boletin de patentes - Instituto Nacional de la Propiedad Industrial
boletin de patentes - Instituto Nacional de la Propiedad Industrial
boletin de patentes - Instituto Nacional de la Propiedad Industrial
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
(10) AR051275 A1<br />
(21) P050103270<br />
(22) 04/08/05<br />
(30) EP 04018801.3 07/08/04<br />
(51) C08L 51/00, C08F 265/04, A61L 15/00<br />
(54) PARTICULA DE POLIMERO SUPERABSORBEN-<br />
TE, METODO PARA ELABORAR PARTICULAS<br />
DE POLIMERO SUPERABSORBENTE QUE TIE-<br />
NEN EL AGREGADO DE GRUPOS FUNCIONA-<br />
LES Y ARTICULO ABSORBENTE QUE COM-<br />
PRENDE PARTICULAS DE POLIMERO SUPE-<br />
RABSORBENTE<br />
(57) Partícu<strong>la</strong>s <strong>de</strong> polímero superabsorbentes que tienen<br />
grupos funcionales unidos en forma covalente<br />
a <strong>la</strong> superficie <strong>de</strong> partícu<strong>la</strong>s precursoras <strong>de</strong> polímero<br />
superabsorbente y un proceso para e<strong>la</strong>borar estas<br />
partícu<strong>la</strong>s <strong>de</strong> polímero superabsorbentes. Los<br />
grupos funcionales contienen una unidad injertada<br />
con un grupo activable por radiación y una unidad<br />
funcional unida en forma covalente a <strong>la</strong> unidad injertada.<br />
La unidad injertada está en<strong>la</strong>zada con un<br />
grupo C-H alifático contenido en <strong>la</strong> superficie <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong><br />
partícu<strong>la</strong> precursora <strong>de</strong> polímero superabsorbente.<br />
La unidad funcional compren<strong>de</strong> estructuras químicas<br />
que no se encuentran presentes en <strong>la</strong> partícu<strong>la</strong><br />
precursora <strong>de</strong> polímero superabsorbente. Estas<br />
unida<strong>de</strong>s funcionales agregan una función adicional<br />
a <strong>la</strong> partícu<strong>la</strong> precursora <strong>de</strong> polímero superabsorbente<br />
o modifican una función existente <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong><br />
partícu<strong>la</strong>.<br />
(71) THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY<br />
ONE PROCTER & GAMBLE PLAZA, CINCINNATI, OHIO<br />
45202, US<br />
(72) FLOHR, ANDREAS - LINDNER, TORSTEN<br />
(74) 782<br />
(41) Fecha: 03/01/2007<br />
Bol. Nro.: 388<br />
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––<br />
(10) AR051276 A1<br />
(21) P050103295<br />
(22) 05/08/05<br />
(30) US 60/599207 05/08/04<br />
(51) C09F 7/00<br />
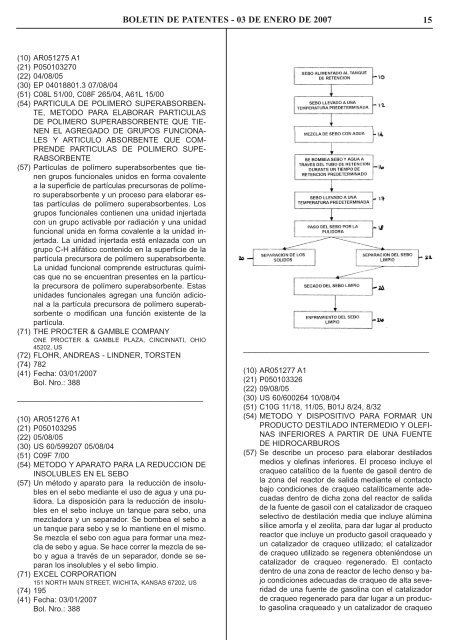
(54) METODO Y APARATO PARA LA REDUCCION DE<br />
INSOLUBLES EN EL SEBO<br />
(57) Un método y aparato para <strong>la</strong> reducción <strong>de</strong> insolubles<br />
en el sebo mediante el uso <strong>de</strong> agua y una pulidora.<br />
La disposición para <strong>la</strong> reducción <strong>de</strong> insolubles<br />
en el sebo incluye un tanque para sebo, una<br />
mezc<strong>la</strong>dora y un separador. Se bombea el sebo a<br />
un tanque para sebo y se lo mantiene en el mismo.<br />
Se mezc<strong>la</strong> el sebo con agua para formar una mezc<strong>la</strong><br />
<strong>de</strong> sebo y agua. Se hace correr <strong>la</strong> mezc<strong>la</strong> <strong>de</strong> sebo<br />
y agua a través <strong>de</strong> un separador, don<strong>de</strong> se separan<br />
los insolubles y el sebo limpio.<br />
(71) EXCEL CORPORATION<br />
151 NORTH MAIN STREET, WICHITA, KANSAS 67202, US<br />
(74) 195<br />
(41) Fecha: 03/01/2007<br />
Bol. Nro.: 388<br />
BOLETIN DE PATENTES - 03 DE ENERO DE 2007 15<br />
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––<br />
(10) AR051277 A1<br />
(21) P050103326<br />
(22) 09/08/05<br />
(30) US 60/600264 10/08/04<br />
(51) C10G 11/18, 11/05, B01J 8/24, 8/32<br />
(54) METODO Y DISPOSITIVO PARA FORMAR UN<br />
PRODUCTO DESTILADO INTERMEDIO Y OLEFI-<br />
NAS INFERIORES A PARTIR DE UNA FUENTE<br />
DE HIDROCARBUROS<br />
(57) Se <strong>de</strong>scribe un proceso para e<strong>la</strong>borar <strong>de</strong>sti<strong>la</strong>dos<br />
medios y olefinas inferiores. El proceso incluye el<br />
craqueo catalítico <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> fuente <strong>de</strong> gasoil <strong>de</strong>ntro <strong>de</strong><br />
<strong>la</strong> zona <strong>de</strong>l reactor <strong>de</strong> salida mediante el contacto<br />
bajo condiciones <strong>de</strong> craqueo catalíticamente a<strong>de</strong>cuadas<br />
<strong>de</strong>ntro <strong>de</strong> dicha zona <strong>de</strong>l reactor <strong>de</strong> salida<br />
<strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> fuente <strong>de</strong> gasoil con el catalizador <strong>de</strong> craqueo<br />
selectivo <strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong>sti<strong>la</strong>ción media que incluye alúmina<br />
sílice amorfa y el zeolita, para dar lugar al producto<br />
reactor que incluye un producto gasoil craqueado y<br />
un catalizador <strong>de</strong> craqueo utilizado; el catalizador<br />
<strong>de</strong> craqueo utilizado se regenera obteniéndose un<br />
catalizador <strong>de</strong> craqueo regenerado. El contacto<br />
<strong>de</strong>ntro <strong>de</strong> una zona <strong>de</strong> reactor <strong>de</strong> lecho <strong>de</strong>nso y bajo<br />
condiciones a<strong>de</strong>cuadas <strong>de</strong> craqueo <strong>de</strong> alta severidad<br />
<strong>de</strong> una fuente <strong>de</strong> gasolina con el catalizador<br />
<strong>de</strong> craqueo regenerado para dar lugar a un producto<br />
gasolina craqueado y un catalizador <strong>de</strong> craqueo