Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
General Introduction<br />
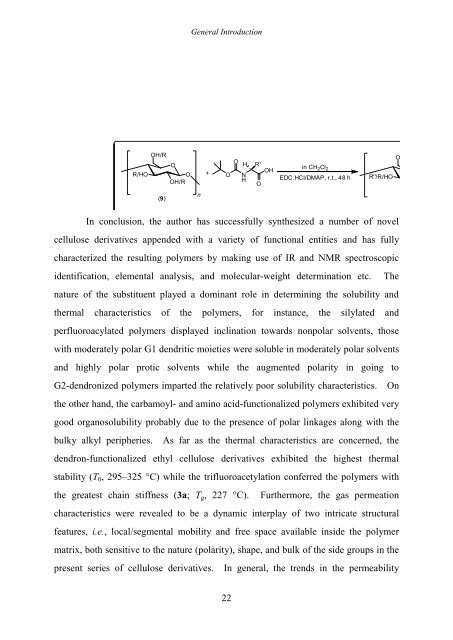
In conclusion, the author has successfully synthesized a number R'' of = novel<br />
H<br />
R =<br />
R/HO<br />
OH/R<br />
C<br />
H2 O<br />
O<br />
OH/R<br />
+<br />
cellulose derivatives appended with a variety of functional entities <strong>and</strong> has fully<br />
characterized the resulting polymers by making use of IR <strong>and</strong> NMR spectroscopic<br />
identification, elemental analysis, <strong>and</strong> molecular-weight determination etc. The<br />
nature of the substituent played a dominant role in determining the solubility <strong>and</strong><br />
thermal characteristics of the polymers, for instance, the silylated <strong>and</strong><br />
perfluoroacylated polymers displayed inclination towards nonpolar solvents, those<br />
with moderately polar G1 dendritic moieties were soluble in moderately polar solvents<br />
<strong>and</strong> highly polar protic solvents while the augmented polarity in going to<br />
G2-dendronized polymers imparted the relatively poor solubility characteristics. On<br />
the other h<strong>and</strong>, the carbamoyl- <strong>and</strong> amino acid-functionalized polymers exhibited very<br />
good organosolubility probably due to the presence of polar linkages along with the<br />
bulky alkyl peripheries. As far as the thermal characteristics are concerned, the<br />
dendron-functionalized ethyl cellulose derivatives exhibited the highest thermal<br />
stability (T0, 295–325 °C) while the trifluoroacetylation conferred the polymers with<br />
the greatest chain stiffness (3a; Tg, 227 °C). Furthermore, the gas permeation<br />
characteristics were revealed to be a dynamic interplay of two intricate structural<br />
features, i.e., local/segmental mobility <strong>and</strong> free space available inside the polymer<br />
matrix, both sensitive to the nature (polarity), shape, <strong>and</strong> bulk of the side groups in the<br />
present series of cellulose derivatives. In general, the trends in the permeability<br />
22<br />
in CH 2Cl 2<br />
R''/R/HO<br />
OH/R/R''<br />
n<br />
(9) (10)<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
x<br />
O<br />
O<br />
H<br />
N<br />
H<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
EDC.HCl/DMAP, r.t., 48 h<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH/R/R''<br />
R' = H CH 3 (CH 3) 2CHCH 2 NH 2COCH 2 NH 2COCH 2CH 2 (CH 3) 3COCONH(CH 2) 4<br />
10a 10b 10c 10d 10e 10f<br />
DS Est = 3.0 3.0 1.1 1.0 1.7 3.0<br />
O<br />
O<br />
H<br />
N<br />
H<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
n