- Page 1 and 2: Junos ® OS Interfaces Configuratio
- Page 3 and 4: END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT READ THI
- Page 5 and 6: 12. Commercial Computer Software. T
- Page 7 and 8: Abbreviated Table of Contents About
- Page 9 and 10: Table of Contents About This Guide
- Page 11 and 12: Chapter 3 Aggregated Ethernet Inter
- Page 13 and 14: Logical Interface Settings . . . .
- Page 15 and 16: Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 17 and 18: Account Activation for CDMA EV-DO M
- Page 19 and 20: Data-Link Connection Identifiers .
- Page 21 and 22: About This Guide This preface provi
- Page 23 and 24: Table 2: Text and Syntax Convention
- Page 25 and 26: Opening a Case with JTAC Copyright
- Page 27 and 28: PART 1 Interfaces Overview Copyrigh
- Page 29: CHAPTER 1 Interfaces Overview Inter
- Page 33 and 34: Table 4: Configurable Services Inte
- Page 35 and 36: Table 6: Special Interfaces (contin
- Page 37 and 38: Table 7: Network Interface Names (c
- Page 39 and 40: Related Documentation NOTE: Junos O
- Page 41 and 42: Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 43 and 44: Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 45 and 46: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 47 and 48: Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
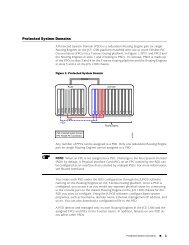
- Page 49 and 50: Restrictions The following restrict
- Page 51 and 52: Previously, IPv4 packets (only) wou
- Page 53 and 54: Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 55 and 56: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 57 and 58: Table 9: Interface Physical Propert
- Page 59 and 60: Related Documentation peaks and dro
- Page 61 and 62: Table 10: MTU Values for J4350 and
- Page 63 and 64: Frame Sequencing Flow Control Data
- Page 65 and 66: Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 67 and 68: PART 2 Ethernet Interfaces Copyrigh
- Page 69 and 70: CHAPTER 2 Ethernet Interfaces Under
- Page 71 and 72: Table 13: Collision Backoff Algorit
- Page 73 and 74: Related Documentation • The Data
- Page 75 and 76: Verification Related Documentation
- Page 77 and 78: Verifying Static ARP Configurations
- Page 79 and 80: Related Documentation • Junos OS
- Page 81 and 82:
CHAPTER 3 Aggregated Ethernet Inter
- Page 83 and 84:
Related Documentation You configure
- Page 85 and 86:
Related Documentation Step-by-Step
- Page 87 and 88:
Related Documentation Understanding
- Page 89 and 90:
Related Documentation Step-by-Step
- Page 91 and 92:
Step-by-Step Procedure Related Docu
- Page 93 and 94:
Understanding VLAN Tagging for Aggr
- Page 95 and 96:
Related Documentation ge-5/0/0.3276
- Page 97 and 98:
3. If you are done configuring the
- Page 99 and 100:
Use the following command to clear
- Page 101 and 102:
Related Documentation all standby l
- Page 103 and 104:
user@host# set reth1 redundant-ethe
- Page 105 and 106:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 107 and 108:
CHAPTER 4 1-Port Gigabit Ethernet S
- Page 109 and 110:
Related Documentation • no-auto-n
- Page 111 and 112:
Step-by-Step Procedure 4. To enable
- Page 113 and 114:
NOTE: In the example shown above, t
- Page 115 and 116:
CHAPTER 5 2-Port 10-Gigabit Etherne
- Page 117 and 118:
Link Speeds Link Settings Related D
- Page 119 and 120:
Verification user@host# set speed 1
- Page 121 and 122:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 123 and 124:
CHAPTER 6 Power over Ethernet Under
- Page 125 and 126:
PoE Options configured on the SRX S
- Page 127 and 128:
Verification Step-by-Step Procedure
- Page 129 and 130:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 131 and 132:
The telemetry status displays the p
- Page 133 and 134:
PART 3 DS1 and DS3 Interfaces Copyr
- Page 135 and 136:
CHAPTER 7 DS1 and DS3 Interfaces DS
- Page 137 and 138:
B8ZS and HDB3 Encoding Neither B8ZS
- Page 139 and 140:
Example: Configuring a T1 Interface
- Page 141 and 142:
Related Documentation • The physi
- Page 143 and 144:
Multiplexing DS1 Signals Four DS1 s
