Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
Synthesis, Characterization, and Gas Permeation Properties
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
General Introduction<br />
The synthesis of cellulose nitrate laid the foundations for the chemical derivatization<br />
of the inexhaustible natural polymer followed by the synthesis of first thermoplastic<br />
polymer called celluloid in 1870, marking a milestone in the history of polymer<br />
science that revolutionized our modern life style. 7,8 Since then there became an<br />
avalanche of man-made or regenerated cellulose fibers based on wood pulp rather than<br />
native cellulose fibers, for textiles <strong>and</strong> technical products. Rayon is the oldest<br />
regenerated cellulosic fiber having been in commercial production since 1880s in<br />
France, where it was originally developed as a cheap alternative to silk, followed by<br />
the viscose process, currently the most important large scale technical process in fiber<br />
production, 9 <strong>and</strong> finally by the Lyocell process, an industrial breakthrough opening<br />
new frontiers in the field of environment-friendly fiber technologies. 10,1a<br />
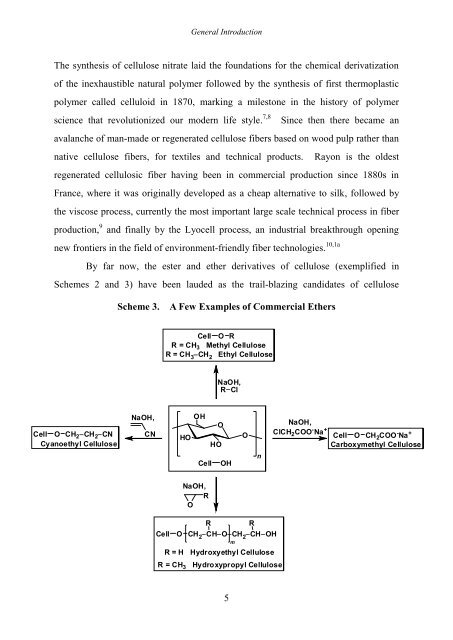
By far now, the ester <strong>and</strong> ether derivatives of cellulose (exemplified in<br />
Schemes 2 <strong>and</strong> 3) have been lauded as the trail-blazing c<strong>and</strong>idates of cellulose<br />
Cell O CH2�CH 2�CN<br />
Cyanoethyl Cellulose<br />
Scheme 3. A Few Examples of Commercial Ethers<br />
NaOH,<br />
CN<br />
Cell O R<br />
R = CH3 Methyl Cellulose<br />
R = CH3�CH 2 Ethyl Cellulose<br />
HO<br />
OH<br />
NaOH,<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O<br />
HO<br />
NaOH,<br />
R�Cl<br />
Cell OH<br />
Cell O CH 2 �CH�O�CH 2 �CH�OH<br />
5<br />
O<br />
R R<br />
R = H Hydroxyethyl Cellulose<br />
R = CH 3 Hydroxypropyl Cellulose<br />
m<br />
n<br />
NaOH,<br />
ClCH 2COO - Na +<br />
Cell O CH2COO Carboxymethyl Cellulose<br />
-Na +