Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Amino Acid Esters of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose<br />
glycine, alanine, <strong>and</strong> lysine derivatized polymers. Moreover, elemental analysis was<br />
carried out <strong>and</strong> the %N content of the polymers was exploited for the sake of<br />
confirmation of the exact degree of amino acid incorporation (DSEst).<br />
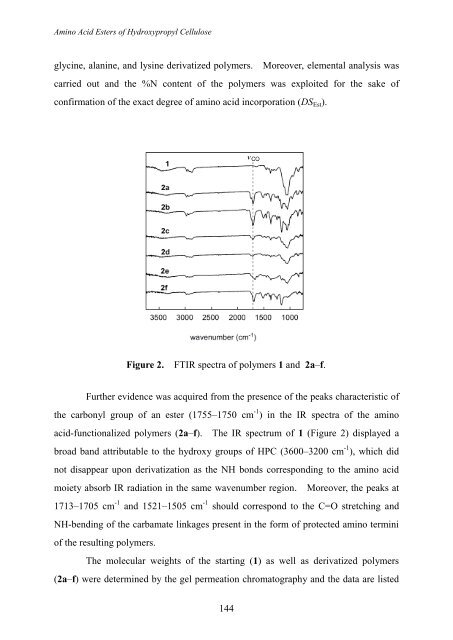
Further evidence was acquired from the presence of the peaks characteristic of<br />
the carbonyl group of an ester (1755–1750 cm -1 ) in the IR spectra of the amino<br />
acid-functionalized polymers (2a–f). The IR spectrum of 1 (Figure 2) displayed a<br />
broad b<strong>and</strong> attributable to the hydroxy groups of HPC (3600–3200 cm -1 ), which did<br />
not disappear upon derivatization as the NH bonds corresponding to the amino acid<br />
moiety absorb IR radiation in the same wavenumber region. Moreover, the peaks at<br />
1713–1705 cm -1 <strong>and</strong> 1521–1505 cm -1 should correspond to the C=O stretching <strong>and</strong><br />
NH-bending of the carbamate linkages present in the form of protected amino termini<br />
of the resulting polymers.<br />
Figure 2. FTIR spectra of polymers 1 <strong>and</strong> 2a–f.<br />
The molecular weights of the starting (1) as well as derivatized polymers<br />
(2a–f) were determined by the gel permeation chromatography <strong>and</strong> the data are listed<br />
144