Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
Septoria and Stagonospora Diseases of Cereals - CIMMYT ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
24<br />
Session 1 — S.B. Goodwin <strong>and</strong> J.R. Cavaletto<br />
plates using a replica plater, <strong>and</strong><br />
incubated upside down at 37°C<br />
overnight.<br />
Colony lifts were made onto 8 x<br />
12 cm pieces <strong>of</strong> Zeta Probe<br />
(BioRad) membranes by briefly<br />
laying the membrane pieces over<br />
the 96 colonies <strong>and</strong> lifting to pick<br />
up the bacteria. Membranes were<br />
placed colony side up onto blotting<br />
paper soaked with 10% SDS for 3<br />
min, then 0.5 M NaOH/1.5 M NaCl<br />
for 5 min, 0.5 M Tris, pH 8.0/1.5 M<br />
NaCl for 5 min, <strong>and</strong> 6x SSC for 5<br />
min. Finally, a UV Stratalinker<br />
(Stratagene) was used to crosslink<br />
the plasmid DNA to the membrane.<br />
For Southern analysis, pSTL70<br />
DNA was labeled using the<br />
R<strong>and</strong>om Primer Fluorescein<br />
labeling kit with antifluorescein-<br />
HRP (DuPont NEN) <strong>and</strong><br />
hybridized according to the<br />
manufacturer’s instructions.<br />
Approximately 4,000 clones (2,000<br />
from each isolate) were screened.<br />
Positive hybridizations were<br />
verified by digesting each positive<br />
clone with Pst I to release the insert,<br />
separating the fragments on<br />
agarose gels, blotting <strong>and</strong> probing<br />
as described above. Clones that<br />
hybridized after two rounds <strong>of</strong><br />
screening were sequenced using a<br />
Pharmacia ALF automated DNA<br />
sequencer.<br />
Results<br />
Among 4,000 clones screened,<br />
five hybridized strongly to pSTL70.<br />
Complete sequences have been<br />
obtained for the original pSTL70<br />
clone <strong>and</strong> three others. Clones<br />
2E11, 9A5 <strong>and</strong> 11E8 each had large<br />
regions <strong>of</strong> near identity with<br />
pSTL70 (Table 1). However, the<br />
three clones shared no similarity<br />
with each other. BLASTX searches<br />
<strong>of</strong> the putative translation products<br />
identified a number <strong>of</strong> GenBank<br />
accessions with similarity to clones<br />
pSTL70, 2E11 <strong>and</strong> 11E8 (Table 1).<br />
The original pSTL70 clone had high<br />
similarity to a two-component<br />
regulator gene from yeast, Sln1,<br />
<strong>and</strong> a similar gene from C<strong>and</strong>ida<br />
albicans.<br />
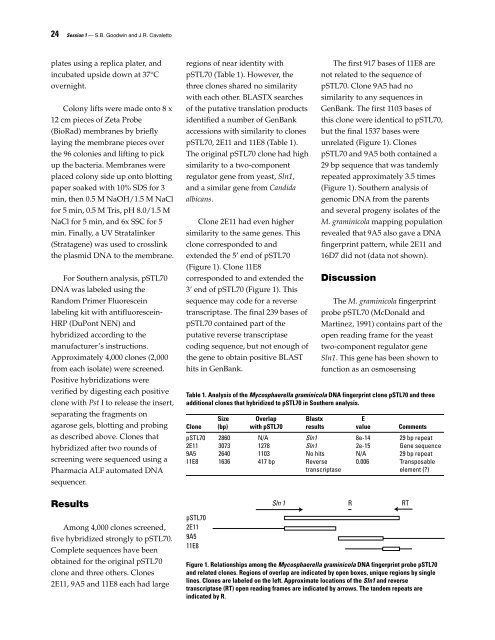
Clone 2E11 had even higher<br />
similarity to the same genes. This<br />
clone corresponded to <strong>and</strong><br />
extended the 5’ end <strong>of</strong> pSTL70<br />
(Figure 1). Clone 11E8<br />
corresponded to <strong>and</strong> extended the<br />
3’ end <strong>of</strong> pSTL70 (Figure 1). This<br />
sequence may code for a reverse<br />
transcriptase. The final 239 bases <strong>of</strong><br />
pSTL70 contained part <strong>of</strong> the<br />
putative reverse transcriptase<br />
coding sequence, but not enough <strong>of</strong><br />
the gene to obtain positive BLAST<br />
hits in GenBank.<br />
Table 1. Analysis <strong>of</strong> the Mycosphaerella graminicola DNA fingerprint clone pSTL70 <strong>and</strong> three<br />
additional clones that hybridized to pSTL70 in Southern analysis.<br />
Size Overlap Blastx E<br />
Clone (bp) with pSTL70 results value Comments<br />
pSTL70 2860 N/A Sln1 8e-14 29 bp repeat<br />
2E11 3073 1278 Sln1 2e-15 Gene sequence<br />
9A5 2640 1103 No hits N/A 29 bp repeat<br />
11E8 1636 417 bp Reverse 0.006 Transposable<br />
transcriptase element (?)<br />
pSTL70<br />
2E11<br />
9A5<br />
11E8<br />
The first 917 bases <strong>of</strong> 11E8 are<br />
not related to the sequence <strong>of</strong><br />
pSTL70. Clone 9A5 had no<br />
similarity to any sequences in<br />
GenBank. The first 1103 bases <strong>of</strong><br />
this clone were identical to pSTL70,<br />
but the final 1537 bases were<br />
unrelated (Figure 1). Clones<br />
pSTL70 <strong>and</strong> 9A5 both contained a<br />
29 bp sequence that was t<strong>and</strong>emly<br />
repeated approximately 3.5 times<br />
(Figure 1). Southern analysis <strong>of</strong><br />
genomic DNA from the parents<br />
<strong>and</strong> several progeny isolates <strong>of</strong> the<br />
M. graminicola mapping population<br />
revealed that 9A5 also gave a DNA<br />
fingerprint pattern, while 2E11 <strong>and</strong><br />
16D7 did not (data not shown).<br />
Discussion<br />
The M. graminicola fingerprint<br />
probe pSTL70 (McDonald <strong>and</strong><br />
Martinez, 1991) contains part <strong>of</strong> the<br />
open reading frame for the yeast<br />
two-component regulator gene<br />
Sln1. This gene has been shown to<br />
function as an osmosensing<br />
Sln 1 R<br />
RT<br />
Figure 1. Relationships among the Mycosphaerella graminicola DNA fingerprint probe pSTL70<br />
<strong>and</strong> related clones. Regions <strong>of</strong> overlap are indicated by open boxes, unique regions by single<br />
lines. Clones are labeled on the left. Approximate locations <strong>of</strong> the Sln1 <strong>and</strong> reverse<br />
transcriptase (RT) open reading frames are indicated by arrows. The t<strong>and</strong>em repeats are<br />
indicated by R.