Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The seedlings were inoculated<br />
when the second leaves were fully<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>ed with a 1 x 10 6 spore/ml<br />
suspension <strong>of</strong> an aggressive isolate<br />
(S353/88). The plantlets were then<br />
placed in propagators <strong>and</strong><br />
transferred to growth chambers for<br />
72 h at 15 o C in complete darkness<br />
to establish infection. Once this had<br />
been completed, the plants were<br />
moved to a containment glasshouse<br />
<strong>and</strong> removed from their<br />
propagators. Disease was scored at<br />
10 <strong>and</strong> 17 days post-inoculation<br />
<strong>and</strong> expressed as the percentage <strong>of</strong><br />
leaf area lesioned (at the intervals 1,<br />
5, 10, 25, 40, 60, 75, 90, <strong>and</strong> 100%).<br />
The scores were transformed using<br />
the angular transformation <strong>and</strong> an<br />
analysis <strong>of</strong> variance carried out<br />
using the GENSTAT 5 statistical<br />
package. The significance <strong>of</strong><br />
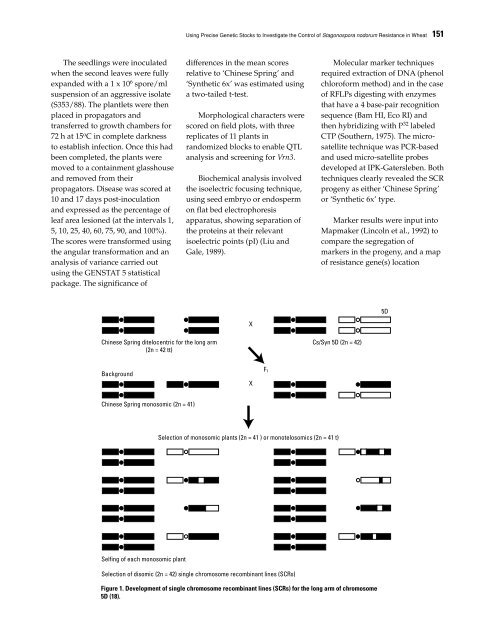
Chinese Spring ditelocentric for the long arm<br />
(2n = 42 tt)<br />
Background<br />
Chinese Spring monosomic (2n = 41)<br />
Selfing <strong>of</strong> each monosomic plant<br />
Using Precise Genetic Stocks to Investigate the Control <strong>of</strong> <strong>Stagonospora</strong> nodorum Resistance in Wheat 151<br />
differences in the mean scores<br />
relative to ‘Chinese Spring’ <strong>and</strong><br />
‘Synthetic 6x’ was estimated using<br />
a two-tailed t-test.<br />
Morphological characters were<br />
scored on field plots, with three<br />
replicates <strong>of</strong> 11 plants in<br />
r<strong>and</strong>omized blocks to enable QTL<br />
analysis <strong>and</strong> screening for Vrn3.<br />
Biochemical analysis involved<br />
the isoelectric focusing technique,<br />
using seed embryo or endosperm<br />
on flat bed electrophoresis<br />
apparatus, showing separation <strong>of</strong><br />
the proteins at their relevant<br />
isoelectric points (pI) (Liu <strong>and</strong><br />
Gale, 1989).<br />
X<br />
X<br />
Cs/Syn 5D (2n = 42)<br />
Selection <strong>of</strong> monosomic plants (2n = 41 ) or monotelosomics (2n = 41 t)<br />
Selection <strong>of</strong> disomic (2n = 42) single chromosome recombinant lines (SCRs)<br />
Figure 1. Development <strong>of</strong> single chromosome recombinant lines (SCRs) for the long arm <strong>of</strong> chromosome<br />
5D (18).<br />
F1<br />
Molecular marker techniques<br />
required extraction <strong>of</strong> DNA (phenol<br />
chlor<strong>of</strong>orm method) <strong>and</strong> in the case<br />
<strong>of</strong> RFLPs digesting with enzymes<br />
that have a 4 base-pair recognition<br />
sequence (Bam HI, Eco RI) <strong>and</strong><br />
then hybridizing with P 32 labeled<br />
CTP (Southern, 1975). The microsatellite<br />
technique was PCR-based<br />
<strong>and</strong> used micro-satellite probes<br />
developed at IPK-Gatersleben. Both<br />
techniques clearly revealed the SCR<br />
progeny as either ‘Chinese Spring’<br />
or ‘Synthetic 6x’ type.<br />
Marker results were input into<br />
Mapmaker (Lincoln et al., 1992) to<br />
compare the segregation <strong>of</strong><br />
markers in the progeny, <strong>and</strong> a map<br />
<strong>of</strong> resistance gene(s) location<br />
5D