98 and 99:
84 Chapter 9 Motor cortex UMN UMN C
- Page 100 and 101:
86 Chapter 9 Motor cortex UMN UMN C
- Page 102 and 103:
88 Chapter 10 Motor cortex UMN Supe
- Page 104 and 105:
90 Chapter 10 Table 10-1: The Trige
- Page 106 and 107:
CHAPTER 11 Diencephalon Objectives
- Page 108 and 109:
94 Chapter 11 III Blood Supply. The
- Page 110 and 111:
96 Chapter 11 Paraventricular nucle
- Page 112 and 113:
98 Chapter 11 VL VP MD F X Thalamus
- Page 114 and 115:
CHAPTER 12 Auditory System Objectiv
- Page 116 and 117:
102 Chapter 12 III Hearing Defects
- Page 118 and 119:
CHAPTER 13 Vestibular System Object
- Page 120 and 121:
106 Chapter 13 1. Bipolar neurons p
- Page 122 and 123:
CHAPTER 14 Visual System Objectives
- Page 124 and 125:
110 Chapter 14 Choroid Choriocapill
- Page 126 and 127:
112 Chapter 14 Pretectal nucleus Br
- Page 128 and 129:
114 Chapter 14 Lateral rectus Left
- Page 130 and 131:
CHAPTER 15 Limbic System Objectives
- Page 132 and 133:
118 Chapter 15 D. The cingulate gyr
- Page 134 and 135:
CHAPTER 16 Basal Nuclei and Extrapy
- Page 136 and 137:
122 Chapter 16 Caudate nucleus, hea
- Page 138 and 139:
Septum pellucidum Longitudinal cere
- Page 140 and 141:
CHAPTER 17 Cerebellum Objectives 1.
- Page 142 and 143:
128 Chapter 17 C. Cerebellar Cortex
- Page 144 and 145:
130 Chapter 17 CASE 17-1 A 50-year-
- Page 146 and 147:
132 Chapter 18 Figure 18-1 Neurocor
- Page 148 and 149:
134 Chapter 18 A Sensory Homunculus
- Page 150 and 151:
136 Chapter 18 A Right hemiplegia H
- Page 152 and 153:
138 Chapter 18 C. Test (Figure 18-8
- Page 154 and 155:
140 Chapter 18 5. Quadrantanopia 6.
- Page 156 and 157:
CHAPTER 19 Cross-Sectional Anatomy
- Page 158 and 159:
Thalamus Central sulcus Corpus call
- Page 160 and 161:
Thalamus Cingulate sulcus Central s
- Page 162 and 163:
148 Chapter 19 Septum pellucidum In
- Page 164 and 165:
150 Chapter 19 Corpus callosum Caud
- Page 166 and 167:
Cingulate gyrus Fornix Caudate nucl
- Page 168 and 169:
Internal capsule (ant. limb) Fornix
- Page 170 and 171:
Hypothalamus Gyrus rectus Anterior
- Page 172 and 173:
158 Chapter 19 Longitudinal cerebra
- Page 174 and 175:
160 Chapter 19 Optic nerve Sphenoid
- Page 176 and 177:
162 Chapter 20 Figure 20-2 Synthesi
- Page 178 and 179:
164 Chapter 20 2. Enkephalins are t
- Page 180 and 181:
166 Chapter 20 is fatigable weaknes
- Page 182 and 183:
168 Appendix I Cranial Nerve Type O
- Page 184 and 185:
APPENDIX II Table of Common Neurolo
- Page 186 and 187:
172 Appendix II Disease State Locke
- Page 188 and 189:
174 Glossary aphonia Loss of the vo
- Page 190 and 191:
176 Glossary dysdiadochokinesia Ina
- Page 192 and 193:
178 Glossary lipofuscin (ceroid) No
- Page 194 and 195:
180 Glossary psychosis Severe menta
- Page 197 and 198:
INDEX Page numbers followed by “f
- Page 199 and 200:
Index 185 E Emissary veins, 29 Ence
- Page 201 and 202:
Index 187 catecholamines, 161 nonop