iv. mezioborové setkênè mladðch biologů ... - Chemické listy
iv. mezioborové setkênè mladðch biologů ... - Chemické listy
iv. mezioborové setkênè mladðch biologů ... - Chemické listy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chem. Listy 98, 271 – 314 (2004) IV. Amerika 2004.<br />
ANTICANCER DRUG ELLIPTICINE FORMS DNA<br />
ADDUCTS IN VIVO; A NOVEL MODE OF ITS<br />
ANTINEOPLATIC ACTION<br />
DAGMAR AIMOVÁ and MARIE STIBOROVÁ<br />
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Charles<br />
Un<strong>iv</strong>ersity, Albertov 2030, 128 40 Prague 2, The Czech<br />
Republic<br />
dagmar_aimova@seznam.cz<br />
Ellipticine is a potent antineoplastic agent, whose mode<br />
of action is considered to be based mainly on DNA<br />
intercalation and/or inhibition of topoisomerase II. We found<br />
that ellipticine also forms covalent DNA adducts in vitro and<br />
that the formation of DNA adducts is dependent on the<br />
act<strong>iv</strong>ation of ellipticine by cytochrome P450 (CYP) (cit. 1 ).<br />
This implicates the potential importance of several CYPs in<br />
producing more act<strong>iv</strong>e ellipticine metabolite(s). Here, we<br />
investigated the capacity of ellipticine to form DNA adducts in<br />
v<strong>iv</strong>o. Male Wistar rats were treated with ellipticine, and DNA<br />
from various organs was analyzed by<br />
32 P-postlabeling.<br />
Ellipticine-specific DNA adduct patterns, similar to those<br />
found in vitro, were detected in most test organs. The highest<br />
level of DNA adducts was found in l<strong>iv</strong>er, followed by spleen,<br />
lung, kidney, heart and brain. One major and one minor<br />
ellipticine-DNA adducts were found in DNA of all these<br />
organs of rats exposed to ellipticine. Besides these, two or<br />
three additional adducts were detected in DNA of l<strong>iv</strong>er,<br />
kidney, lung and heart. The predominant adduct formed in rat<br />
tissues in v<strong>iv</strong>o was identical to the deoxyguanosine adduct<br />
generated in DNA by ellipticine in vitro. Correlation studies<br />
showed that the formation of this major DNA adduct in v<strong>iv</strong>o is<br />
mediated by CYP3A1- and CYP1A-dependent reactions. The<br />
additional aim of the present work was to study whether<br />
ellipticine could influence the expression of the major CYPs<br />
participating in its metabolism. An expression of CYP1A1/2<br />
proteins in l<strong>iv</strong>er of rats of both sexes is strongly induced by<br />
treatment of animals with ellipticine. The expression levels of<br />
CYP1A1/2 in treated rats are one order of magnitude higher<br />
than those in control animals. The CYP1A1/2 induction is<br />
strongly dependent on concentration of ellipticine applied to<br />
experimental animals and on the time of their exposition. The<br />
induction of other isoforms of cytochromes P450 (CYP2B,<br />
2E1, 3A) was negligible. The results presented here are the<br />
first report showing the formation of CYP-mediated covalent<br />
DNA adducts by ellipticine in v<strong>iv</strong>o, and confirm the formation<br />
of covalent DNA adducts as a new mode of ellipticine action.<br />
In addition, they indicate that a long-term treatment of humans<br />
with ellipticine might stimulate its pharmacological efficiency<br />
against cancer diseases.<br />
Supported by Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (grant<br />
203/01/0996) and the Ministry of Education of the Czech<br />
Republic (grant MSM 1131 00001).<br />
REFERENCES<br />
1) Stiborová M., Bieler C. A., Wiessler M., Frei E.:<br />
Biochem. Pharmacol. 62, 1675 (2001).<br />
VYUŽITÍ DIASTEREOSELEKTIVNÍ [2+2+2]<br />
CYKLOIZOMERACE TRIYNŮ PRO PŘÍPRAVU<br />
HELIKÁLNĚ CHIRÁLNÍCH LÁTEK<br />
ZUZANA ALEXANDROVÁ, IRENA G. STARÁ, FILIP<br />
TEPLÝ, PETR SEHNAL, IVO STARÝ, DAVID ŠAMAN a<br />
MILOŠ BUDĚŠÍNSKÝ<br />
Ústav organické chemie a biochemie AV ČR, Flemingovo n. 2,<br />
166 10 Praha 6<br />
alexa@uochb.cas.cz<br />
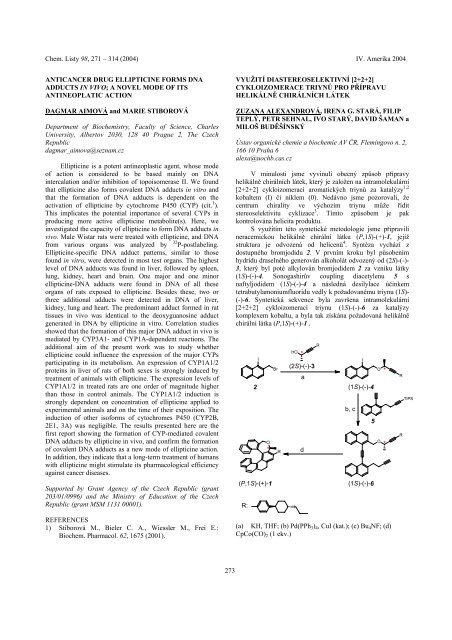
V minulosti jsme vyvinuli obecný způsob přípravy<br />
helikálně chirálních látek, který je založen na intramolekulární<br />
[2+2+2] cykloizomeraci aromatických triynů za katalýzy 1,2<br />
kobaltem (I) či niklem (0). Nedávno jsme pozorovali, že<br />
centrum chirality ve výchozím triynu může řídit<br />
stereoselekt<strong>iv</strong>itu cyklizace 3 . Tímto způsobem je pak<br />
kontrolována helicita produktu.<br />
S využitím této syntetické metodologie jsme připravili<br />
neracemickou helikálně chirální látku (P,1S)-(+)-1, jejíž<br />
struktura je odvozená od helicenů 4 . Syntéza vychází z<br />
dostupného bromjodidu 2. V prvním kroku byl působením<br />
hydridu draselného generován alkoholát odvozený od (2S)-(-)-<br />
3, který byl poté alkylován bromjodidem 2 za vzniku látky<br />
(1S)-(-)-4. Sonogashirův coupling diacetylenu 5 s<br />
naftyljodidem (1S)-(-)-4 a následná desilylace účinkem<br />
tetrabutylamoniumfluoridu vedly k požadovanému triynu (1S)-<br />
(-)-6. Syntetická sekvence byla završena intramolekulární<br />
[2+2+2] cykloizomerací triynu (1S)-(-)-6 za katalýzy<br />
komplexem kobaltu, a byla tak získána požadovaná helikálně<br />
chirální látka (P,1S)-(+)-1 .<br />
2<br />
I<br />
O<br />
*<br />
(P,1S)-(+)-1<br />
R:<br />
Br<br />
R<br />
HO<br />
*<br />
(2S)-(-)-3<br />
a<br />
d<br />
R<br />
(1S)-(-)-4<br />
b, c<br />
I<br />
5<br />
(1S)-(-)-6<br />
(a) KH, THF; (b) Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 , CuI (kat.); (c) Bu 4 NF; (d)<br />
CpCo(CO) 2 (1 ekv.)<br />
O<br />
O<br />
*<br />
*<br />
R<br />
R<br />
TIPS<br />
273