- Page 145 and 146:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 147 and 148:
Related Documentation Example: Conf
- Page 149 and 150:
3. Click Start. The output appears
- Page 151 and 152:
CHAPTER 8 1-Port Clear Channel DS3/
- Page 153 and 154:
Table 17: 1-Port Clear Channel DS3/
- Page 155 and 156:
Related Documentation user@host# se
- Page 157 and 158:
Requirements Overview Configuration
- Page 159 and 160:
CHAPTER 9 Channelized Interfaces
- Page 161 and 162:
Related Documentation or up to 31 D
- Page 163 and 164:
user@host# set framing esf user@hos
- Page 165 and 166:
Step-by-Step Procedure set interfac
- Page 167 and 168:
Related Documentation Verifying Cle
- Page 169 and 170:
Example: Configuring a Channelized
- Page 171 and 172:
If you are done configuring the dev
- Page 173 and 174:
user@host# set ct1-6/0/0 partition
- Page 175 and 176:
3. Configure device R1. [edit inter
- Page 177 and 178:
user@host# set ct1-3/0/1 partition
- Page 179 and 180:
ISDN PRI Operation • Junos OS Int
- Page 181 and 182:
Step-by-Step Procedure The followin
- Page 183 and 184:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 185 and 186:
PART 4 ISDN and VoIP Interfaces Cop
- Page 187 and 188:
CHAPTER 10 ISDN Understanding ISDN
- Page 189 and 190:
ISDN Call Setup termination type 1
- Page 191 and 192:
Related Documentation ISDN Interfac
- Page 193 and 194:
• On a channelized E1 interface,
- Page 195 and 196:
Step-by-Step Procedure The followin
- Page 197 and 198:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 199 and 200:
user@host# edit interfaces dl0 user
- Page 201 and 202:
Step-by-Step Procedure Related Docu
- Page 203 and 204:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 205 and 206:
Dialer Watch Related Documentation
- Page 207 and 208:
pool dw-group; watch-list { 172.27.
- Page 209 and 210:
Table 18: Encapsulation Monitoring
- Page 211 and 212:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 213 and 214:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 215 and 216:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 217 and 218:
Related Documentation • Junos OS
- Page 219 and 220:
Parent: None Device flags : Present
- Page 221 and 222:
• In the J-Web configuration edit
- Page 223 and 224:
Interface: bc-6/0/0:1 Status: No ca
- Page 225 and 226:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 227 and 228:
Related Documentation The output sh
- Page 229 and 230:
CHAPTER 11 Voice over Internet Prot
- Page 231 and 232:
Related Documentation • The VoIP
- Page 233 and 234:
Table 19: J2320 and J2350 Avaya VoI
- Page 235 and 236:
• Understanding the TGM550 Teleph
- Page 237 and 238:
To enable easier administration of
- Page 239 and 240:
Related Documentation • A console
- Page 241 and 242:
• Avaya VoIP Modules Overview on
- Page 243 and 244:
TGM550 LEDs TGM550 LEDs indicate li
- Page 245 and 246:
Table 25: TIM508 Connector Pinout P
- Page 247 and 248:
• System Capacities Table for Ava
- Page 249 and 250:
TIM510 LEDs Table 29: LEDs for TIM5
- Page 251 and 252:
TIM514 Connector Pinout The TIM514
- Page 253 and 254:
• Avaya VoIP Modules Configuratio
- Page 255 and 256:
Table 33: TIM516 Connector Pinout (
- Page 257 and 258:
• System Capacities Table for Ava
- Page 259 and 260:
Table 36: TIM518 Connector Pinout (
- Page 261 and 262:
TIM518 LEDs Table 38: LEDs for TIM5
- Page 263 and 264:
Table 39: LEDs for TIM521 (continue
- Page 265 and 266:
• Dynamic Call Admission Control
- Page 267 and 268:
Dynamic Call Admission Control Over
- Page 269 and 270:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 271 and 272:
Example: Configuring VoIP Interface
- Page 273 and 274:
2. Configure the source IPv4 addres
- Page 275 and 276:
user@host# set dynamic-call-admissi
- Page 277 and 278:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 279 and 280:
Related Documentation t1-6/0/0.0 up
- Page 281 and 282:
1. Connect to the TGM550 through th
- Page 283 and 284:
TGM550 Module and VoIP Interface Tr
- Page 285 and 286:
PART 5 DSL and Modem Interfaces Cop
