synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 5<br />
Synthesis <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>vitro</strong> <strong>pharmacology</strong> <strong>of</strong> a <strong>series</strong> <strong>of</strong> new<br />
1,4-dihydropyrid<strong>in</strong>es. 1.<br />
Diethyl 2-(co-am<strong>in</strong>oalkylthio)methyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-<br />
[(substituted)phenyl]-l,4-dihydropyrid<strong>in</strong>e-3,5-dicarboxylates<br />
as potent calcium channel blockers 1<br />
Chapter 5<br />
1 Introduction<br />
The 1,4-dihydropyrid<strong>in</strong>e (DHP) calcium channel blockers are important drugs <strong>in</strong><br />
antiang<strong>in</strong>al <strong>and</strong> antihypertensive therapy [1-51 because <strong>of</strong> their vasodilator<br />
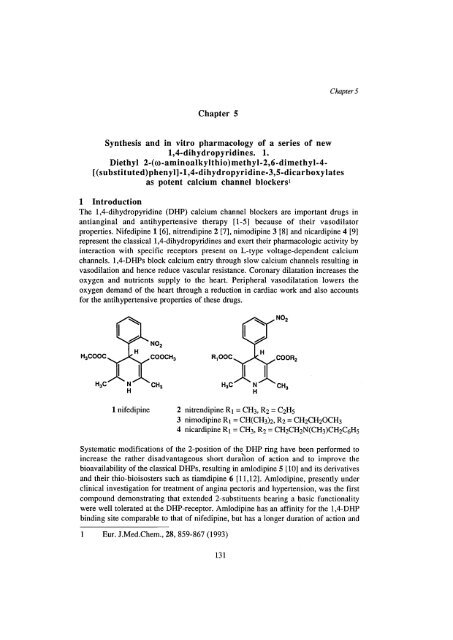
properties. Nifedip<strong>in</strong>e 1 [6], nitrendip<strong>in</strong>e 2 [7], nimodip<strong>in</strong>e 3 [8] <strong>and</strong> nicardip<strong>in</strong>e 4 [9]<br />
represent the classical 1,4-dihydropyrid<strong>in</strong>es <strong>and</strong> exert their pharmacologic activity by<br />
<strong>in</strong>teraction with specific receptors present on L-type voltage-dependent calcium<br />
channels. 1,4-DHPs block calcium entry through slow calcium channels result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong><br />
vasodilation <strong>and</strong> hence reduce vascular resistance. Coronary dilatation <strong>in</strong>creases the<br />
oxygen <strong>and</strong> nutrients supply to the heart. Peripheral vasodilatation lowers the<br />
oxygen dem<strong>and</strong> <strong>of</strong> the heart through a reduction <strong>in</strong> cardiac work <strong>and</strong> also accounts<br />
for the antihypertensive properties <strong>of</strong> these drugs.<br />
H H<br />
1 nifedip<strong>in</strong>e 2 nitrendip<strong>in</strong>e Ri = CH 3, R 2 = C2H5<br />
3 nimodip<strong>in</strong>e Ri = CH(CH 3) 2, R2 = CH 2CH 2OCH 3<br />
4 nicardip<strong>in</strong>e Ri = CH 3, R 2 = CH 2CH 2N(CH 3)CH 2C 6H 5<br />
Systematic modifications <strong>of</strong> the 2-position <strong>of</strong> the DHP r<strong>in</strong>g have been performed to<br />
<strong>in</strong>crease the rather disadvantageous short duration <strong>of</strong> action <strong>and</strong> to improve the<br />
bioavailability <strong>of</strong> the classical DHPs, result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> amlodip<strong>in</strong>e 5 [10] <strong>and</strong> its derivatives<br />
<strong>and</strong> their thio-bioisosters such as tiamdip<strong>in</strong>e 6 [11,12]. Amlodip<strong>in</strong>e, presently under<br />
cl<strong>in</strong>ical <strong>in</strong>vestigation for treatment <strong>of</strong> ang<strong>in</strong>a pectoris <strong>and</strong> hypertension, was the first<br />
compound demonstrat<strong>in</strong>g that extended 2-substituents bear<strong>in</strong>g a basic functionality<br />
were well tolerated at the DHP-receptor. Amlodip<strong>in</strong>e has an aff<strong>in</strong>ity for the 1,4-DHP<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g site comparable to that <strong>of</strong> nifedip<strong>in</strong>e, but has a longer duration <strong>of</strong> action <strong>and</strong><br />
1 Eur. J.Med.Chem., 28, 859-867 (1993)<br />
131