Non-pharmacological interventions for caregivers ... - Update Software
Non-pharmacological interventions for caregivers ... - Update Software
Non-pharmacological interventions for caregivers ... - Update Software
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
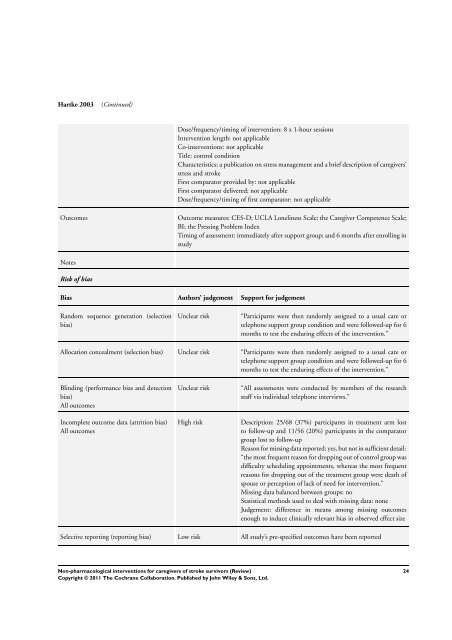
Hartke 2003 (Continued)<br />
Dose/frequency/timing of intervention: 8 x 1-hour sessions<br />
Intervention length: not applicable<br />
Co-<strong>interventions</strong>: not applicable<br />
Title: control condition<br />
Characteristics: a publication on stress management and a brief description of <strong>caregivers</strong>’<br />
stress and stroke<br />
First comparator provided by: not applicable<br />
First comparator delivered: not applicable<br />
Dose/frequency/timing of first comparator: not applicable<br />
Outcomes Outcome measures: CES-D; UCLA Loneliness Scale; the Caregiver Competence Scale;<br />
BI; the Pressing Problem Index<br />
Timing of assessment: immediately after support group; and 6 months after enrolling in<br />
study<br />
Notes<br />
Risk of bias<br />
Bias Authors’ judgement Support <strong>for</strong> judgement<br />
Random sequence generation (selection<br />
bias)<br />
Unclear risk “Participants were then randomly assigned to a usual care or<br />
telephone support group condition and were followed-up <strong>for</strong> 6<br />
months to test the enduring effects of the intervention.”<br />
Allocation concealment (selection bias) Unclear risk “Participants were then randomly assigned to a usual care or<br />
telephone support group condition and were followed-up <strong>for</strong> 6<br />
months to test the enduring effects of the intervention.”<br />
Blinding (per<strong>for</strong>mance bias and detection<br />
bias)<br />
All outcomes<br />
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias)<br />
All outcomes<br />
Unclear risk “All assessments were conducted by members of the research<br />
staff via individual telephone interviews.”<br />
High risk Description: 25/68 (37%) participants in treatment arm lost<br />
to follow-up and 11/56 (20%) participants in the comparator<br />
group lost to follow-up<br />
Reason <strong>for</strong> missing data reported: yes, but not in sufficient detail:<br />
“the most frequent reason <strong>for</strong> dropping out of control group was<br />
difficulty scheduling appointments, whereas the most frequent<br />
reasons <strong>for</strong> dropping out of the treatment group were death of<br />
spouse or perception of lack of need <strong>for</strong> intervention.”<br />
Missing data balanced between groups: no<br />
Statistical methods used to deal with missing data: none<br />
Judgement: difference in means among missing outcomes<br />
enough to induce clinically relevant bias in observed effect size<br />
Selective reporting (reporting bias) Low risk All study’s pre-specified outcomes have been reported<br />
<strong>Non</strong>-<strong>pharmacological</strong> <strong>interventions</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>caregivers</strong> of stroke survivors (Review)<br />
Copyright © 2011 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.<br />
24