- Page 287 and 288:
CHAPTER 12 DSL Interfaces ADSL Inte
- Page 289 and 290:
ADSL2 and ADSL2+ ATM CoS Support Co
- Page 291 and 292:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 293 and 294:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 295 and 296:
Related Documentation The following
- Page 297 and 298:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 299 and 300:
Verification If you are done config
- Page 301 and 302:
• The physical interface is enabl
- Page 303 and 304:
Step-by-Step Procedure [edit] set c
- Page 305 and 306:
Verification unit 3 { encapsulation
- Page 307 and 308:
physical interface. To clear the st
- Page 309 and 310:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 311 and 312:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 313 and 314:
Verifying a PPPoA Configuration for
- Page 315 and 316:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 317 and 318:
Configuration Verification Step-by-
- Page 319 and 320:
CHAPTER 13 G.SHDSL Interfaces SHDSL
- Page 321 and 322:
tolerance. By default, unspecified
- Page 323 and 324:
Related Documentation • ether-ove
- Page 325 and 326:
Verification annex annex-a; line-ra
- Page 327 and 328:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 329 and 330:
Input packets: 0 Output packets: 0
- Page 331 and 332:
Example: Configuring the G.SHDSL In
- Page 333 and 334:
Configuration CLI Quick Configurati
- Page 335 and 336:
Step-by-Step Procedure The followin
- Page 337 and 338:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 339 and 340:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 341 and 342:
Related Documentation Copyright ©
- Page 343 and 344:
CHAPTER 14 VDSL2 Mini-PIM Interface
- Page 345 and 346:
Related Documentation Figure 23: Ty
- Page 347 and 348:
Related Documentation • NOTE: The
- Page 349 and 350:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 351 and 352:
Related Documentation • Status of
- Page 353 and 354:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 355 and 356:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces pp
- Page 357 and 358:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 359 and 360:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 361 and 362:
Step-by-Step Procedure [edit] user@
- Page 363 and 364:
Verification 3. Configure the PPPoE
- Page 365 and 366:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 367 and 368:
Verifying the VDSL2 Mini-PIM for En
- Page 369 and 370:
Output packets: 0 0 pps Security: Z
- Page 371 and 372:
Logical interface pp0.0 (Index 70)
- Page 373 and 374:
Device flags : Present Running Inte
- Page 375 and 376:
Action 1. Verifying the interface s
- Page 377 and 378:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 379 and 380:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 381 and 382:
[edit] user@host# set interfaces at
- Page 383 and 384:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 385 and 386:
Step-by-Step Procedure set interfac
- Page 387 and 388:
user@host# set interfaces pp0 unit
- Page 389 and 390:
Verification Copyright © 2011, Jun
- Page 391 and 392:
Output packets: 1000 Logical interf
- Page 393 and 394:
Subfunction : 0x00 Seconds in showt
- Page 395 and 396:
Interface Admin Link Proto Local Re
- Page 397 and 398:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 399 and 400:
Input packets : 0 Output packets: 0
- Page 401 and 402:
Related Documentation Keepalive: In
- Page 403 and 404:
CHAPTER 15 3G Wireless Modems for W
- Page 405 and 406:
Related Documentation Dialer Interf
- Page 407 and 408:
Related Documentation • As a dial
- Page 409 and 410:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 411 and 412:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 413 and 414:
3G Wireless Modem Interface This to
- Page 415 and 416:
Related Documentation You configure
- Page 417 and 418:
Understanding Account Activation fo
- Page 419 and 420:
Related Documentation user@host> re
- Page 421 and 422:
Related Documentation user@host> ta
