CT4860 STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF PAVEMENTS
CT4860 STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF PAVEMENTS
CT4860 STRUCTURAL DESIGN OF PAVEMENTS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
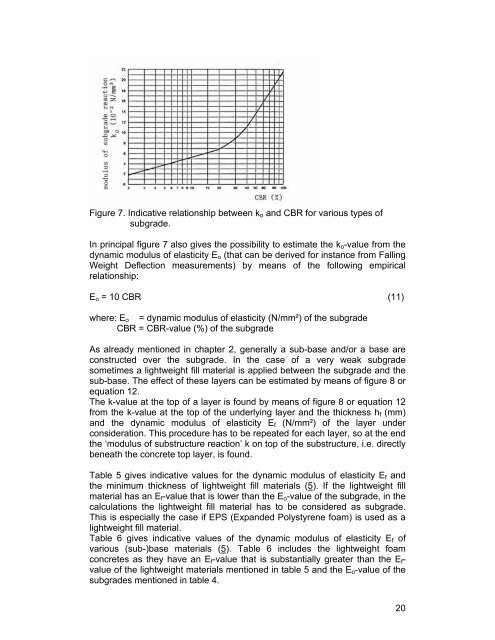
Figure 7. Indicative relationship between ko and CBR for various types of<br />
subgrade.<br />
In principal figure 7 also gives the possibility to estimate the ko-value from the<br />
dynamic modulus of elasticity Eo (that can be derived for instance from Falling<br />
Weight Deflection measurements) by means of the following empirical<br />
relationship:<br />
Eo = 10 CBR (11)<br />
where: Eo = dynamic modulus of elasticity (N/mm²) of the subgrade<br />
CBR = CBR-value (%) of the subgrade<br />
As already mentioned in chapter 2, generally a sub-base and/or a base are<br />
constructed over the subgrade. In the case of a very weak subgrade<br />
sometimes a lightweight fill material is applied between the subgrade and the<br />
sub-base. The effect of these layers can be estimated by means of figure 8 or<br />
equation 12.<br />
The k-value at the top of a layer is found by means of figure 8 or equation 12<br />
from the k-value at the top of the underlying layer and the thickness hf (mm)<br />
and the dynamic modulus of elasticity Ef (N/mm²) of the layer under<br />
consideration. This procedure has to be repeated for each layer, so at the end<br />
the ‘modulus of substructure reaction’ k on top of the substructure, i.e. directly<br />
beneath the concrete top layer, is found.<br />
Table 5 gives indicative values for the dynamic modulus of elasticity Ef and<br />
the minimum thickness of lightweight fill materials (5). If the lightweight fill<br />
material has an Ef-value that is lower than the Eo-value of the subgrade, in the<br />
calculations the lightweight fill material has to be considered as subgrade.<br />
This is especially the case if EPS (Expanded Polystyrene foam) is used as a<br />
lightweight fill material.<br />
Table 6 gives indicative values of the dynamic modulus of elasticity Ef of<br />
various (sub-)base materials (5). Table 6 includes the lightweight foam<br />
concretes as they have an Ef-value that is substantially greater than the Efvalue<br />
of the lightweight materials mentioned in table 5 and the Eo-value of the<br />
subgrades mentioned in table 4.<br />
20