synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
synthesis and in vitro pharmacology of a series of histamine h2 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 1<br />
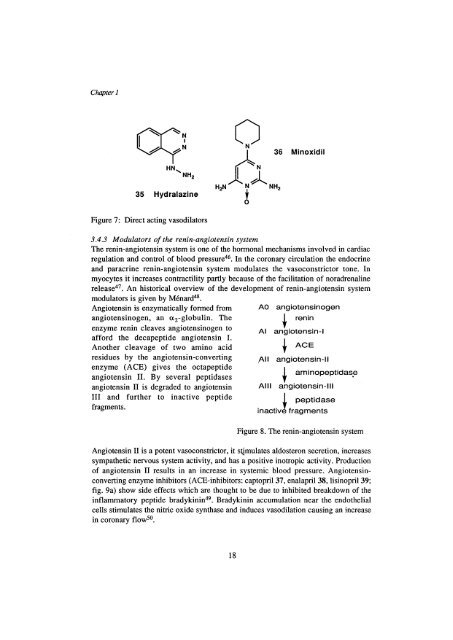
Figure 7: Direct act<strong>in</strong>g vasodilators<br />
3.4.3 Modulators <strong>of</strong> the ren<strong>in</strong>-angiotens<strong>in</strong> system<br />
The ren<strong>in</strong>-angiotens<strong>in</strong> system is one <strong>of</strong> the hormonal mechanisms <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> cardiac<br />
regulation <strong>and</strong> control <strong>of</strong> blood pressure 46<br />
. In the coronary circulation the endocr<strong>in</strong>e<br />
<strong>and</strong> paracr<strong>in</strong>e ren<strong>in</strong>-angiotens<strong>in</strong> system modulates the vasoconstrictor tone. In<br />
myocytes it <strong>in</strong>creases contractility partly because <strong>of</strong> the facilitation <strong>of</strong> noradrenal<strong>in</strong>e<br />
release 47<br />
. An historical overview <strong>of</strong> the development <strong>of</strong> ren<strong>in</strong>-angiotens<strong>in</strong> system<br />
modulators is given by Menard 48<br />
.<br />
Angiotens<strong>in</strong> is enzymatically formed from<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong>ogen, an a 2-globul<strong>in</strong>. The<br />
enzyme ren<strong>in</strong> cleaves angiotens<strong>in</strong>ogen to<br />
afford the decapeptide angiotens<strong>in</strong> I.<br />
Another cleavage <strong>of</strong> two am<strong>in</strong>o acid<br />
residues by the angiotens<strong>in</strong>-convert<strong>in</strong>g<br />
enzyme (ACE) gives the octapeptide<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong> II. By several peptidases<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong> II is degraded to angiotens<strong>in</strong><br />
HI <strong>and</strong> further to <strong>in</strong>active peptide<br />
fragments.<br />
AO<br />
AI<br />
All<br />
AMI<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong>ogen<br />
^ ren<strong>in</strong><br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong>-l<br />
J ACE<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong>-l I<br />
^ am<strong>in</strong>opeptidase<br />
angiotens<strong>in</strong>-lll<br />
I peptidase<br />
<strong>in</strong>activé fragments<br />
Figure 8. The ren<strong>in</strong>-angiotens<strong>in</strong> system<br />
Angiotens<strong>in</strong> II is a potent vasoconstrictor, it stimulates aldosteron secretion, <strong>in</strong>creases<br />
sympathetic nervous system activity, <strong>and</strong> has a positive <strong>in</strong>otropic activity. Production<br />
<strong>of</strong> angiotens<strong>in</strong> II results <strong>in</strong> an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> systemic blood pressure. Angiotens<strong>in</strong>convert<strong>in</strong>g<br />
enzyme <strong>in</strong>hibitors (ACE-<strong>in</strong>hibitors: Captopril 37, enalapril 38, lis<strong>in</strong>opril 39;<br />
fig. 9a) show side effects which are thought to be due to <strong>in</strong>hibited breakdown <strong>of</strong> the<br />
<strong>in</strong>flammatory peptide bradyk<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> 49<br />
. Bradyk<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> accumulation near the endothelial<br />
cells stimulates the nitric oxide synthase <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>duces vasodilation caus<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>crease<br />
<strong>in</strong> coronary flow 50<br />
.<br />
18