- Page 423 and 424:
CHAPTER 16 USB Modems for Dial Back
- Page 425 and 426:
USB Modem Configuration Overview Co
- Page 427 and 428:
Table 47: Incoming Map Options (con
- Page 429 and 430:
Related Documentation • Junos OS
- Page 431 and 432:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 433 and 434:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 435 and 436:
Example: Configuring a Dialer Inter
- Page 437 and 438:
• Example: Configuring a USB Mode
- Page 439 and 440:
CHAPTER 17 DOCSIS Mini-PIM Interfac
- Page 441 and 442:
Software Features Supported on DOCS
- Page 443 and 444:
Verification user@host# set interfa
- Page 445 and 446:
Related Documentation Invalid zone
- Page 447 and 448:
CHAPTER 18 Serial Interfaces Serial
- Page 449 and 450:
Signal Polarity Serial Clocking Mod
- Page 451 and 452:
The EIA-530 interface supports asyn
- Page 453 and 454:
Related Documentation • Signal El
- Page 455 and 456:
64 bytes from 10.10.10.10: icmp_seq
- Page 457 and 458:
PART 6 Link Services and Special In
- Page 459 and 460:
CHAPTER 19 Link Services Interfaces
- Page 461 and 462:
Link Services Exceptions on J Serie
- Page 463 and 464:
Using lsq-0/0/0, CRTP can be applie
- Page 465 and 466:
Configuring Link-Layer Overhead Rel
- Page 467 and 468:
Configuring Link Services This topi
- Page 469 and 470:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 471 and 472:
user@host# show interfaces se-1/0/0
- Page 473 and 474:
Step-by-Step Procedure Related Docu
- Page 475 and 476:
Step-by-Step Procedure [edit] set c
- Page 477 and 478:
Verification To confirm that the co
- Page 479 and 480:
Step-by-Step Procedure set interfac
- Page 481 and 482:
Verification To confirm that the co
- Page 483 and 484:
Verifying Link Services Interface S
- Page 485 and 486:
Output packets are segmented into o
- Page 487 and 488:
Multilink Frame Relay to the lsq-0/
- Page 489 and 490:
user@host# set family inet address
- Page 491 and 492:
• Example: Configuring Multilink
- Page 493 and 494:
Results From configuration mode, co
- Page 495 and 496:
Related Documentation • NOTE: •
- Page 497 and 498:
Verification To confirm that the co
- Page 499 and 500:
Step-by-Step Procedure The followin
- Page 501 and 502:
Determine Which CoS Components Are
- Page 503 and 504:
are PPP-encapsulated and interleave
- Page 505 and 506:
2. Verify packet encapsulation. To
- Page 507 and 508:
Copyright © 2011, Juniper Networks
- Page 509 and 510:
• The total number of packets tra
- Page 511 and 512:
CHAPTER 20 Special Interfaces • U
- Page 513 and 514:
Related Documentation is the prefer
- Page 515 and 516:
PART 7 Encapsulation Copyright © 2
- Page 517 and 518:
CHAPTER 21 Interface Encapsulation
- Page 519 and 520:
Data-Link Connection Identifiers Co
- Page 521 and 522:
separate CHAP handshakes are requir
- Page 523 and 524:
Related Documentation • Normal Re
- Page 525 and 526:
CHAPTER 22 Point-to-Point Protocol
- Page 527 and 528:
PPPoE Session Stage Related Documen
- Page 529 and 530:
[edit interfaces pp0 unit 0] user@h
- Page 531 and 532:
Auto-reconnect timeout: 1 seconds,
- Page 533 and 534:
Related Documentation • Junos OS
- Page 535 and 536:
CLI Quick Configuration Step-by-Ste
- Page 537 and 538:
Related Documentation If you set th
- Page 539 and 540:
Verifying CHAP Authentication Purpo
- Page 541 and 542:
Example: Configuring the PPPoE-Base
- Page 543 and 544:
PART 8 Index Copyright © 2011, Jun
- Page 545 and 546:
Index Symbols #, comments in config
- Page 547 and 548:
ackward-explicit congestion notific
- Page 549 and 550:
connection process ISDN BRI interfa
- Page 551 and 552:
discard interface..................
- Page 553 and 554:
frames framing DS2 M-frame format..
- Page 555 and 556:
Q.931 timer........................
- Page 557 and 558:
link-local unicast IPv6 addresses..
- Page 559 and 560:
ping, verifying link states........
- Page 561 and 562:
V.35...............................
- Page 563 and 564:
terminal endpoint identifier See st
- Page 565 and 566:
wireless modem.....................